What Electron Pattern Can Be Observed With The Noble Gases
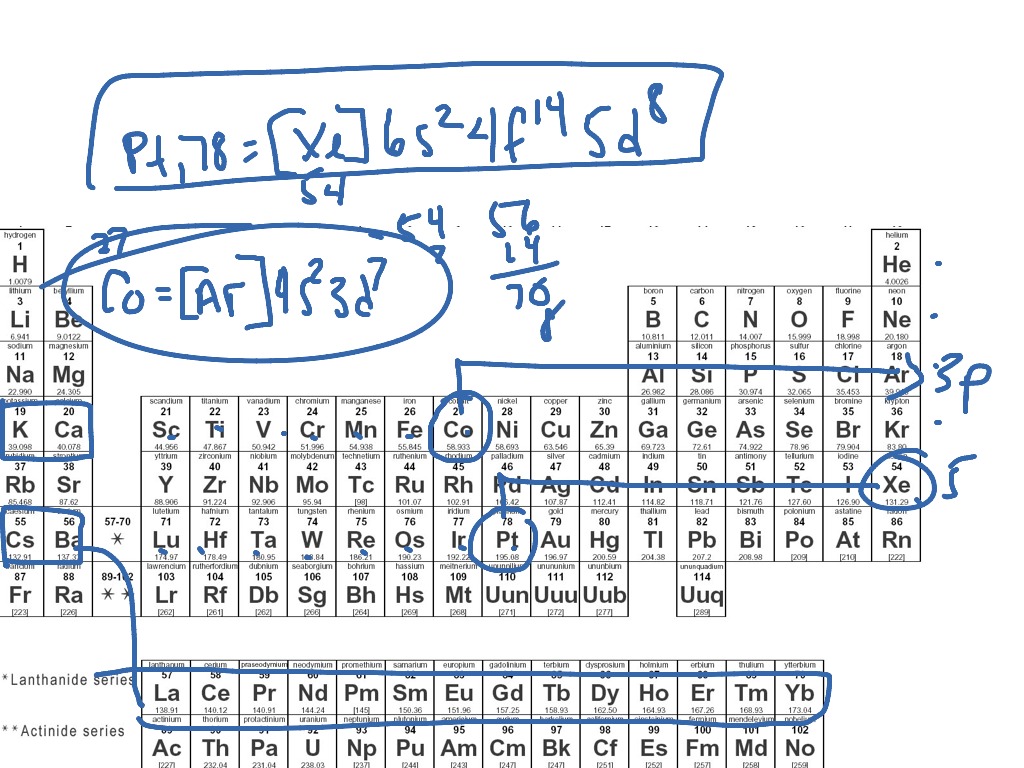
What Electron Pattern Can Be Observed With The Noble Gases - Web the electron patterns observed with the noble gases can be described using the electron configuration. Would it be [ar] or [ne]3s^23p^6? The aufbau principle states that electrons fill lower energy levels before adding to higher energy levels. These electron arrangements are especially stable, leaving the noble gases without a tendency to gain or loose electrons. He = 1s^2 ne =[he]2s^2 2p^6 ar = [ne]3s^2 3p^6 kr = [ar]4s^2 3d^10 4p^6 xe =[kr]5s^2 4d^10 5p^6 rn =[xe]6s^2 4f^14 5d^10 6p^6 the electron pattern is that all of them have fully filled subshells. The electronic configuration is that noble gases have fully filled subshells. Web what would the noble gas electron configuration for an element look like if the element is a noble gas? (electron configurations) 3.5 periodic variations in element. Fun with microscope we used scanning transmission electron microscopy to. Noble gases, which include helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon, have a full outer electron shell, making them stable and unreactive. These electron arrangements are especially stable, leaving the noble gases without a tendency to gain or loose electrons. Fun with microscope we used scanning transmission electron microscopy to. Each d shell holds up to 10 electrons. For helium, that limit is just two electrons. Scientists could have picked any group of elements, but the noble gases prevail because of their. This full electron configuration makes them very stable and inert or nonreactive. (electron configurations) 3.5 periodic variations in element. The ionization energies of the noble gases decrease with increasing atomic number. Web an abbreviated electron configuration, also known as a noble gas abbreviated electron configuration, uses one of the elements from the last column of the periodic table, which contains. He = 1s^2 ne =[he]2s^2 2p^6 ar = [ne]3s^2 3p^6 kr = [ar]4s^2 3d^10 4p^6 xe =[kr]5s^2 4d^10 5p^6 rn =[xe]6s^2 4f^14 5d^10 6p^6 the electron pattern is that all of them have fully filled subshells. The electronic configuration is that noble gases have fully filled subshells. The halogens, directly to the left of the noble gases, readily gain electrons. Web it's just common convention to reduce the size of the electronic configurations. Helium (he) neon (ne) argon (ar) krypton (kr) xenon (xe) radon (rn) Would it be [ar] or [ne]3s^23p^6? Web what electron pattern can be observed with the noble gases? The noble gases are present in the last group of the periodic table having the maximum possible number. They are therefore held less tightly by the atom. Web the elements in group 18 are the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon). Web the noble gases are in group viii of the periodic table. Helium has a full outer shell of two \(s\) electrons. Web each p shell holds up to 6 electrons. Web potassium has nineteen electrons, one more than the noble gas argon, so its configuration could be written as \(\left[ \ce{ar} \right] 4s^1\). The ionization potential decreases with an increasing radius, because the valence electrons in the larger noble gases are further away from the nucleus; Follow the aufbau rule and write the full electron configuration. (electron configurations) 3.5 periodic. Noble gases are found at the end of the periodic table (group 18) and consist of the maximum number of electrons allowed for that particular period. The noble gases are colorless, odorless, tasteless, and nonflammable under standard conditions. Each f shell holds up to 14 electrons. Web the noble gases, in the column on the right, almost never react, since. The noble gases are colorless, odorless, tasteless, and nonflammable under standard conditions. For helium, that limit is just two electrons. Web for all except helium, the maximum capacity of the outer electron shell of the noble gas atom is eight electrons. Web what electron pattern can be observed with the noble gases? The ionization energies of the noble gases decrease. Then the remaining electrons are listed explicitly. Web oxygen, for example, has the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4, whereas the oxygen anion has the electron configuration of the noble gas neon (ne), 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6. Web electron configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and. The halogens, directly to the left of the noble gases, readily gain electrons and react with metals. The ionization energies of the noble gases decrease with increasing atomic number. Web the elements in group 18 are the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon). He = 1s^2 ne =[he]2s^2 2p^6 ar = [ne]3s^2 3p^6 kr = [ar]4s^2 3d^10. The ionization potential decreases with an increasing radius, because the valence electrons in the larger noble gases are further away from the nucleus; Web what electron pattern can be observed with the noble gases? Each f shell holds up to 14 electrons. This provides the basis for a shorthand notation for electron configurations called the noble gas configuration. Follow the aufbau rule and write the full electron configuration. This full electron configuration makes them very stable and inert or nonreactive. Web on the right hand column of the periodic table, you will see elements in group 0. Scientists could have picked any group of elements, but the noble gases prevail because of their completely filled shells and stability. Web it was observed that highly recognizable unique micro plasma pattern formations can be controlled on a large scale by varying the discharge key parameters and driving modes. The electronic configuration is that noble gases have fully filled subshells. Web the elements in group 18 are the noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon). Web the electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: The aufbau principle states that electrons fill lower energy levels before adding to higher energy levels. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron (n = 1, l = 0, m l = 0, m s = + 1 2 m s = + 1 2). Web potassium has nineteen electrons, one more than the noble gas argon, so its configuration could be written as \(\left[ \ce{ar} \right] 4s^1\). These electron arrangements are especially stable, leaving the noble gases without a tendency to gain or loose electrons.
Noble Gas Electron Configuration Chart
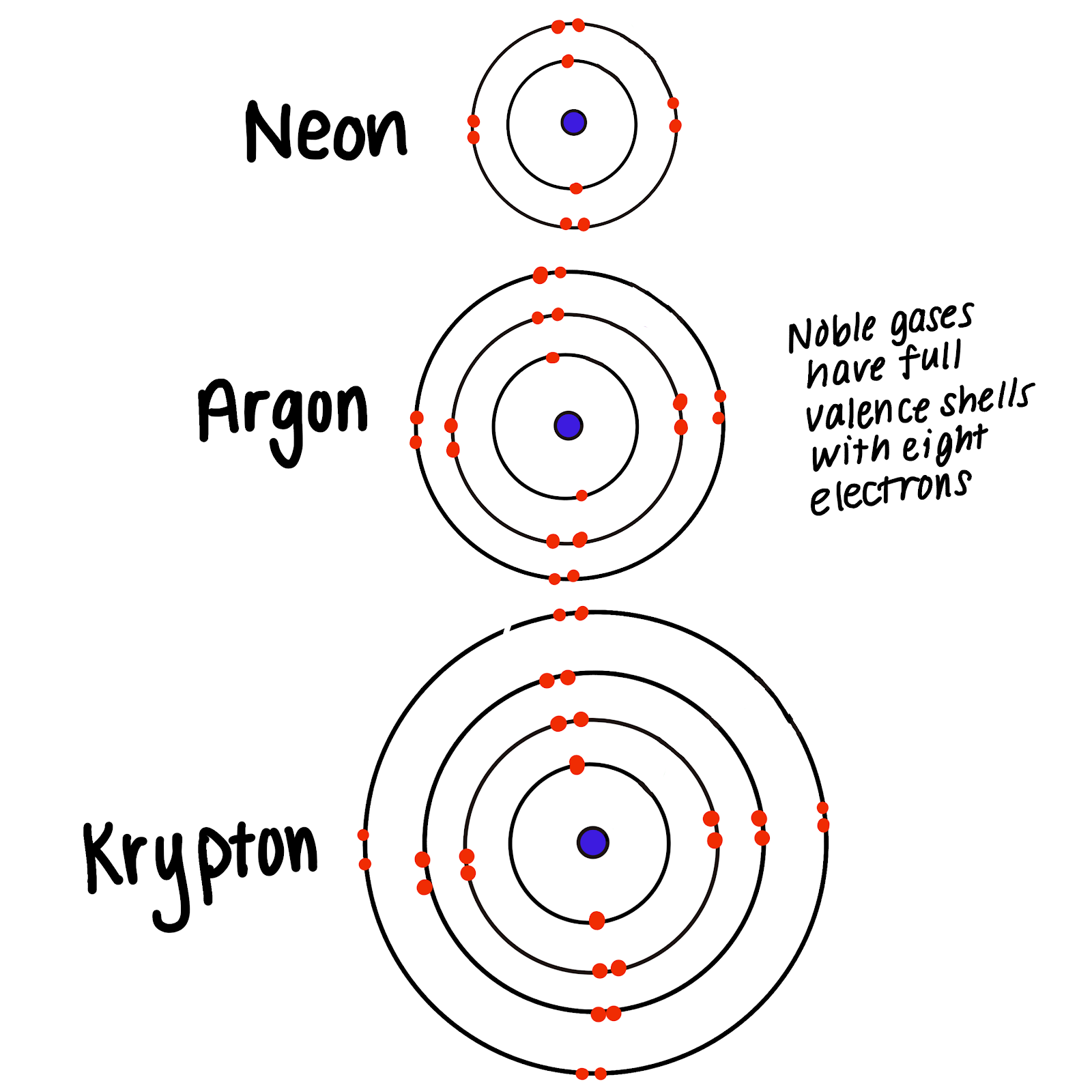
Group 18 The Noble Gases
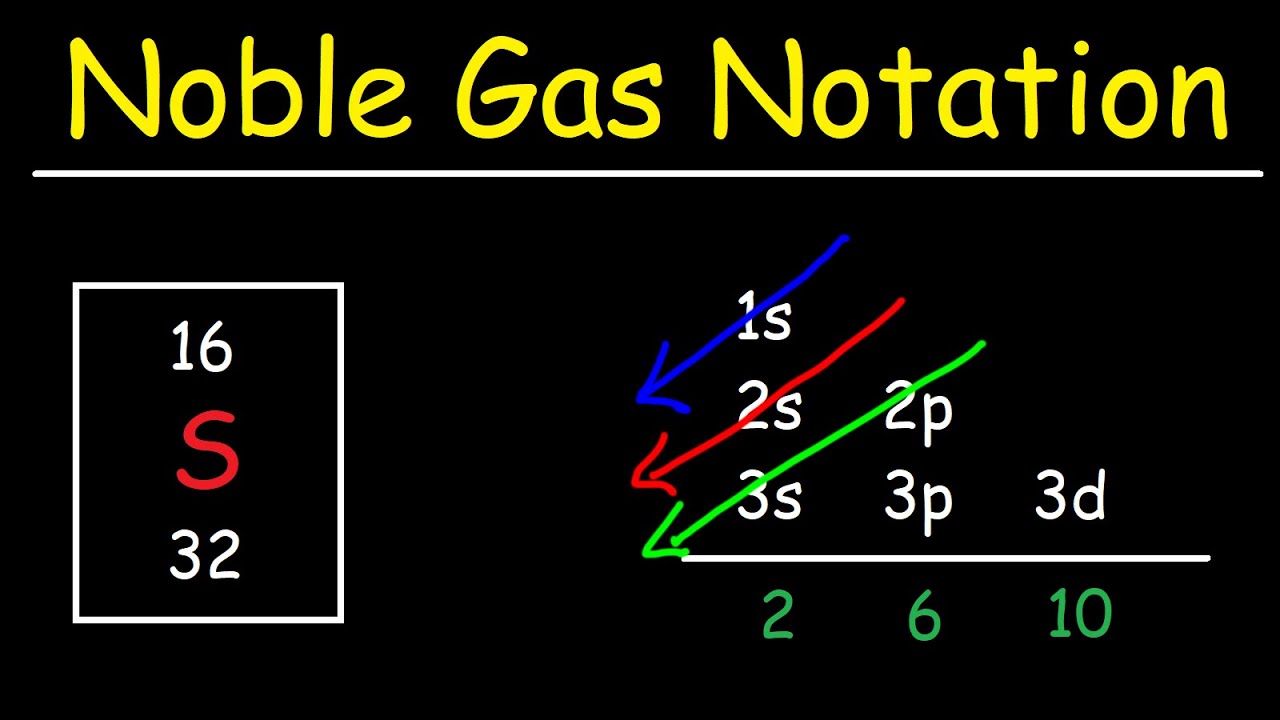
Electron Configuration With Noble Gas Notation YouTube

Electrons in Atoms Lesson7 Noble Gas Configuration YouTube
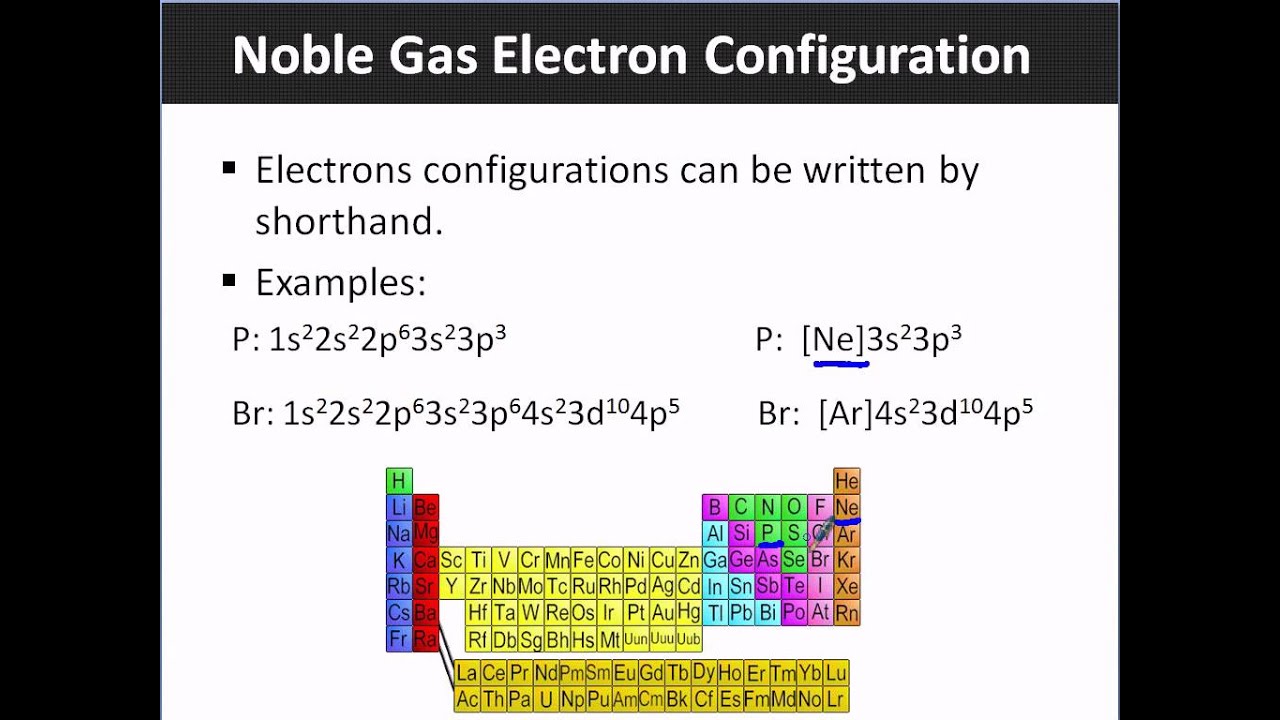
Noble Gas Electron Configurations YouTube
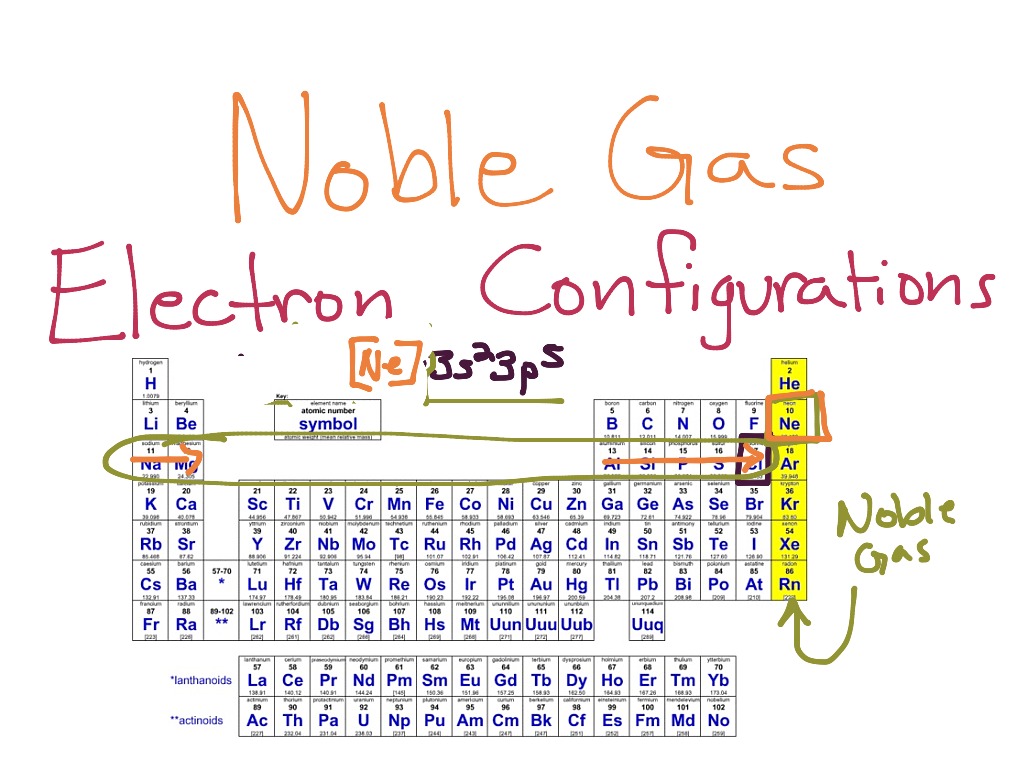
Noble Gas Electron Configurations Electron Configuration, High School
What's So Noble About Noble Gases? Owlcation Education

Electron Configurations with Noble Gas Notation YouTube
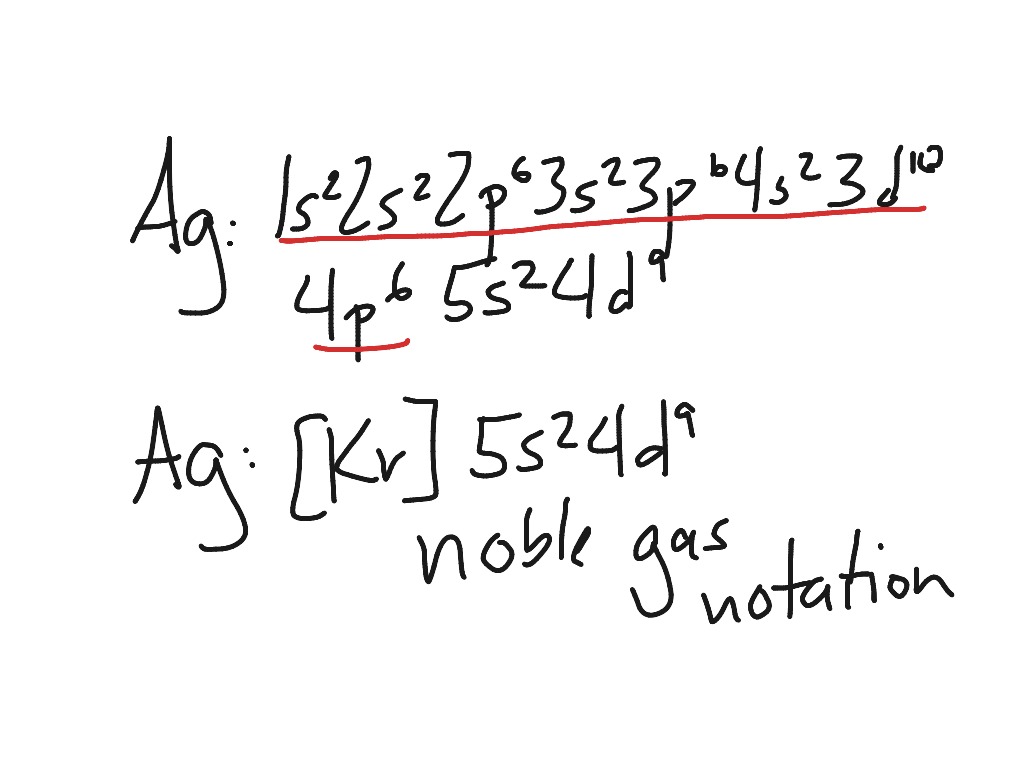
Noble Gases Electron Configuration
Noble Gases Electron Configuration
The Ionization Energies Of The Noble Gases Decrease With Increasing Atomic Number.
Helium Has A Full Outer Shell Of Two \(S\) Electrons.
Each D Shell Holds Up To 10 Electrons.
Web The Noble Gases Are In Group Viii Of The Periodic Table.
Related Post: