Tulip Bubble Chart
Tulip Bubble Chart - Web the tulip bubble chart is a classic depiction of speculative mania and its eventual unravelling. But months later, the bubble burst. The purpose to understand this bubble is to highlight the risks of speculative investing and the potential consequences of irrational market behavior. The netherlands was therefore primed for a new trade, which was to become tulip mania. Tulips were introduced into europe from turkey shortly after 1550, and the delicately formed, vividly colored flowers became a popular if costly item. Web this chart shows a comparison of price developments during the tulip mania in 1637 and the current bitcoin bonanza of 2017. Web tulip bulb speculation became so widespread by 1636 that they were traded on amsterdam’s stock exchange and in rotterdam, haarlem, leyden, alkmar, hoorn, and other towns. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then dramatically collapsed in february 1637. Web like many flowers, they can come in a variety of different colours: Tulips became the talk of the fledgling dutch republic. Web tulip mania ( dutch: Web tulip mania was a period during the 17th century where contract prices for tulip bulbs reached extremely high levels before crashing in 1637. Web economist peter garber collected data on the sales of 161 bulbs of 39 varieties between 1633 and 1637, with 53 being recorded by gw. Web the dutch tulip bulb market. Web people got wiped out. the flowers that cost more than houses. The purpose to understand this bubble is to highlight the risks of speculative investing and the potential consequences of irrational market behavior. The netherlands was therefore primed for a new trade, which was to become tulip mania. Web the dutch tulip bulb market bubble, also known as tulipmania,. And if it bursts, the. Tulips became the talk of the fledgling dutch republic. Tulpenmanie) was a period during the dutch golden age when contract prices for some bulbs of the recently introduced and fashionable tulip reached extraordinarily high levels. Web this chart shows a comparison of price developments during the tulip mania in 1637 and the current bitcoin bonanza. The netherlands was therefore primed for a new trade, which was to become tulip mania. A bubble is a significant increase in an asset's price that is not reflected in. Web this chart shows a comparison of price developments during the tulip mania in 1637 and the current bitcoin bonanza of 2017. Tulpenmanie) was a period during the dutch golden. But months later, the bubble burst. The causes of tulip mania have perhaps been distorted over the centuries, with many assuming it was one of the first examples of a market bubble bursting. Tulips became the talk of the fledgling dutch republic. Web economist peter garber collected data on the sales of 161 bulbs of 39 varieties between 1633 and. Tulpenmanie) was a period during the dutch golden age when contract prices for some bulbs of the recently introduced and fashionable tulip reached extraordinarily high levels. Web economist peter garber collected data on the sales of 161 bulbs of 39 varieties between 1633 and 1637, with 53 being recorded by gw. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then dramatically. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then dramatically collapsed in february 1637. As tulip prices shot up by 1,000 percent in the 1630s, dutch investors scrambled to buy up bulbs still in the ground. Web tulipmania took hold of the netherlands in the 1600s and is widely viewed as the first financial asset bubble. Web people got wiped out.. Around the same time, tulip speculation even spread to paris and england, where tulips were traded on the london stock exchange. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then dramatically collapsed in february 1637. The causes of tulip mania have perhaps been distorted over the centuries, with many assuming it was one of the first examples of a market bubble. Web economist peter garber collected data on the sales of 161 bulbs of 39 varieties between 1633 and 1637, with 53 being recorded by gw. In both cities, traders strove to. When the price of something goes up and up, not because of its intrinsic value, but because people who buy it expect to. Web the dutch tulip bulb market. A bubble is a significant increase in an asset's price that is not reflected in. And tulips figure prominently in many of the 22 ravishing. Web updated march 22, 2020. Web tulip bulb speculation became so widespread by 1636 that they were traded on amsterdam’s stock exchange and in rotterdam, haarlem, leyden, alkmar, hoorn, and other towns. Web the tulip. The major acceleration started in 1634 and then dramatically collapsed in february 1637. When the price of something goes up and up, not because of its intrinsic value, but because people who buy it expect to. Web january 1, 2024 by victoria e. Web tulip bulb speculation became so widespread by 1636 that they were traded on amsterdam’s stock exchange and in rotterdam, haarlem, leyden, alkmar, hoorn, and other towns. Tulips became the talk of the fledgling dutch republic. Web tulipmania took hold of the netherlands in the 1600s and is widely viewed as the first financial asset bubble. Web economist peter garber collected data on the sales of 161 bulbs of 39 varieties between 1633 and 1637, with 53 being recorded by gw. And if it bursts, the. And tulips figure prominently in many of the 22 ravishing. Web tulip mania is often cited as the classic example of a financial bubble: Web tulip mania was a period during the 17th century where contract prices for tulip bulbs reached extremely high levels before crashing in 1637. A bubble is a significant increase in an asset's price that is not reflected in. The demand for rare tulip species in diverse hues quickly surpassed the supply, causing the price of individual bulbs to rise to unjustifiable heights across northern europe. The term tulip mania is now often used metaphorically to refer to any large economic bubble when asset prices deviate from intrinsic values. Web the amsterdam stock exchange opened in 1602 and the baltic grain trade, an informal futures market itself, had begun decades earlier. Tulpenmanie) was a period during the dutch golden age when contract prices for some bulbs of the recently introduced and fashionable tulip reached extraordinarily high levels.
tulipomania Burbuja, Tulipanes, Sociología

Bitcoin tulip bulb or another gold? Varchev Finance
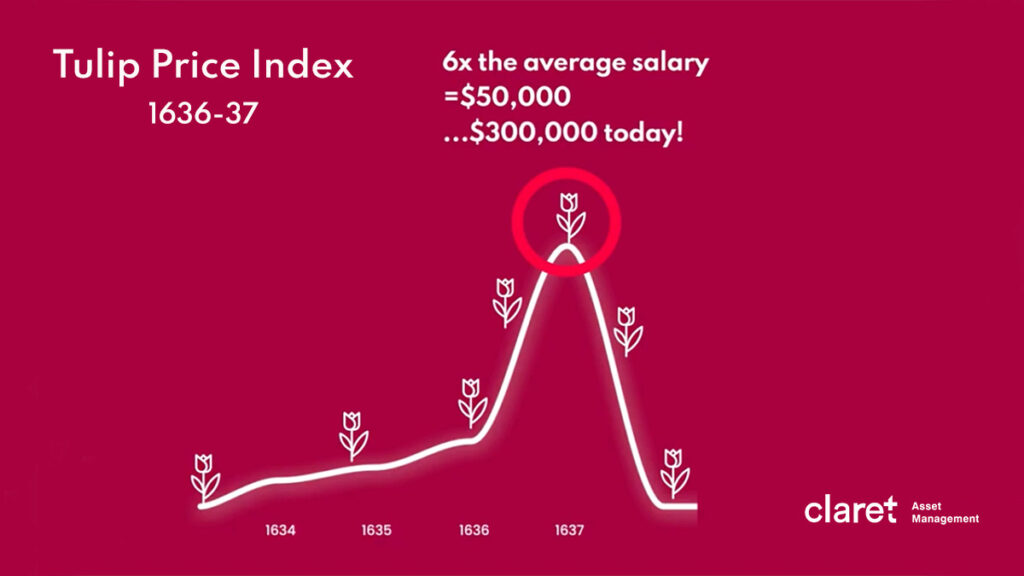
5 Stages of a Financial Bubble, From Birth to Bust » Claret

Not PC This Time It's Different, Episode IX 'The Rise and fall of
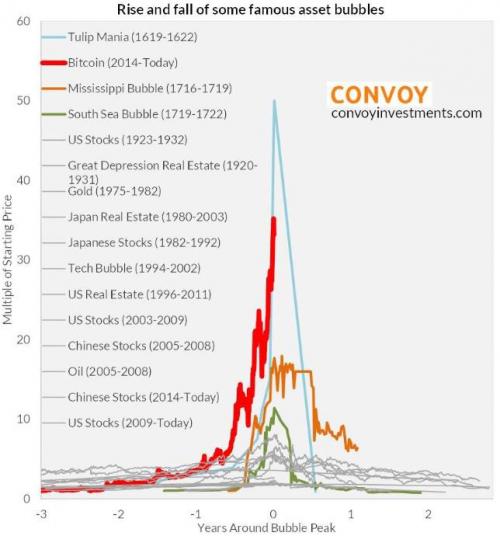
It’s Official Bitcoin Surpasses “Tulip Mania”, Is Now The Biggest
The Index of Tulip Market during Tulip Bubble [10] Download

Tulip Bubble Chart
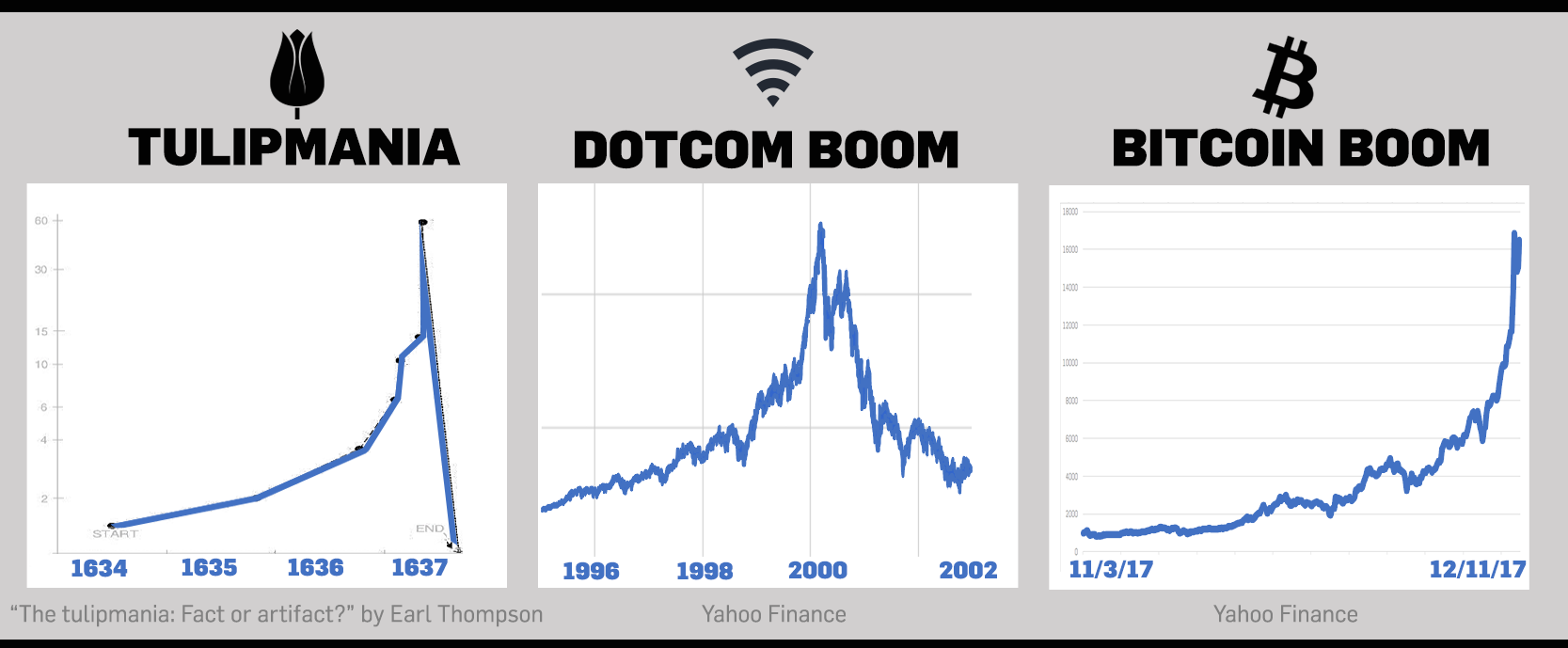
Look How Bitcoin's Rise Stacks up Against the Bubble and
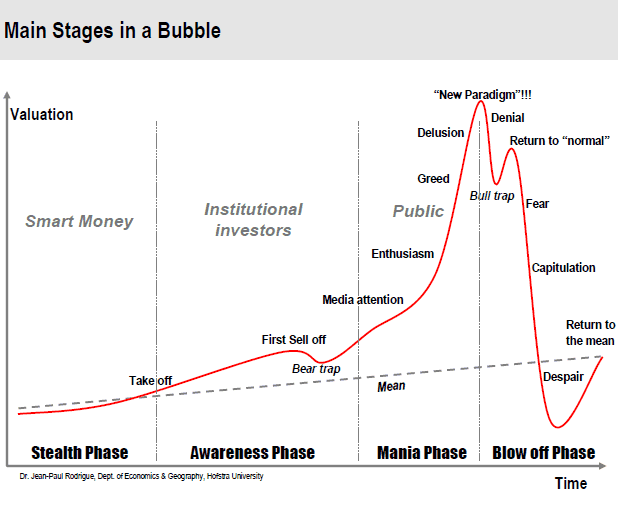
Is TSLA A 1,000 Stock Or A Tulip Mania Bubble? Robert McCarty

the anatomy of a Bubble. the tulip Bubble in 163637. Download
As Tulip Prices Shot Up By 1,000 Percent In The 1630S, Dutch Investors Scrambled To Buy Up Bulbs Still In The Ground.
Around The Same Time, Tulip Speculation Even Spread To Paris And England, Where Tulips Were Traded On The London Stock Exchange.
In Both Cities, Traders Strove To.
The Causes Of Tulip Mania Have Perhaps Been Distorted Over The Centuries, With Many Assuming It Was One Of The First Examples Of A Market Bubble Bursting.
Related Post: