How Do Wind Patterns Affect Ocean Movement
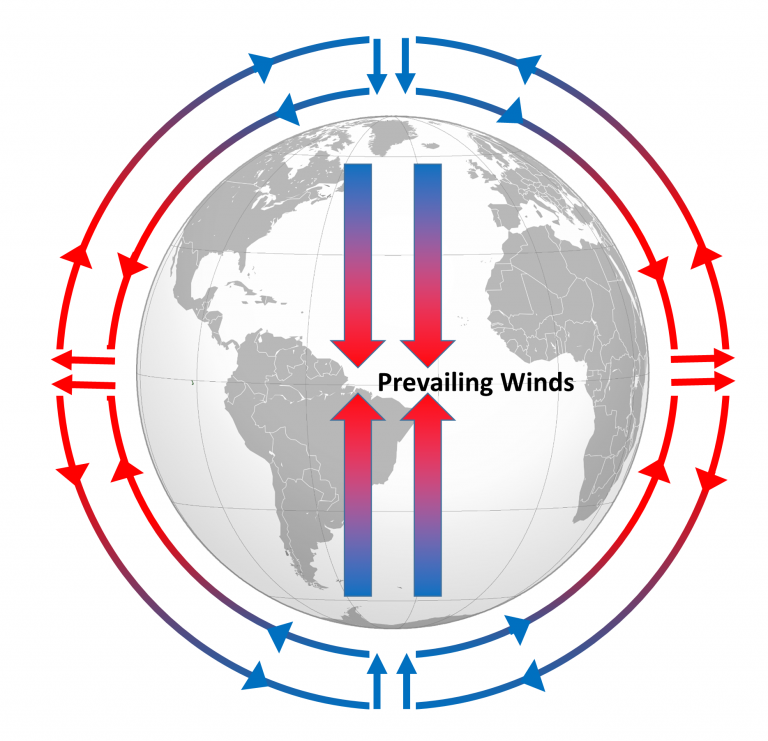
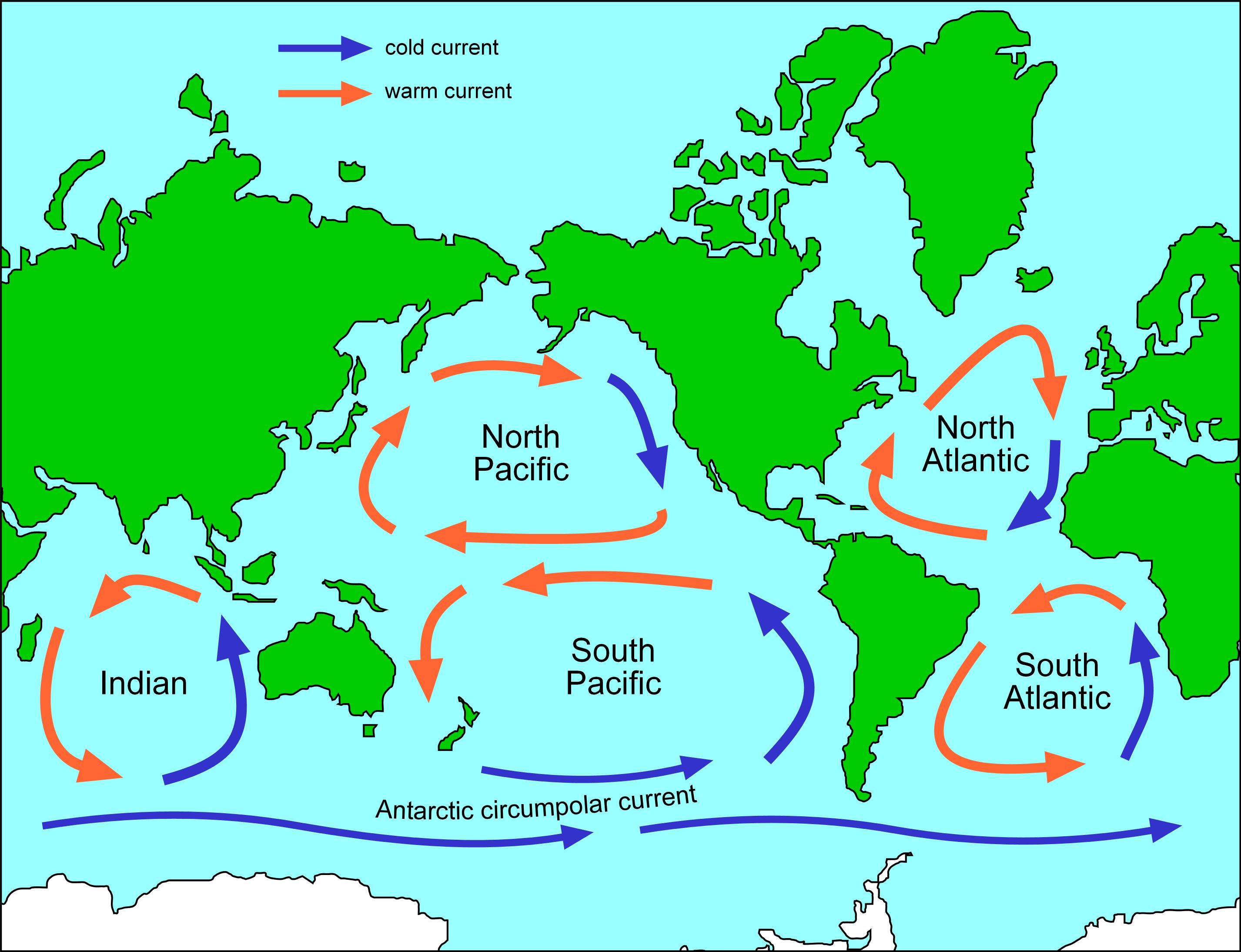
How Do Wind Patterns Affect Ocean Movement - Global wind patterns, earth’s rotation, and earth’s landmasses. Furthermore, wind plays virtually no role at all when it. The distribution and concentration of. These global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’. Gravity pulls the water away from hills and toward valleys and earth’s. Web three forces cause the circulation of a gyre: Large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. Web winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Web ocean surface currents are produced by global winds, the coriolis effect and the shape of each ocean basin. Web the movement of this heat through local and global ocean currents affects the regulation of local weather conditions and temperature extremes, stabilization of. The distribution and concentration of. The major overall global wind patterns, the rotation of the earth, and the shape of ocean basins. Earth’s rotation results in the. Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to. Unequal heating of the earth. When you blow across a cup of hot chocolate, you create tiny ripples on its surface that continue to move after. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. As prevailing winds blow across the ocean, they create surface currents in the water. Web the westerlies—or westerly winds—play an important role in weather and climate both locally. Web ocean movements are the consequence of many separate factors: Furthermore, wind plays virtually no role at all when it. Global wind patterns, earth’s rotation, and earth’s landmasses. Web the sun’s radiation creates prevailing wind patterns, which push ocean water to bunch in hills and valleys. Web three forces cause the circulation of a gyre: Global wind patterns, earth’s rotation, and earth’s landmasses. Gravity pulls the water away from hills and toward valleys and earth’s. Web wind affects various earth system processes and phenomena, including: Large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. Wind, tides, coriolis effect, water density differences, and the shape of the ocean basins. Wind is the movement of air caused by the uneven heating of the earth by the sun. Web wind affects various earth system processes and phenomena, including: Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to. Web the sun’s radiation creates prevailing wind patterns, which push ocean water to bunch in hills and valleys. Gravity pulls the water away from. Web while wind can play a role, often minor, in shaping surface ocean currents, it is not the main or only factor. It does not have much substance—you cannot see it or hold it—but you can. Large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. These global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’. Web. Web winds, water density, and tides all drive ocean currents. Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to. These global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’. Earth’s rotation results in the. The distribution and concentration of. The pacific and atlantic oceans have a circular pattern of surface. Web thus the pattern of global winds is affected by: Regional temperatures, humidity, and precipitation patterns. These global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’. Web these global wind patterns drive large bodies of air called air masses. Web these global wind patterns drive large bodies of air called air masses. The pacific and atlantic oceans have a circular pattern of surface. Web three forces cause the circulation of a gyre: Wind is the movement of air caused by the uneven heating of the earth by the sun. Web currents on the surface are determined by three major. Web the movement of this heat through local and global ocean currents affects the regulation of local weather conditions and temperature extremes, stabilization of. Web wind affects various earth system processes and phenomena, including: Web outside of earth’s equatorial areas, weather patterns are driven largely by ocean currents. Gravity pulls the water away from hills and toward valleys and earth’s.. Coastal and sea floor features influence their location, direction, and speed. Web wind affects various earth system processes and phenomena, including: Web ocean movements are the consequence of many separate factors: Web three forces cause the circulation of a gyre: Currents are movements of ocean water in a continuous flow, created largely by. Large global wind systems are created by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface. Web outside of earth’s equatorial areas, weather patterns are driven largely by ocean currents. Explain how environmental factors can result in atmospheric circulation. Gravity pulls the water away from hills and toward valleys and earth’s. Web the movement of this heat through local and global ocean currents affects the regulation of local weather conditions and temperature extremes, stabilization of. Web currents on the surface are determined by three major factors: These global wind systems, in turn, drive the oceans’. Furthermore, wind plays virtually no role at all when it. Wind drags on the ocean surface, causing water to. Web the westerlies—or westerly winds—play an important role in weather and climate both locally and on a global scale, by influencing precipitation patterns,. Regional temperatures, humidity, and precipitation patterns.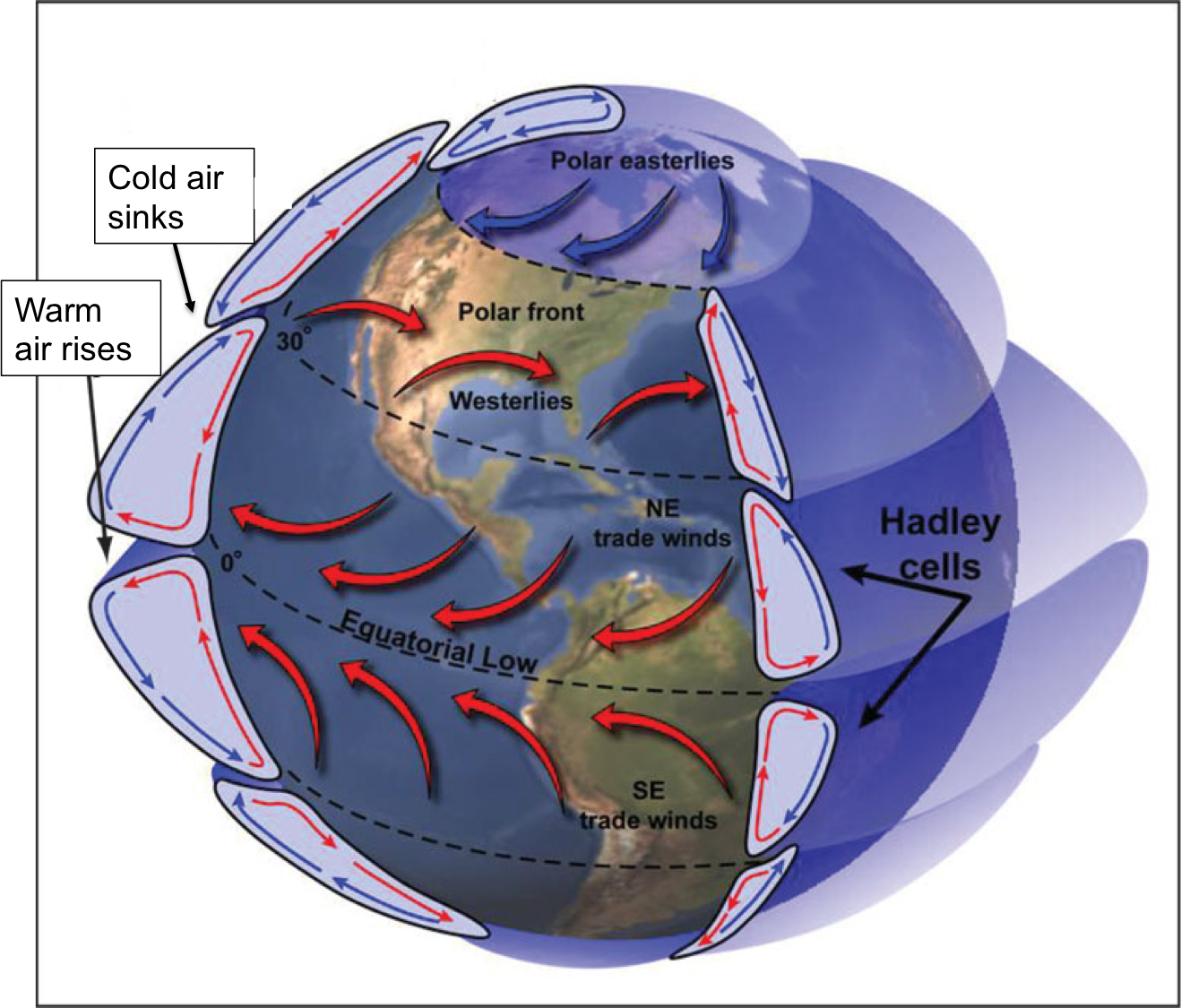
Ocean Currents Ocean Tracks
8.2 Winds and the Coriolis Effect Introduction to Oceanography
Global wind, precipitation, ocean current patterns Lucky Sci
Ocean motion — Science Learning Hub

The three wind patterns of the Earth
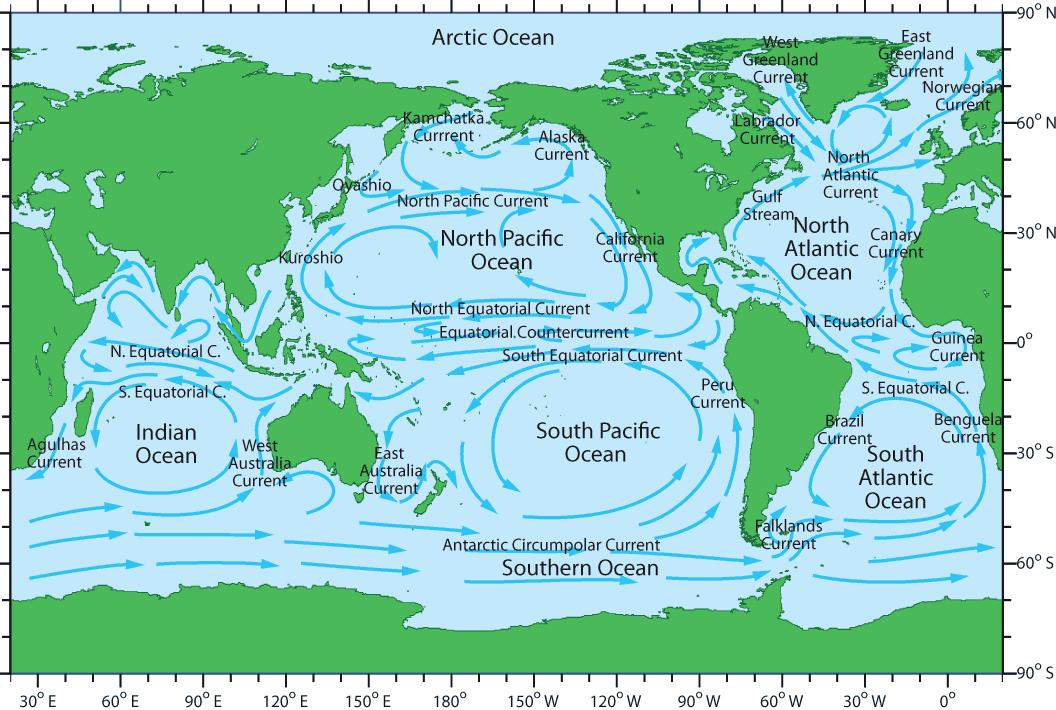
Global wind, precipitation, ocean current patterns Lucky Sci

Currents, Waves, and Tides Smithsonian Ocean
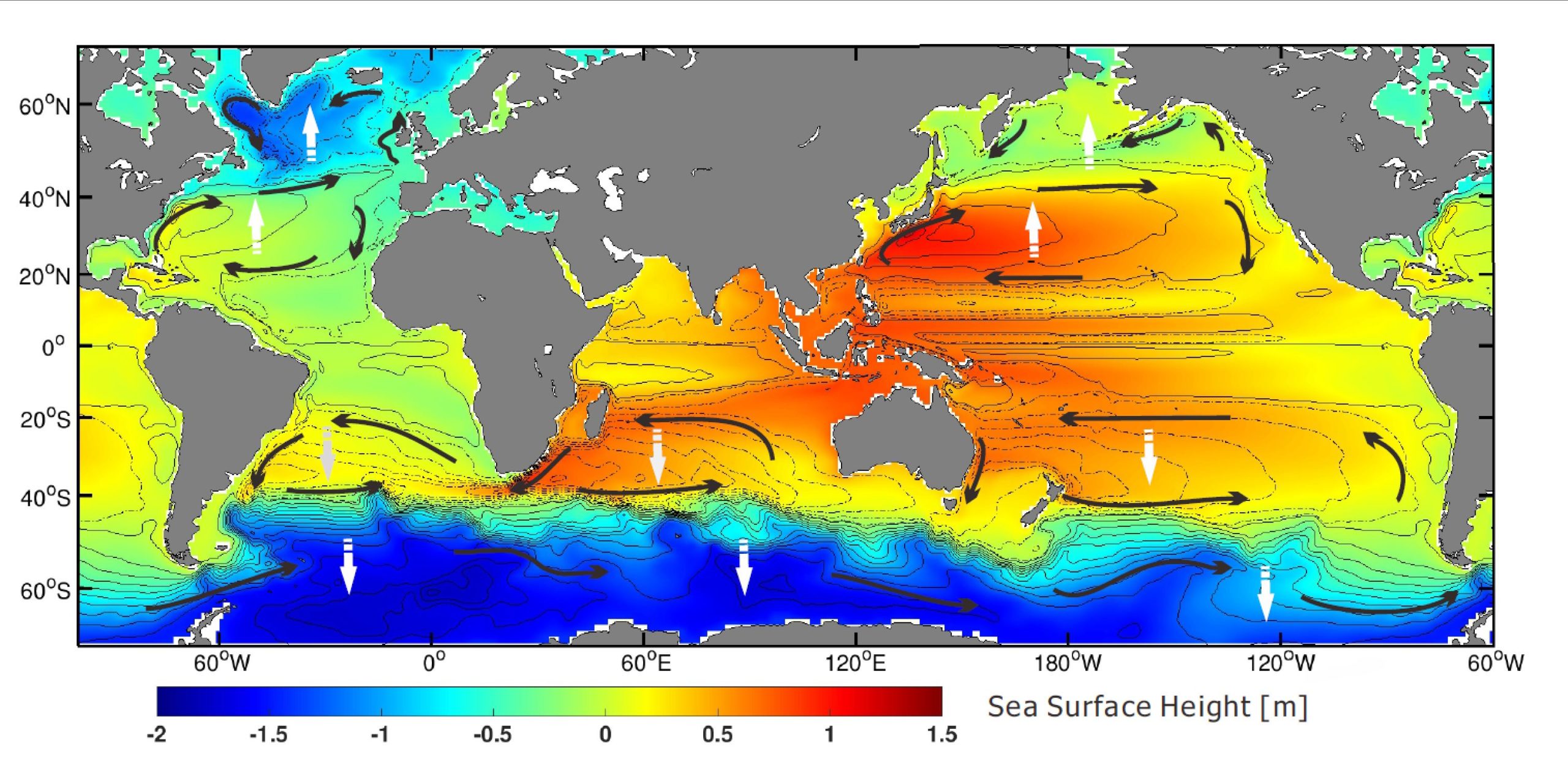
Major winddriven ocean currents shifting toward the poles AGU Newsroom

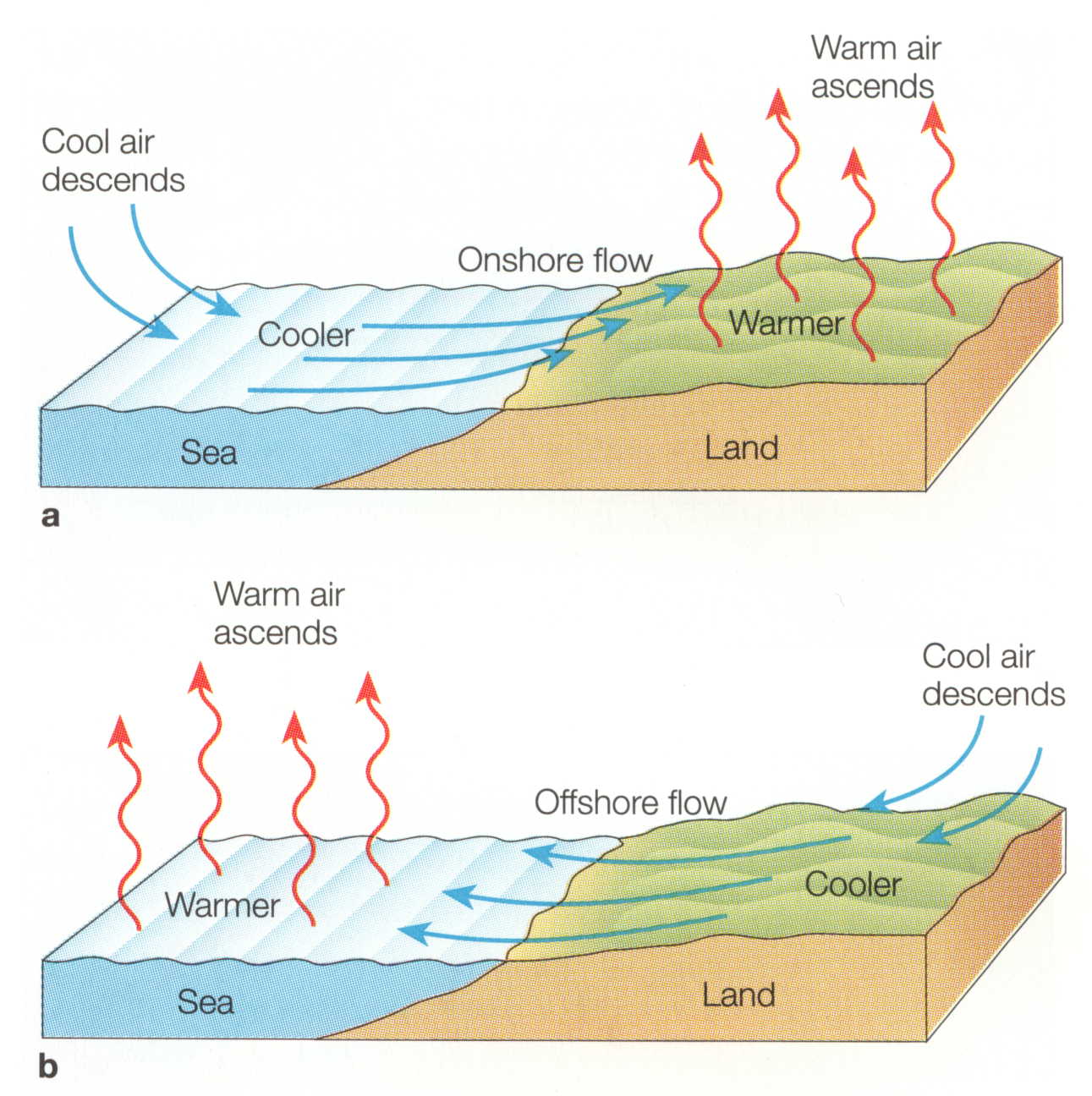
Sea breeze Coastal Winds, Oceanic Airflows & Marine Climate Britannica

Ocean Motion Definition Ocean in Motion Geostrophic Flow
Web These Global Wind Patterns Drive Large Bodies Of Air Called Air Masses.
Wind Is The Movement Of Air Caused By The Uneven Heating Of The Earth By The Sun.
Web The Global Pattern Of Prevailing Winds Is Caused By The Uneven Heating Of Earth’s Surface.
The Resilience Of Biodiversity In The Face Of Climate Change Depends On Gene Flow And Range Shifts.
Related Post: