Type 2 Brugada Pattern
Type 2 Brugada Pattern - A heterozygous scn5a p.r893c variant was found by genetic testing in the proband’s father and sister. Can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of st segment elevation. Patients with type 2 brp often have underlying type 1 brp; Web electrocardiography can show two brugada patterns (brp). Web brugada pattern type 2 diagnosis unmasked by aspiration pneumonia. Web type 2 brugada pattern is characterized by “saddleback” pattern of st elevation with positive or biphasic t wave. Web this would be particularly important, since (1) up to 40% of the patients with brs with drug‐induced type i pattern also demonstrate spontaneous type i pattern during follow‐up, 6, 7 (2) high type i burden is associated with symptoms and spontaneous arrhythmias, 34, 35, 36 and (3) certain ecg features and additional leads expressing. Web type 2 and 3 brugada occurs in 58/10,000 people 1. Type 3 brugada pattern is characterized by coved or saddle back with st elevation between 1. Decrease inward sodium or calcium currents or. Type 1, type 2, and type 3 from left to right, seen in leads v1,. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. (ii) type‐2 or saddle‐back pattern, depicting an r’ wave in lead v 1 followed by st‐segment elevation,. Type 2 brp can appear during circumstances that result. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. A type 2 pattern can be converted to a type 1 pattern upon pharmacological challenge or other stressors such as fever. Web there are 3 patterns of brugada syndrome, classified based on ecg parameters. People with brugada syndrome have an increased. It increases the risk of abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Brugada type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped st elevation. Decrease inward sodium or calcium currents or. Type 2 brp can appear during circumstances that result in delayed sodium channel opening, such as fever, pneumonia, or use of sodium channel blockers. Web there are 3 patterns of brugada. 2, 23, 24 fluctuations in heart frequency during holter monitoring have suggested that increased vagal activity precedes vf. Web this would be particularly important, since (1) up to 40% of the patients with brs with drug‐induced type i pattern also demonstrate spontaneous type i pattern during follow‐up, 6, 7 (2) high type i burden is associated with symptoms and spontaneous. Brugada syndrome results from mutations that. It increases the risk of abnormal heart rhythms and sudden cardiac death. Type 3 brugada pattern (on high right precordial lead placement). Web brugada syndrome ( brs) is a genetic disorder in which the electrical activity of the heart is abnormal due to channelopathy. Brugada type 3 can be the morphology of either type. Their father showed a spontaneous type 1 brugada electrocardiogram pattern. Can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of st segment elevation. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. (ii) type‐2 or saddle‐back pattern, depicting an r’ wave in lead v 1. Brugada type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped st elevation. Can be the morphology of either type 1 or type 2, but with <2mm of st segment elevation. Web electrocardiography can show two brugada patterns (brp). The 2013 diagnostic criteria excluded the requirement for associated clinical features, with diagnosis based purely on the ecg phenotype. Ecg pattern can wax and. Type 3 brugada pattern is characterized by coved or saddle back with st elevation between 1. The abnormal heart rhythms seen in those with brugada syndrome often occur at. Web type 2 and 3 brugada occurs in 58/10,000 people 1. Type 2 brp can appear during circumstances that result in delayed sodium channel opening, such as fever, pneumonia, or use. Brugada syndrome results from mutations that. A heterozygous scn5a p.r893c variant was found by genetic testing in the proband’s father and sister. Type 2 is not diagnostic of brugada syndrome, but may raise suspicion for brugada syndrome, and should lead to further testing. Prevalance of brugada pattern ecg: Web brugada type 2 has >2mm of saddleback shaped st elevation. Web brugada syndrome ( brs) is a genetic disorder in which the electrical activity of the heart is abnormal due to channelopathy. Asia (0.36%), europe (0.25%), and in the usa (0.03%) 2. Web this would be particularly important, since (1) up to 40% of the patients with brs with drug‐induced type i pattern also demonstrate spontaneous type i pattern during. Web brugada syndrome ecg patterns. Decrease inward sodium or calcium currents or. A type 2 pattern can be converted to a type 1 pattern upon pharmacological challenge or other stressors such as fever. Type 1, type 2, and type 3 from left to right, seen in leads v1,. (i) type‐1, or coved pattern, depicting st‐segment elevation, followed by a symmetric negative t wave in the right precordial leads and; Furthermore, the proband’s genetic testing. 2, 23, 24 fluctuations in heart frequency during holter monitoring have suggested that increased vagal activity precedes vf. Type 1 brp usually causes sudden cardiac arrest (sca). Web the brugada ecg pattern is usually more pronounced at night or at rest 22 and after large meals, 23 when most vf episodes and sudden deaths in the brugada syndrome also occur. Web electrocardiography can show two brugada patterns (brp). Type 2 is not diagnostic of brugada syndrome, but may raise suspicion for brugada syndrome, and should lead to further testing. Web this would be particularly important, since (1) up to 40% of the patients with brs with drug‐induced type i pattern also demonstrate spontaneous type i pattern during follow‐up, 6, 7 (2) high type i burden is associated with symptoms and spontaneous arrhythmias, 34, 35, 36 and (3) certain ecg features and additional leads expressing. Web type 2 brugada pattern is characterized by “saddleback” pattern of st elevation with positive or biphasic t wave. Brugada syndrome results from mutations that. Patients have abnormal findings on the surface electrocardiogram (ecg) but do not usually have any apparent cardiac structural abnormalities. Web there are 3 patterns of brugada syndrome, classified based on ecg parameters.
Brugada syndrome Types 1, 2 and 3 There are three GrepMed

Twelvelead electrocardiogram showing type 2 Brugada pattern

Brugada Syndrome Causes, ECG, Symptoms, Treatment

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Is this Type 2 Brugada syndrome/ECG pattern?

Brugada Syndrome Circulation Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology

Figure 3 from New electrocardiographic criteria to differentiate the
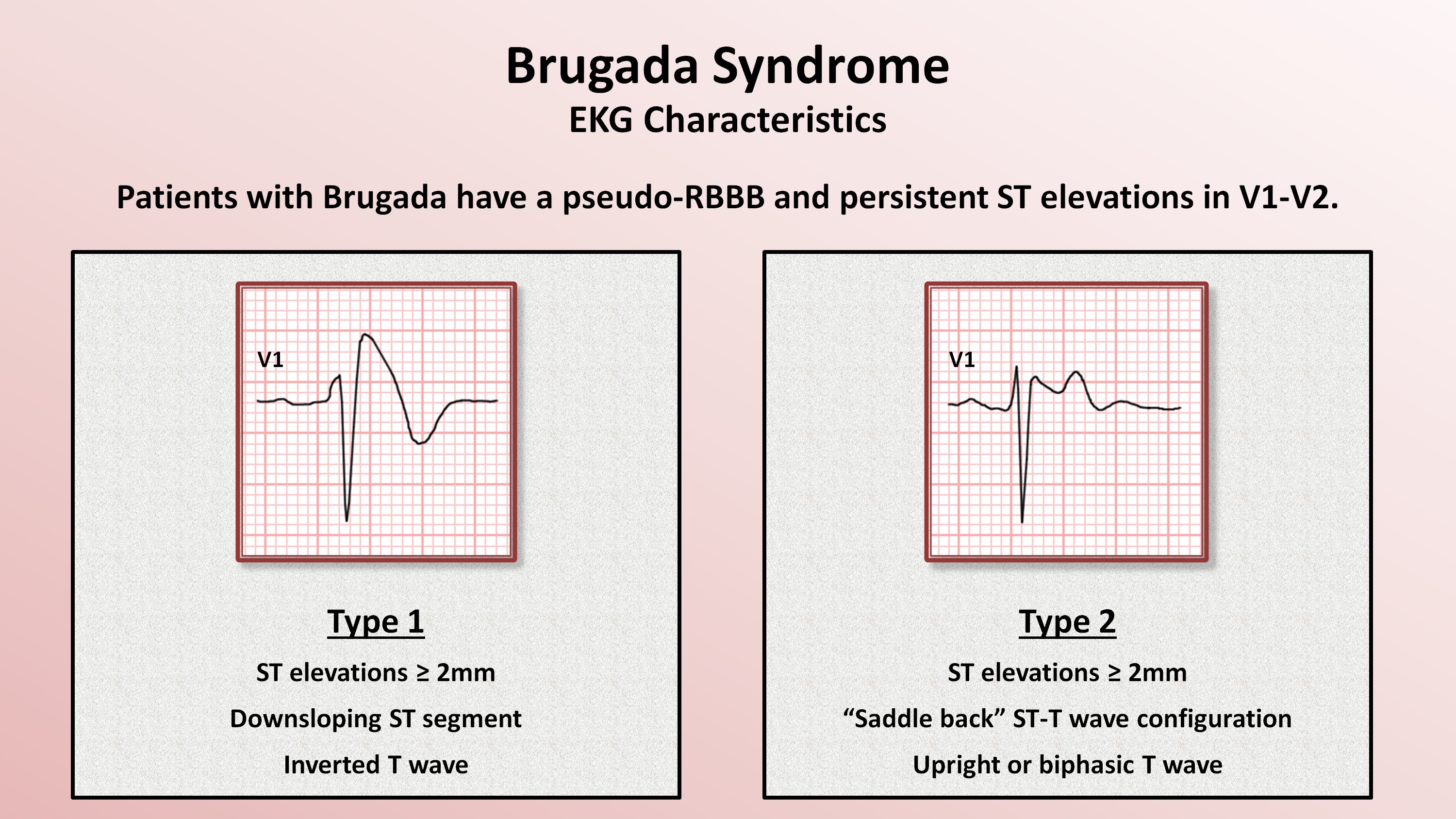
Brugada Syndrome

Brugada Syndrome Causes, ECG, Symptoms, Treatment

Epicardial ablation of a Brugada syndrome patient. (A) Baseline type 2
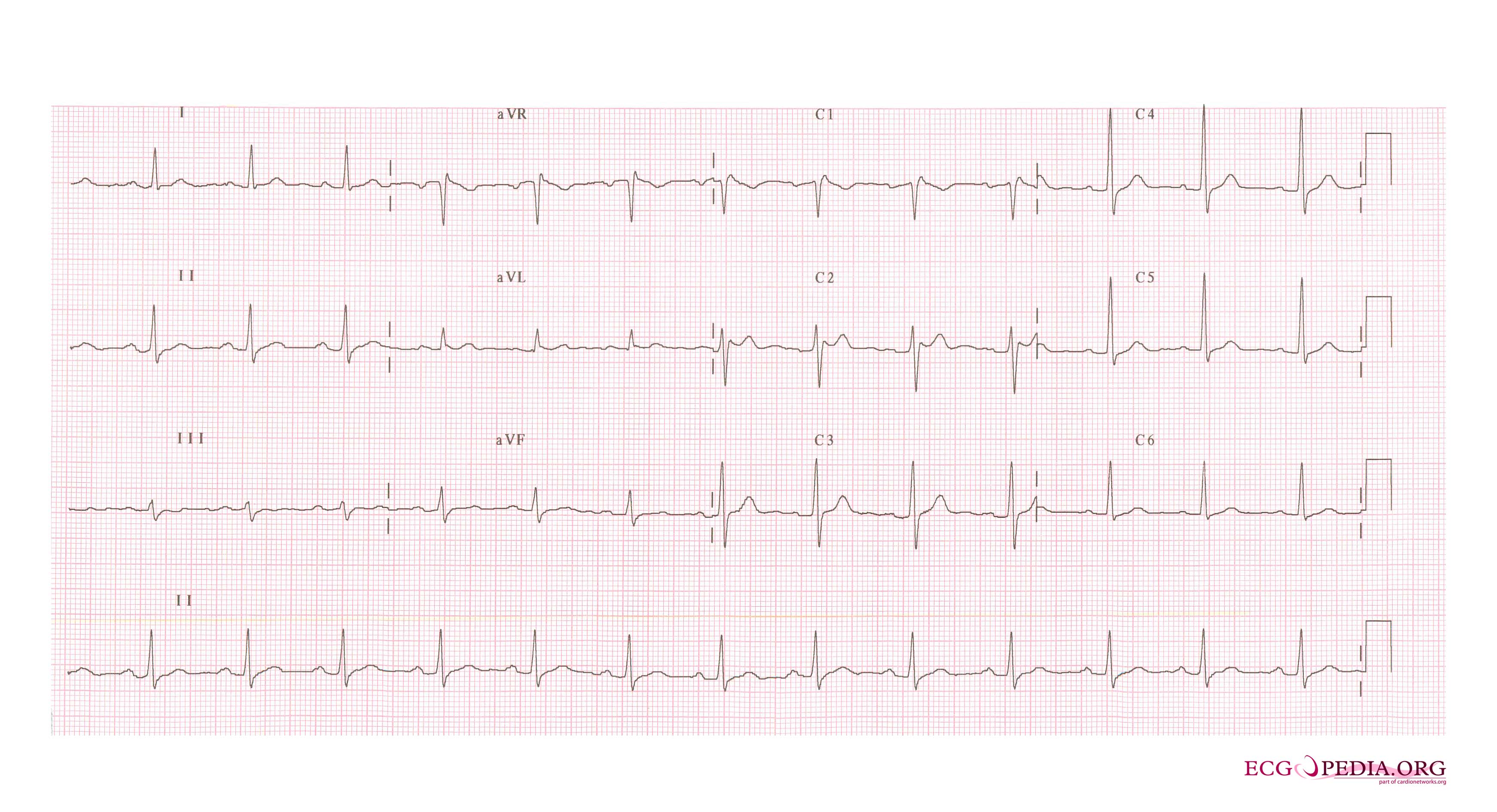
FileBrugada syndrome type2 example2.jpg ECGpedia
Brugada Type 3 Can Be The Morphology Of Either Type 1 Or Type 2, But With <2Mm Of St Segment Elevation.
Web The Brugada Syndrome May Present With Three Different Ecg Patterns, Referred To As Type 1, Type 2, And Type 2 Brugada Syndrome Ecg.
Web There Are 3 Patterns Of Brugada Syndrome, Classified Based On Ecg Parameters.
Brugada Syndrome Results From Mutations That.
Related Post: