The Rhythmic Electrical Patterns Of The Brain Are Called
The Rhythmic Electrical Patterns Of The Brain Are Called - A new study emphasizes the importance of brain rhythms in understanding cognition. Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Every known oscillation in one species is also found in virtually all other mammals. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web but to learn whether a specific cell is setting up a particular rhythm, researchers must be able to stimulate it directly and record its tiny, subthreshold. The research explores how rhythmic electrical fields,. Web brain waves, also known as neural oscillations, are rhythmic electrical patterns generated by the synchronous firing of large groups of neurons in the brain. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. The most studied central pattern generator is an intraspinal network of. Web researchers studying the brain have long been interested in its neural oscillations, the rhythmic electrical activity that plays an important role in the transmission of. Rem is an acronym that stands for: Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Web but to learn whether a specific cell is. The most studied central pattern generator is an intraspinal network of. Web electrical rhythms of the brain range across different frequencies, from 1 to 250 hertz. A remarkable aspect of brain rhythms is their evolutionarily conserved nature. Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Web in this framework, the. The research explores how rhythmic electrical fields,. Using these different frequencies the brain regulates how relevant information. Rem is an acronym that stands for: Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Web the rhythmic electrical patterns of the brain are called: Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Web in this framework, the rhythmic pattern of neural activity related to bodily rhythms is important as it would open or close windows of communication. Rem is an acronym that stands for: Web electrical rhythms of the brain range across different frequencies,. A remarkable aspect of brain rhythms is their evolutionarily conserved nature. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Using these different frequencies the brain regulates how relevant information. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by. The most studied central pattern generator is an intraspinal network of. Web electrical rhythms of the brain range across different frequencies, from 1 to 250 hertz. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web the rhythmic electrical patterns of the brain are called:. Web mit researchers have identified unique electrical activity patterns in the brain’s cortical layers, consistent across different species. Web in this framework, the rhythmic pattern of neural activity related to bodily rhythms is important as it would open or close windows of communication. Web neuroscientists have long known of the existence of brain waves — rhythmic fluctuations of electrical activity. Web electrical rhythms of the brain range across different frequencies, from 1 to 250 hertz. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Rem is an acronym that stands for: Web brain waves, also known as neural oscillations, are rhythmic electrical patterns generated by. The most studied central pattern generator is an intraspinal network of. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web in this framework, the rhythmic pattern of neural activity related to bodily rhythms is important as it would open or close windows of communication.. Web in this framework, the rhythmic pattern of neural activity related to bodily rhythms is important as it would open or close windows of communication. Web linking brain rhythms and cognition through rhythmic sampling is particularly attractive because it allows using global mechanistic principles to bridge two. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are. There are four basic brain rhythms: Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web electrical rhythms of the brain range across different frequencies, from 1 to 250 hertz. Using these different frequencies the brain regulates how relevant information. A new study emphasizes the importance of brain rhythms in understanding cognition. Web neuroscientists have long known of the existence of brain waves — rhythmic fluctuations of electrical activity believed to reflect the brain’s state. Web many of our bodily functions, such as walking, breathing, and chewing, are controlled by brain circuits called central oscillators, which generate rhythmic firing. Web researchers studying the brain have long been interested in its neural oscillations, the rhythmic electrical activity that plays an important role in the transmission of. Web but to learn whether a specific cell is setting up a particular rhythm, researchers must be able to stimulate it directly and record its tiny, subthreshold. A remarkable aspect of brain rhythms is their evolutionarily conserved nature. Web in this framework, the rhythmic pattern of neural activity related to bodily rhythms is important as it would open or close windows of communication. Rem is an acronym that stands for: Every known oscillation in one species is also found in virtually all other mammals. The research explores how rhythmic electrical fields,. Web linking brain rhythms and cognition through rhythmic sampling is particularly attractive because it allows using global mechanistic principles to bridge two. Web the rhythmic electrical patterns of the brain are called:
2 The typical normal brain rhythms with their amplitude levels

Beta, alpha, theta, delta, gamma brain waves. Set of brain waves
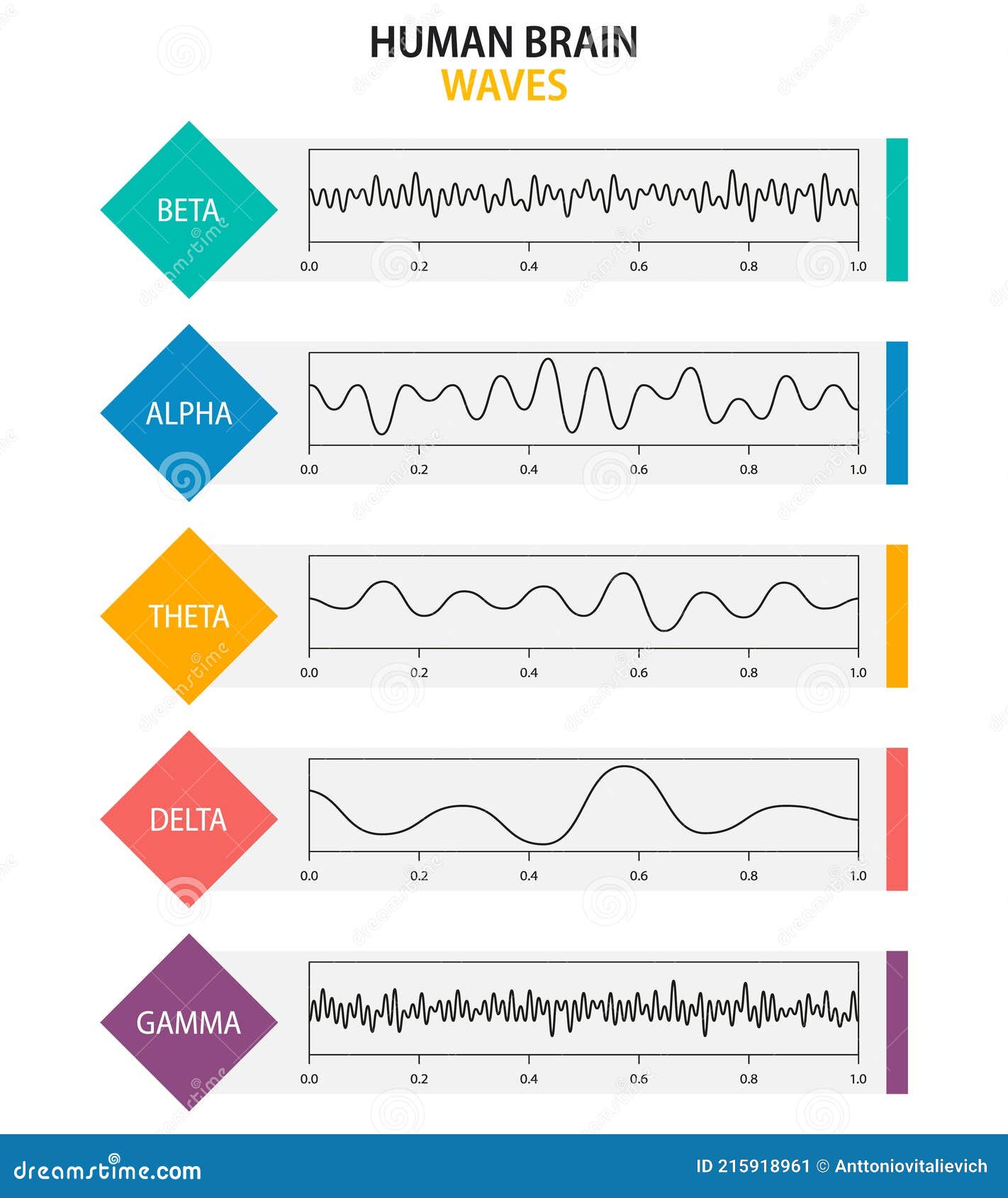
Set of Brain Waves Oscillation. Beta, Alpha, Theta, Delta, Gamma Brain

Brainwave Frequencies Explained
How brain waves guide memory formation MIT News Massachusetts

The brain electrical waves stock vector. Illustration of hypnotherapy
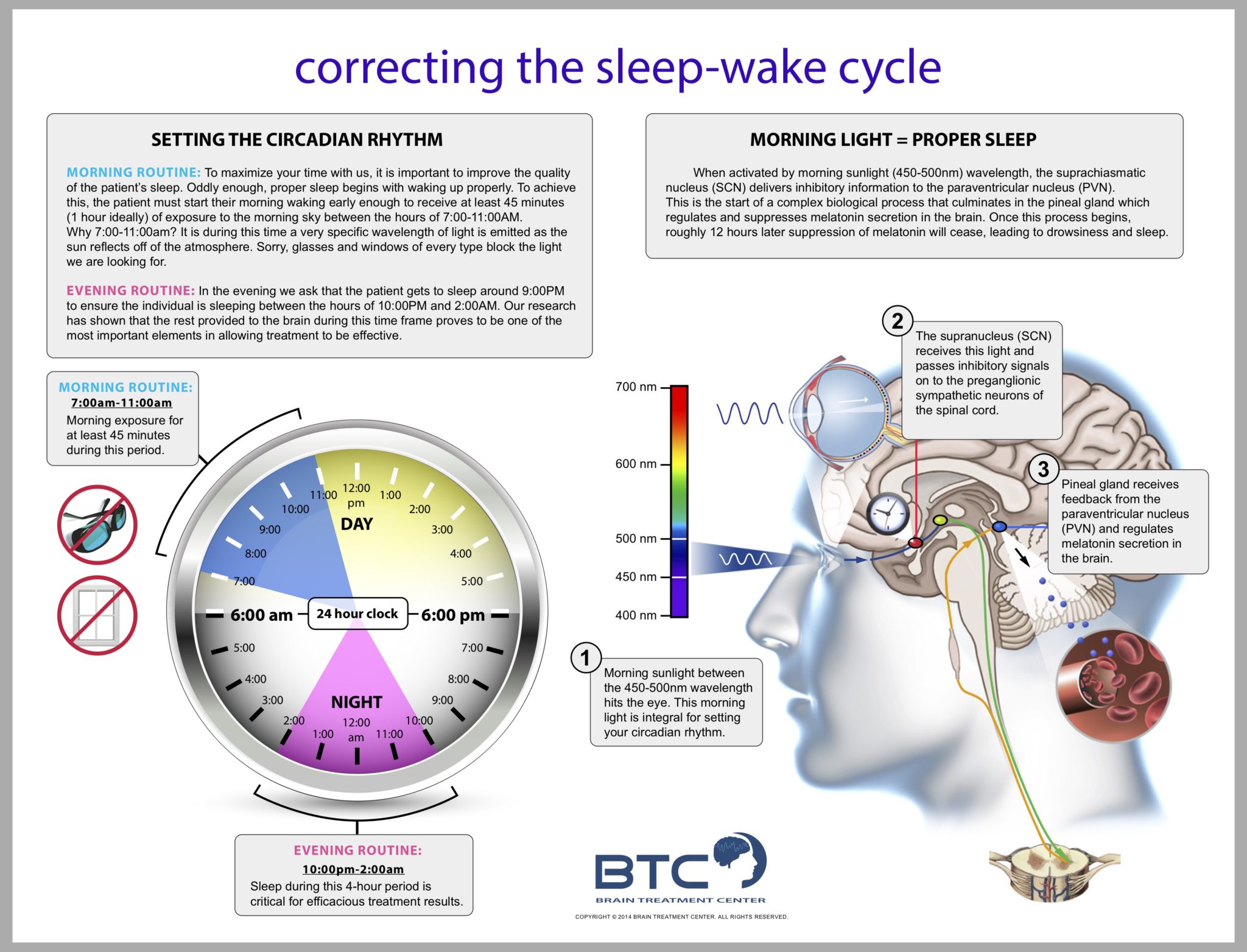
Circadian Rhythm Poster Brain Treatment Center of Dallas
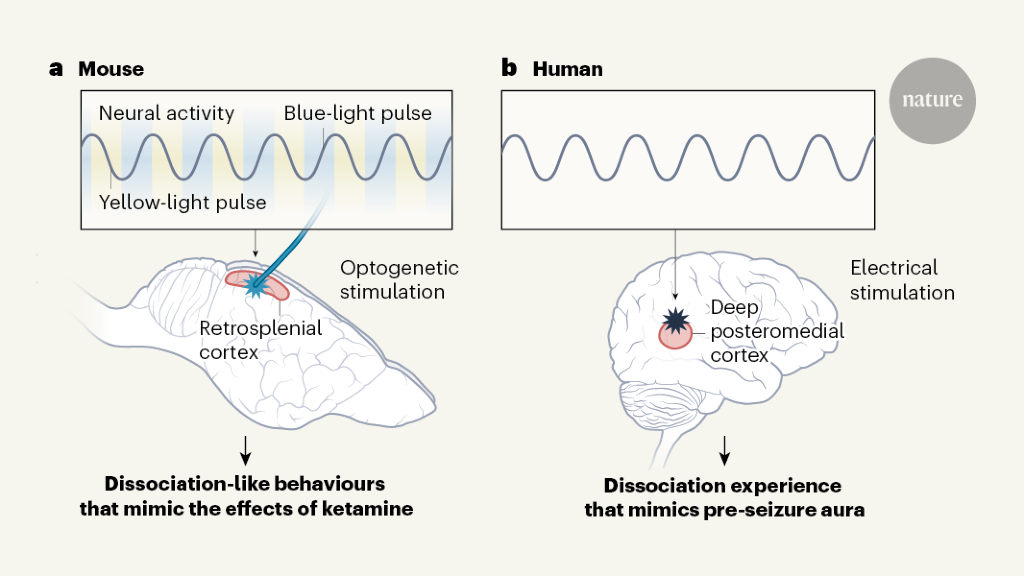
The brain rhythms that detach us from reality
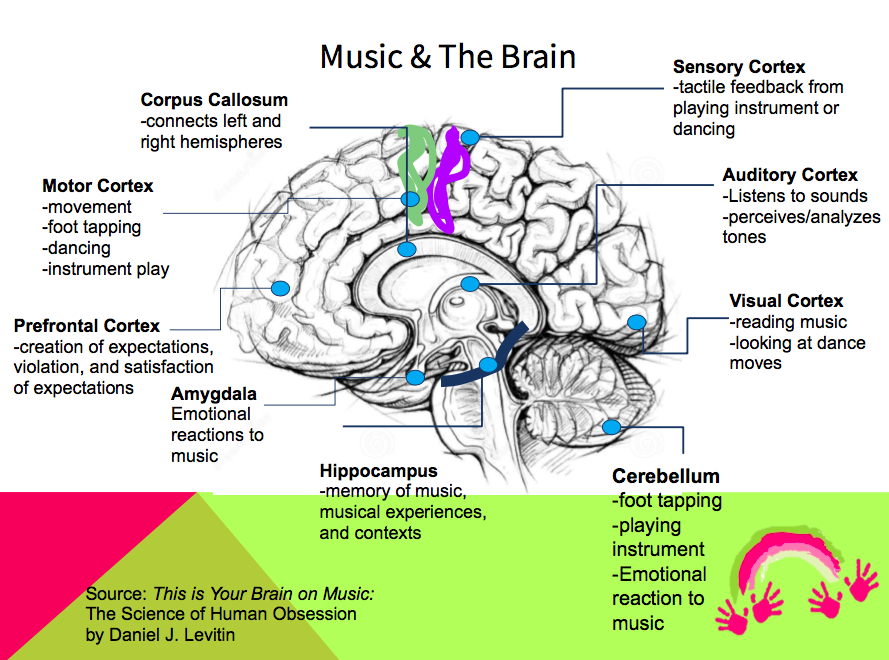
Rhythm, Music, and The Brain — Therabeat, Inc.Rhythm, Music, and The

The brain, circadian rhythms, and clock genes The BMJ
Web Many Of Our Bodily Functions, Such As Walking, Breathing, And Chewing, Are Controlled By Brain Circuits Called Central Oscillators, Which Generate Rhythmic Firing.
The Most Studied Central Pattern Generator Is An Intraspinal Network Of.
Web Brain Waves, Also Known As Neural Oscillations, Are Rhythmic Electrical Patterns Generated By The Synchronous Firing Of Large Groups Of Neurons In The Brain.
Web Mit Researchers Have Identified Unique Electrical Activity Patterns In The Brain’s Cortical Layers, Consistent Across Different Species.
Related Post: