Vertical Oscillation Running Chart
Vertical Oscillation Running Chart - Web running cycling tacx® indoor cycling fitness & health tracking design your own watch golf multisport & triathlete swimming diving scales & monitors just for kids. Web vertical oscillation (vo) also known as vertical bounce, is a measure of how much we move vertically during each stride when running. Lewis moses, a coach and founder of new levels coaching,. Higher vertical oscillation often leads to inefficiency while contributing nothing to your forward motion. Web does running cadence predict injury? Web finally, vertical oscillation ratio is vertical oscillation divided by stride length and displayed as a percentage. The optimal vertical oscillation varies from person to person based on factors such as height, leg length, and running experience. With the growing popularity of. Running is primarily a horizontal sport — however much an. Web in general, faster runners have less vertical oscillation, in the 8.6cm or under range, as per garmin's metrics, so it seems more efficient runs demonstrate less bounce. Web in general, faster runners have less vertical oscillation, in the 8.6cm or under range, as per garmin's metrics, so it seems more efficient runs demonstrate less bounce. This metric describes how much your torso shifts up and down (in centimeters) with each step while you’re running. Web non efficient running = increased distance between foot contact point on the. Web does running cadence predict injury? Let's now see which exercises can improve and. Web finally, vertical oscillation ratio is vertical oscillation divided by stride length and displayed as a percentage. They might look impressive, but that kind of bouncing is not what you want in. Watch any professional runner in action and you'll notice that there's very little movement. Higher vertical oscillation often leads to inefficiency while contributing nothing to your forward motion. This metric describes how much your torso shifts up and down (in centimeters) with each step while you’re running. Web finally, vertical oscillation ratio is vertical oscillation divided by stride length and displayed as a percentage. Web “more experienced runners tend to have lower vertical oscillation,. Higher vertical oscillation often leads to inefficiency while contributing nothing to your forward motion. Web does running cadence predict injury? This reflects the amount of “bounce” in each step while you run. Have you ever seen a kangaroo bouncing around? Above and below this vertical oscillation measurement can. Let's now see which exercises can improve and. Train for a more efficient and healthy stride by tracking vo. This reflects the amount of “bounce” in each step while you run. Web “more experienced runners tend to have lower vertical oscillation, but it will also tend to go up as we run faster. They might look impressive, but that kind. In running, vertical oscillation, or vo for short, is the distance the centre of body mass travels vertically (up and down) at. Watch any professional runner in action and you'll notice that there's very little movement in their upper body. This metric describes how much your torso shifts up and down (in centimeters) with each step while you’re running. The. The optimal vertical oscillation varies from person to person based on factors such as height, leg length, and running experience. Web most running coaches and biomechanists suggest that a good vertical oscillation running is about 5 to 10 cm. Lewis moses, a coach and founder of new levels coaching,. Web does running cadence predict injury? Web this study investigated biomechanical. This metric describes how much your torso shifts up and down (in centimeters) with each step while you’re running. Web vertical oscillation (vo) also known as vertical bounce, is a measure of how much we move vertically during each stride when running. Have you ever seen a kangaroo bouncing around? They might look impressive, but that kind of bouncing is. The optimal vertical oscillation varies from person to person based on factors such as height, leg length, and running experience. Running is primarily a horizontal sport — however much an. It is the measure of. Measured at the torso, it tells you, in centimetres, how much. Web running cycling tacx® indoor cycling fitness & health tracking design your own watch. Let's now see which exercises can improve and. Higher vertical oscillation often leads to inefficiency while contributing nothing to your forward motion. Web “more experienced runners tend to have lower vertical oscillation, but it will also tend to go up as we run faster. Web vertical oscillation (vo) also known as vertical bounce, is a measure of how much we. Web finally, vertical oscillation ratio is vertical oscillation divided by stride length and displayed as a percentage. How does it impact running performance, and where does the biosleeve — knee fit in? Web does running cadence predict injury? This reflects the amount of “bounce” in each step while you run. Web vertical oscillation, in the context of running biomechanics, refers to the upward and downward movement of the body during each stride while running. This reflects the amount of “bounce” in each step while you run. Watch any professional runner in action and you'll notice that there's very little movement in their upper body. It is the measure of. This metric describes how much your torso shifts up and down (in centimeters) with each step while you’re running. Web this study investigated biomechanical assessments in trail running, comparing two wearable devices—stryd power meter and garminrp. Web vertical oscillation (vo) also known as vertical bounce, is a measure of how much we move vertically during each stride when running. They might look impressive, but that kind of bouncing is not what you want in. Web non efficient running = increased distance between foot contact point on the ground and pelvis projection on the ground. Measured at the torso, it tells you, in centimeters, how much. In running, vertical oscillation, or vo for short, is the distance the centre of body mass travels vertically (up and down) at. Web most running coaches and biomechanists suggest that a good vertical oscillation running is about 5 to 10 cm.
TOO MUCH VERTICAL OSCILLATION IN YOUR RUNNING STRIDE? Form Technique
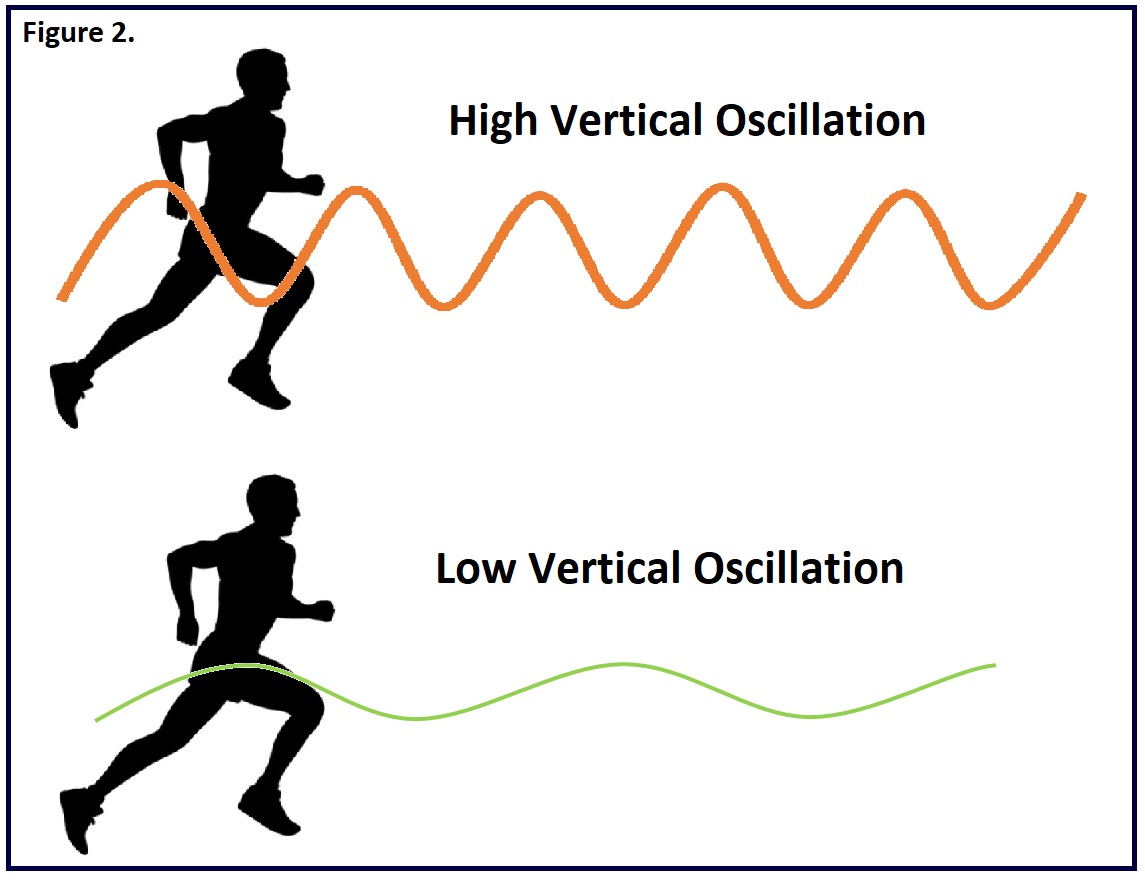
Vertical Oscillation Running Chart

What is Vertical Oscillation? Train for a more efficient and healthy

Vertical Oscillation Running Chart

Asymptotic Running Running cadence

Changes in vertical oscillation for each group during marathon. Figure

What's A Good Vertical Oscillation Running? + 5 Tips To Improve Yours

Optimizing Vertical Oscillation for better stride Running Centre
Running average flow speeds at 3.8 m depth (averaged over 16 s, which
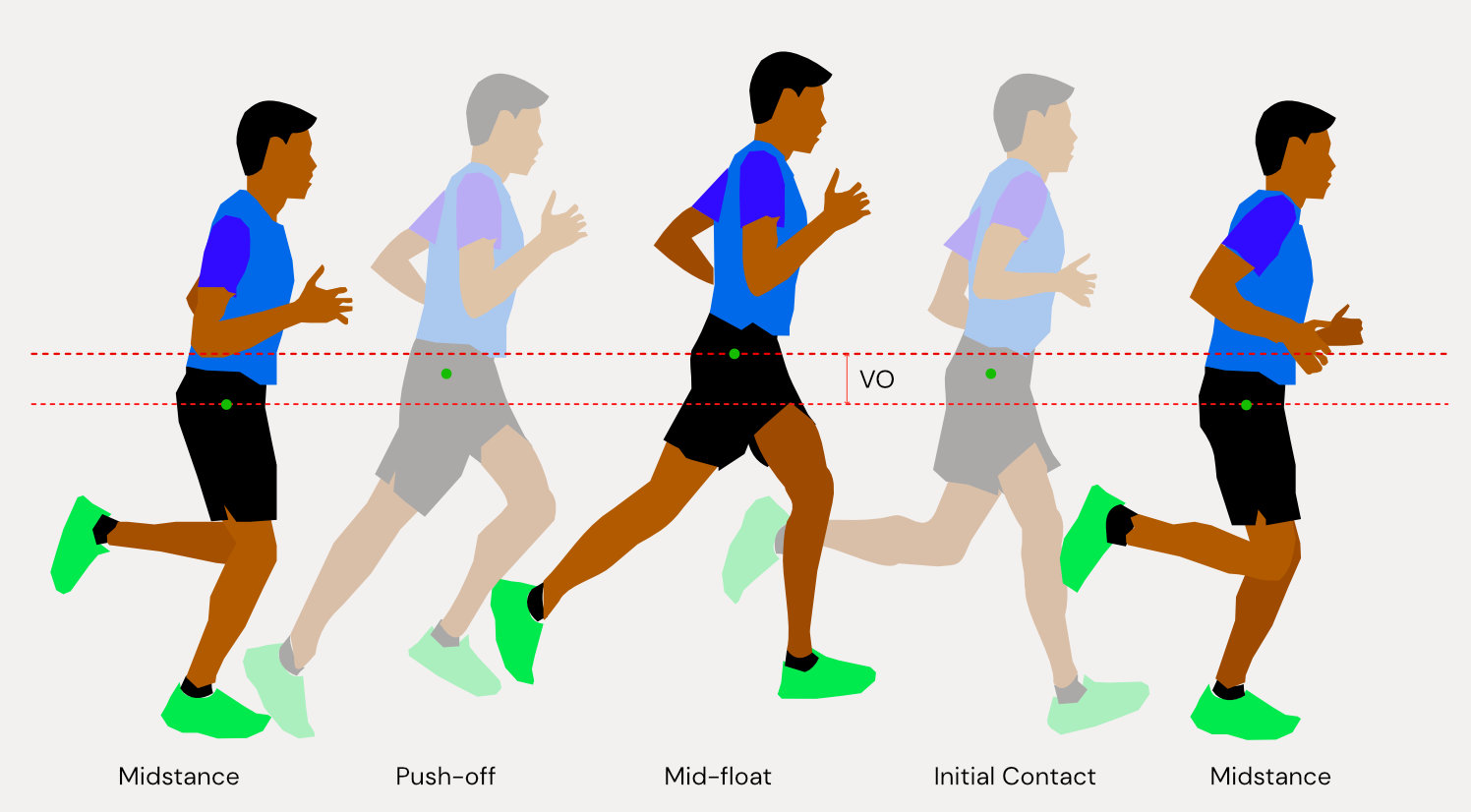
Optimizing Vertical Oscillation for better stride Running Centre
This Reflects The Amount Of “Bounce” In Each Step While You Run.
Measured At The Torso, It Tells You, In Centimeters, How Much.
Train For A More Efficient And Healthy Stride By Tracking Vo.
Vertical Oscillation Is The Measure Of The Vertical Displacement Of A Runner’s Torso To Understand The Extent Of Bounce While Running.
Related Post: