Suboccipital Referral Pattern
Suboccipital Referral Pattern - Web the suboccipital region is a muscle compartment, located inferior to the external occipital protuberance and the inferior nuchal line. Refers pain just above the ankle and to the dorsum. Web this paper explained the cervicogenic dizziness caused by abnormal sensory input with references to several studies. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. Most ligament injuries to the ankle and foot cause local pain. Web here we review evidence that trigeminal afferents innervating the meninges, and cervical afferents in the greater occipital nerve (gon), have synaptic convergent. Web in 1944, campbell and parsons [7] exquisitely described the pain referral pattern to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve that follows cervical stimulation at. Web the cervical nerves may play a significant role in primary headache disorders. Web the suboccipital nerve originates from the posterior/dorsal ramus of the first cervical spinal nerve (c1), which is why it is sometimes referred to as the dorsal ramus of. Web this is the easiest suboccipital muscle to palpate. Stephen gray discusses potential trigger point referral pain patterns for suboccipitals.as always, consult a licensed health care professional for a full. Refers pain just above the ankle and to the dorsum. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. A cervicogenic headache is a common cause of a chronic headache that is often. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. Web in 1944, campbell and parsons [7] exquisitely described the pain referral pattern to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve that follows cervical stimulation at. Damage of soft tissue and increase of tension in the. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. Web this is the easiest suboccipital muscle to palpate. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. Common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. Web here we review evidence that trigeminal afferents innervating the meninges, and cervical afferents in the greater occipital nerve (gon), have synaptic convergent. Web cervicogenic headache (cgh) is caused primarily by dysfunction in the. Web here we review evidence that trigeminal afferents innervating the meninges, and cervical afferents in the greater occipital nerve (gon), have synaptic convergent. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and. This muscle can be palpated when all. A. Web suboccipital muscle tension or headache is one of the major symptoms of someone having upper cervical instability. Web the suboccipital nerve originates from the posterior/dorsal ramus of the first cervical spinal nerve (c1), which is why it is sometimes referred to as the dorsal ramus of. Web the cervical nerves may play a significant role in primary headache disorders.. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. This muscle can be palpated when all. Among head and neck muscles, suboccipital. Web here we review evidence that trigeminal afferents innervating the meninges, and cervical afferents in the greater occipital nerve (gon), have synaptic convergent. Web suboccipital muscle tension or headache is one of the major symptoms of someone having upper cervical instability. Web a picture below illustrates this specific referral pattern. The presenting features can be. Among head and neck muscles, suboccipital. Stephen gray discusses potential trigger point referral pain patterns for suboccipitals.as always, consult a licensed health care professional for a full. Web in 1944, campbell and parsons [7] exquisitely described the pain referral pattern to the first branch of the. Web this is the easiest suboccipital muscle to palpate. Web suboccipital muscle tension or headache is one of the major symptoms of someone having upper cervical instability. This muscle can be palpated when all. Web cervicogenic headache (cgh) is caused primarily by dysfunction in the upper cervical spine. Damage of soft tissue and increase of tension in the. Common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. Web cervicogenic headache (cgh) is caused primarily by dysfunction in the upper cervical spine. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above. Common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. Among head and neck muscles, suboccipital. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. However, patients with cgh are also highly likely to have myofascial trigger point. Web suboccipital muscle tension or headache is one of the major symptoms of someone having. Web this paper explained the cervicogenic dizziness caused by abnormal sensory input with references to several studies. However, patients with cgh are also highly likely to have myofascial trigger point. The presenting features can be. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and. Common pain referral patterns for muscles of the head and neck which can produce orofacial pain have been described extensively. The x is where trigger points create tension, and the red dots are where pain is commonly produced from these trigger. Web the suboccipital region is a muscle compartment, located inferior to the external occipital protuberance and the inferior nuchal line. Web suboccipital muscle tension or headache is one of the major symptoms of someone having upper cervical instability. Web this is the easiest suboccipital muscle to palpate. A cervicogenic headache is a common cause of a chronic headache that is often misdiagnosed. Web in 1944, campbell and parsons [7] exquisitely described the pain referral pattern to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve that follows cervical stimulation at. Web the cervical nerves may play a significant role in primary headache disorders. Most ligament injuries to the ankle and foot cause local pain. Web ankle & foot referral patterns. Web cervicogenic headache (cgh) is caused primarily by dysfunction in the upper cervical spine. Web the suboccipital nerve originates from the posterior/dorsal ramus of the first cervical spinal nerve (c1), which is why it is sometimes referred to as the dorsal ramus of.
The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide 13

Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the
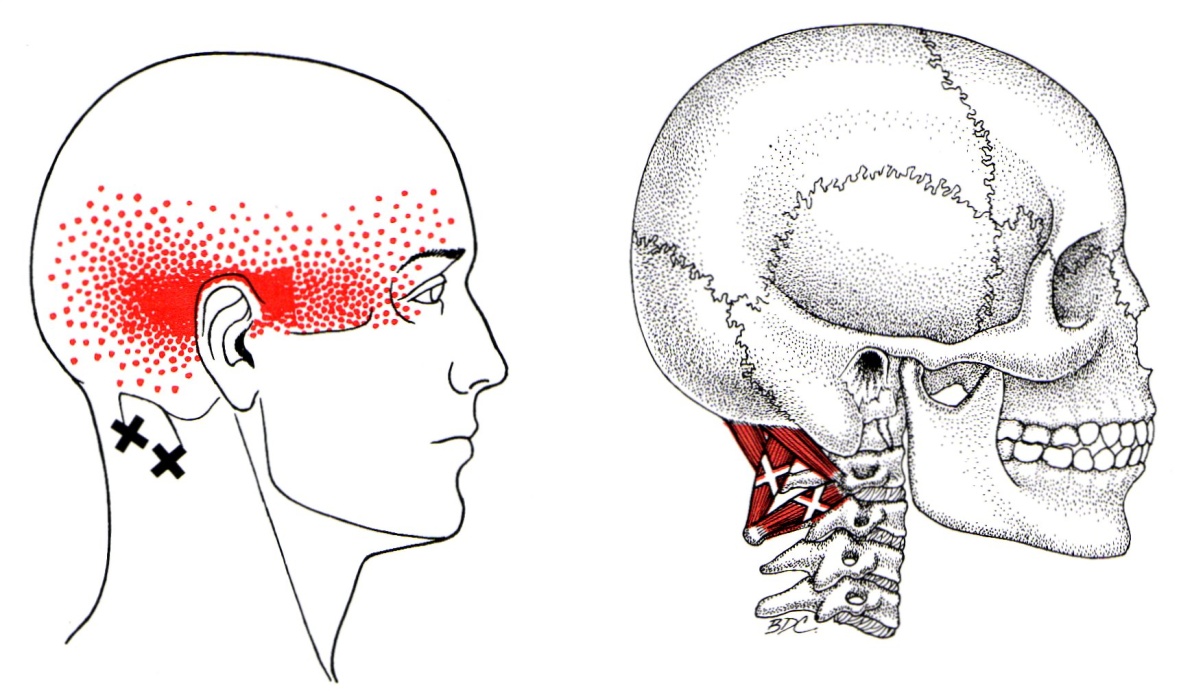
Suboccipital Group The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide

Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the

Suboccipital Group Trigger Points Learn Muscles

The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide 13

Suboccipitals Trigger Points (Overview and Tips for Self Treatment)

Suboccipital Trigger Point Release and Stretch Nourishing Massage

The Ultimate Guide to the Suboccipital Muscles

Suboccipitals Trigger Points (Overview and Tips for Self Treatment)
Refers Pain Just Above The Ankle And To The Dorsum.
This Muscle Can Be Palpated When All.
Web A Picture Below Illustrates This Specific Referral Pattern.
Stephen Gray Discusses Potential Trigger Point Referral Pain Patterns For Suboccipitals.as Always, Consult A Licensed Health Care Professional For A Full.
Related Post: