Spine And Organs Chart
Spine And Organs Chart - It's a delicate structure that contains nerve bundles and cells that carry messages from your brain to the rest of your body. Your spine plays an essential role in supporting the body’s structure and vital functions. Web it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; They begin as nerve roots that emerge from a segment of the spinal cord at a specific level. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. The vertebral column, commonly known as the spine, spinal column, or backbone, is a flexible hollow structure through which the spinal cord runs. The different vertebrae that make up the area of this spine are each connected to certain organs. Web the spine is divided into four regions which contain vertebrae: Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). Web the layers of the back comprise the skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial (extrinsic) and deep (intrinsic) back muscles, the posterior portion of the ribs, and the vertebral column housing the spinal cord and surrounding meninges. Many of the nerves of the peripheral nervous system, or pns, branch out from the. The different vertebrae that make up the area of this spine are each connected to certain organs. Your spinal cord, made up of billions of nerves, lies inside your spinal column, protected on all sides by bone. Web the spine is central to the entire. Web the spine is divided into four regions which contain vertebrae: An anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) root on both right and left sides. It contains the osteology, arthrology and myology of the spine and back. The sections below will cover these elements in more detail. Your spinal cord, made up of billions of nerves, lies inside your spinal column,. Web stretching down the midline of the trunk from the base of the skull to the coccyx, the spine plays an extremely important role in our bodies as it supports the upper body’s weight; It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. Your spinal cord is a. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. It's a delicate structure that contains nerve bundles and cells that carry messages from your brain to the rest of your body. It is within this region that the nerves to the arms arise via the brachial plexus, and where the cervical plexus forms providing. Web it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; Your spine (backbone) is the long, flexible column of bones that protects your spinal cord. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. Five bones in the lower back—the lumbar spine. T4 is connected. Your spine plays an essential role in supporting the body’s structure and vital functions. Hover over each part to see what they do. The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright,. T4 is connected to your gallbladder. Web your spinal column or ‘backbone’ is made up of 24. It is within this region that the nerves to the arms arise via the brachial plexus, and where the cervical plexus forms providing innervation to. Your spinal cord, made up of billions of nerves, lies inside your spinal column, protected on all sides by bone. It protects the nervous system, facilitates movement, and enables communication between the brain. T4 is. Seven in your neck (cervical spine ), 12 in your midback (thoracic spine) and 5 in your lower back (lumbar spine). It protects the nervous system, facilitates movement, and enables communication between the brain. Your spine consists of three sections: Web each spinal nerve contains a mixture of motor and sensory fibres. The spinal nerves send sensory messages to the. T6 is connected to your stomach. Web your spine is made up of vertebrae (bones), disks, joints, soft tissues, nerves and your spinal cord. It begins at the base of your skull and ends in your tailbone, which is part of your pelvis. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. The vertebral. Your spine is made up of 24 small bones (vertebrae) that are stacked on top of each other to create the spinal column. What is the spinal cord? The thoracic spine starts at the base of your neck and ends at the bottom of your ribs. Web the vertebral column (spine or backbone) is a curved structure composed of bony. Your spinal cord, made up of billions of nerves, lies inside your spinal column, protected on all sides by bone. It is part of the axial skeleton and extends from the base of the skull to the tip of the coccyx. The spinal nerves send sensory messages to the sensory roots, then to sensory fibers in the posterior (back or dorsal) part of the spinal cord. The back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright,. It is essential for many functions, such as movement, support, and protecting the spinal cord. Web your spine is made up of vertebrae (bones), disks, joints, soft tissues, nerves and your spinal cord. 12 bones in the chest—the thoracic spine. Web the layers of the back comprise the skin, subcutaneous tissue, superficial (extrinsic) and deep (intrinsic) back muscles, the posterior portion of the ribs, and the vertebral column housing the spinal cord and surrounding meninges. It contains the osteology, arthrology and myology of the spine and back. Web the spine’s four sections, from top to bottom, are the cervical (neck), thoracic (abdomen,) lumbar (lower back), and sacral (toward tailbone). The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends into the pelvis. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. They begin as nerve roots that emerge from a segment of the spinal cord at a specific level. T6 is connected to your stomach. What is the spinal cord? Web your spinal column or ‘backbone’ is made up of 24 vertebrae:
Spinal Nerve Chart, Print 5x7 Spinal nerve, Spinal nerve chart, Nerve

What Vertebrae Are Responsible For What? Ask a Chiropractor!

vertebral column에 대한 이미지 검색결과 Human Anatomy Chart, Human Anatomy

36 best images about body system correlation charts on Pinterest

A chart describing which spinal segment connects to which organs
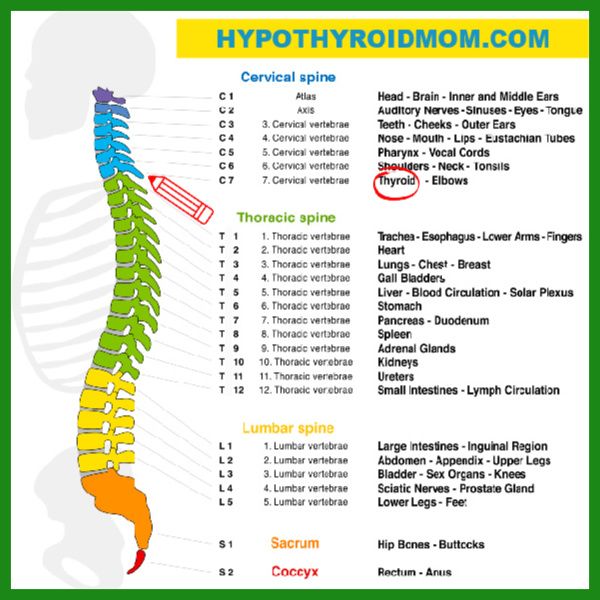
How Your Spine Is Connected To Your Organs (Including The Thyroid

Pin on Bones & Muscles
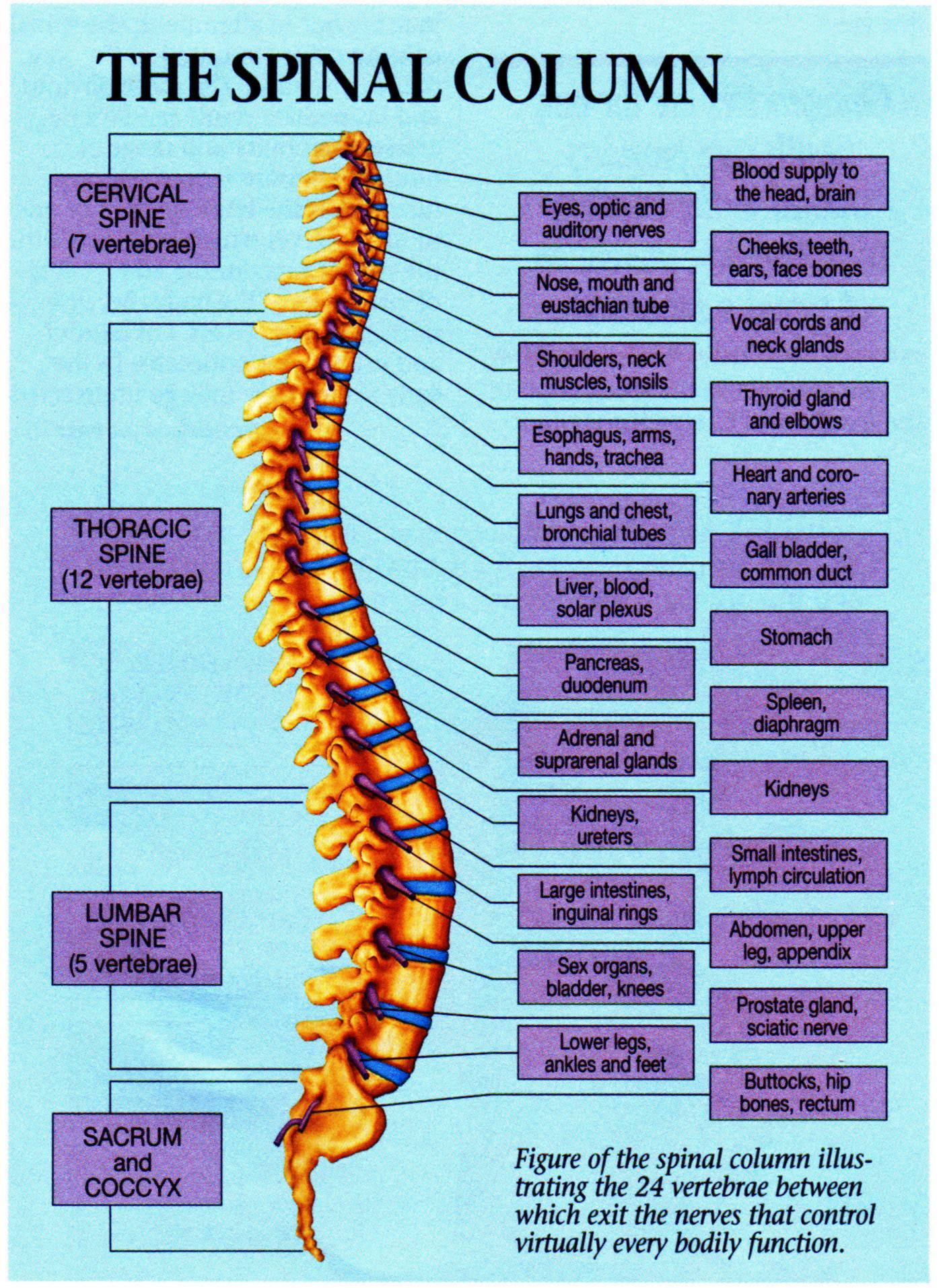
spinal organ chart Premier Chiropractic Centre

Spinal Nerve Function Anatomical Chart Anatomy Models and Anatomical

Rudiger Anatomie The Human Spine Laminated Anatomy Chart
Provides Posture While Allowing For Movement And Flexibility;
Web Thoracic Spine And Your Organs.
Your Spine (Backbone) Is The Long, Flexible Column Of Bones That Protects Your Spinal Cord.
The Sections Below Will Cover These Elements In More Detail.
Related Post: