Soil Bearing Capacity Chart
Soil Bearing Capacity Chart - For soils classified as ch or mh, without either torque probe values or blow count test results, selected anchors must be rated for a. Earth pressure acting on basement walls. The pressure which the soil can easily withstand against load is called allowable bearing pressure. The gross pressure at the base of the foundation at which soil fails is called ultimate bearing capacity. Typical weight and composition of soil. For large buildings or structures constructions, a geotechnical site investigation should be done. For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. Use of the mohr’s circle in soil mechanics. (1) strip foundation of width b (terzaghi, 1943) where: Web the strength and compactness of soil is important when pouring concrete footings. Web soil bearing capacity is the ability of the soil to support the load exerted by a structure without undergoing excessive settlement or shear failure. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure. For large buildings or structures constructions, a geotechnical site investigation should be done. The charts were produced by a new numerical. The charts were produced by a new numerical analysis tool based on discontinuity layout optimisation (dlo) in which a previously proposed homogenisation method was used to define the improvement area. Typical weight and composition of soil. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure. Basic equations for the mohr's circle. Web the strength and. For large buildings or structures constructions, a geotechnical site investigation should be done. Web the values provided in this table have been adjusted for overburden pressure, embedment depth, water table height, or settlement problems. Web the safe bearing capacity of soil should be determined on the basis of soil test data or by performing some field test such as standard. Use of the mohr’s circle in soil mechanics. However, in the absence of soil test data, the values of safe bearing capacity (s.b.c) as given in the following table may be used as a guide for preliminary analysis. Web bearing capacity is the ability of soil to safely carry the pressure placed on the soil from any engineered structure without. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure. Calculate lateral earth pressure acting on basement walls. See a chart of soil bearing capacities for bedrock, sand, clay and more. Web typical values of soil bearing capacity. The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which. Web the strength and compactness of soil is important when pouring concrete footings. It determines the maximum allowable load that can be applied to the soil without causing significant settlements or foundation failure. Web use this chart to determine the soil bearing capacity of where you are working and for determining what size outrigger pad is necessary. Extensive research work. Calculate lateral earth pressure acting on basement walls. Kimmeridge clay is a stiff, heavy fissured clay deposit which can contain sulfates similar. Web the bearing capacity of soil is defined as the capacity of the soil to bear the loads coming from the foundation. The gross pressure at the base of the foundation at which soil fails is called ultimate. Basic equations for the mohr's circle. For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. Web what is bearing capacity of soil and its assessment? Web in geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil. Web the values provided in this table have been adjusted for overburden pressure, embedment depth, water table height, or settlement problems. It determines the maximum allowable load that can be applied to the soil without causing significant settlements or foundation failure. Typical weight and composition of soil. Calculate lateral earth pressure acting on basement walls. How bearing capacity can be. The charts were produced by a new numerical analysis tool based on discontinuity layout optimisation (dlo) in which a previously proposed homogenisation method was used to define the improvement area. See a chart of soil bearing capacities for bedrock, sand, clay and more. Web in geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to. Calculate lateral earth pressure acting on basement walls. Web for a strip foundation, the ultimate bearing capacity is given by the equation: Web the bearing capacity of the soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Web the safe bearing capacity of soil should be determined on the basis of soil test data or by performing some field test such as standard penetration test or plate load test etc. Web bearing capacity is the ability of the underlying soil to support the foundation loads without shear failure. For large buildings or structures constructions, a geotechnical site investigation should be done. (1) strip foundation of width b (terzaghi, 1943) where: Web bearing capacity of soils. Web a series of preliminary design charts were developed to predict the bearing capacity of fully and partially penetrated deep mixing (dm) of soft soil. The requirements for categorizing a site and the planning and construction of a footing for a building of a single residential house or a. Allowable bearing pressures, allowable stresses and design formulas provided in this chapter shall be used with the allowable stress design load combinations specified in section 1605.3. What factor of safety is considered when determining safe bearing capacity? Web in geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. Web use this chart to determine the soil bearing capacity of where you are working and for determining what size outrigger pad is necessary. For preliminary design purposes, bs 8004 [1] gives typical values of allowable bearing capacity which should result in an adequate factor of safety against shaer failure without accounting for the setllemenet criteria [2]. However, in the absence of soil test data, the values of safe bearing capacity (s.b.c) as given in the following table may be used as a guide for preliminary analysis.
Typical Soil Bearing Capacity CivilWeb Spreadsheets

SoilBearingCapacityInfo DICA

Soil Bearing Capacity Chart

Bearing Capacity Of Different Types Of Soil Engineering Discoveries
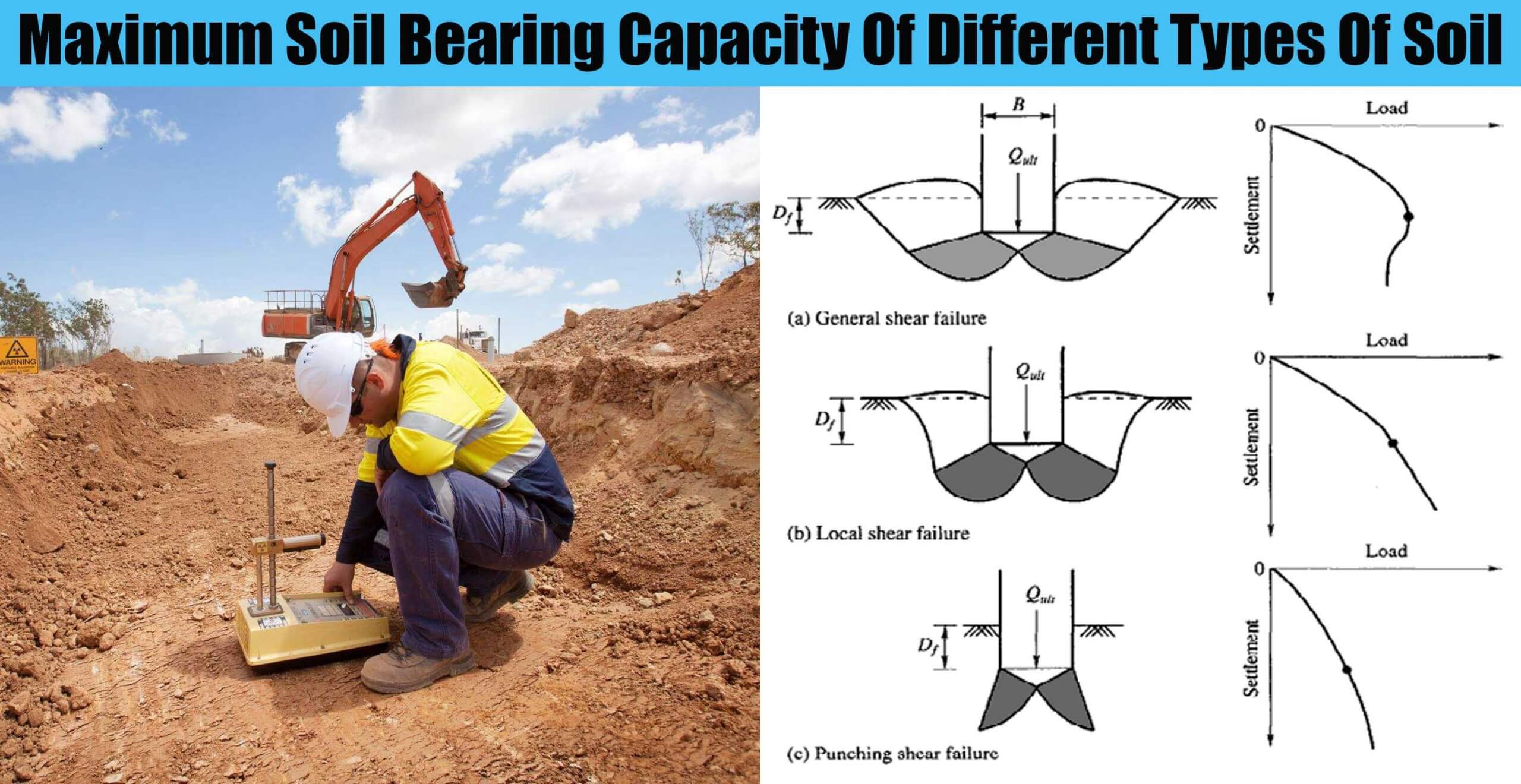
Maximum Soil Bearing Capacity Of Different Types Of Soil Engineering
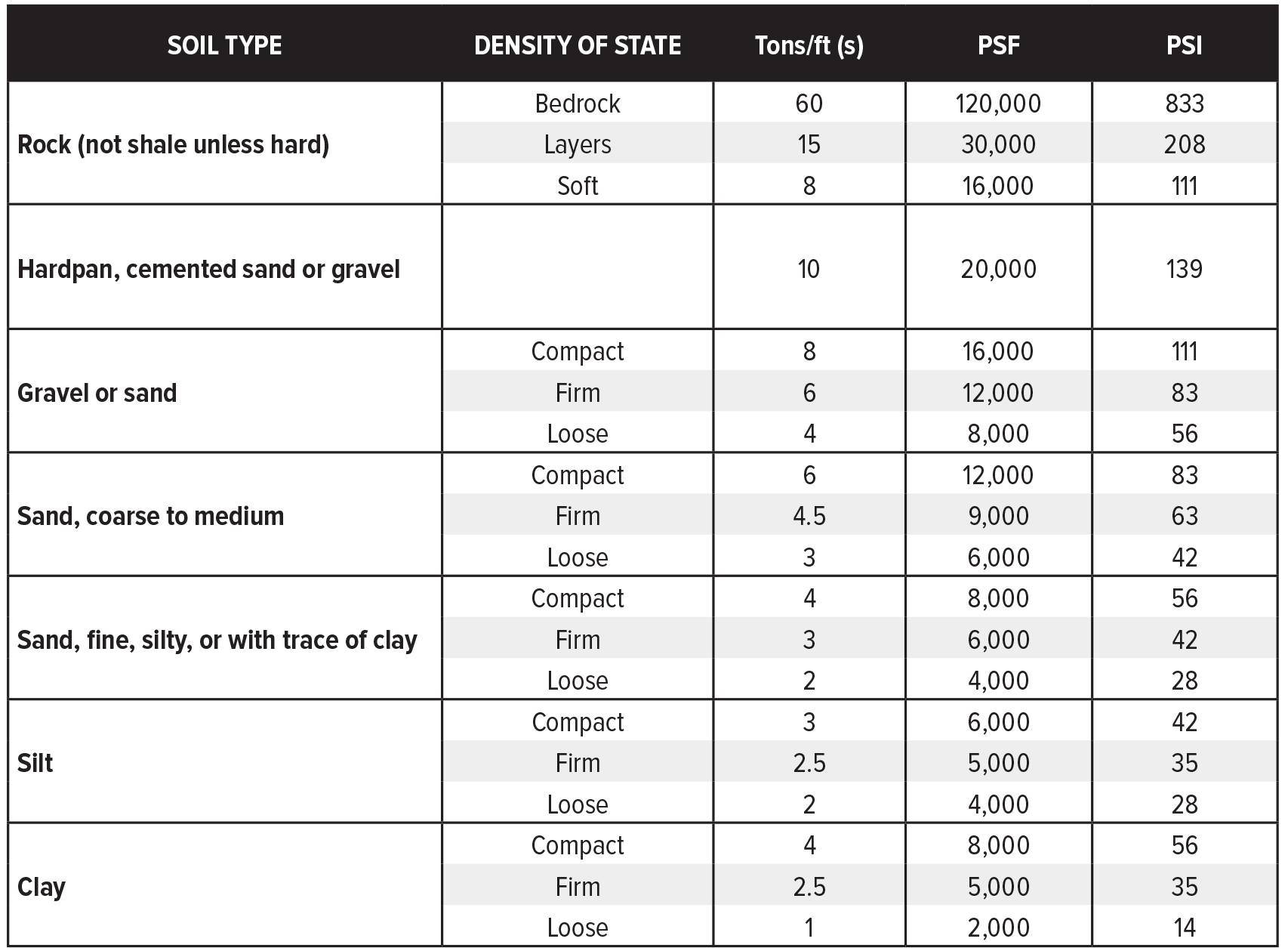
Soil Bearing Capacity Chart Rock, Sand, Clay & More DICA

Typical Soil Bearing Capacity CivilWeb Spreadsheets
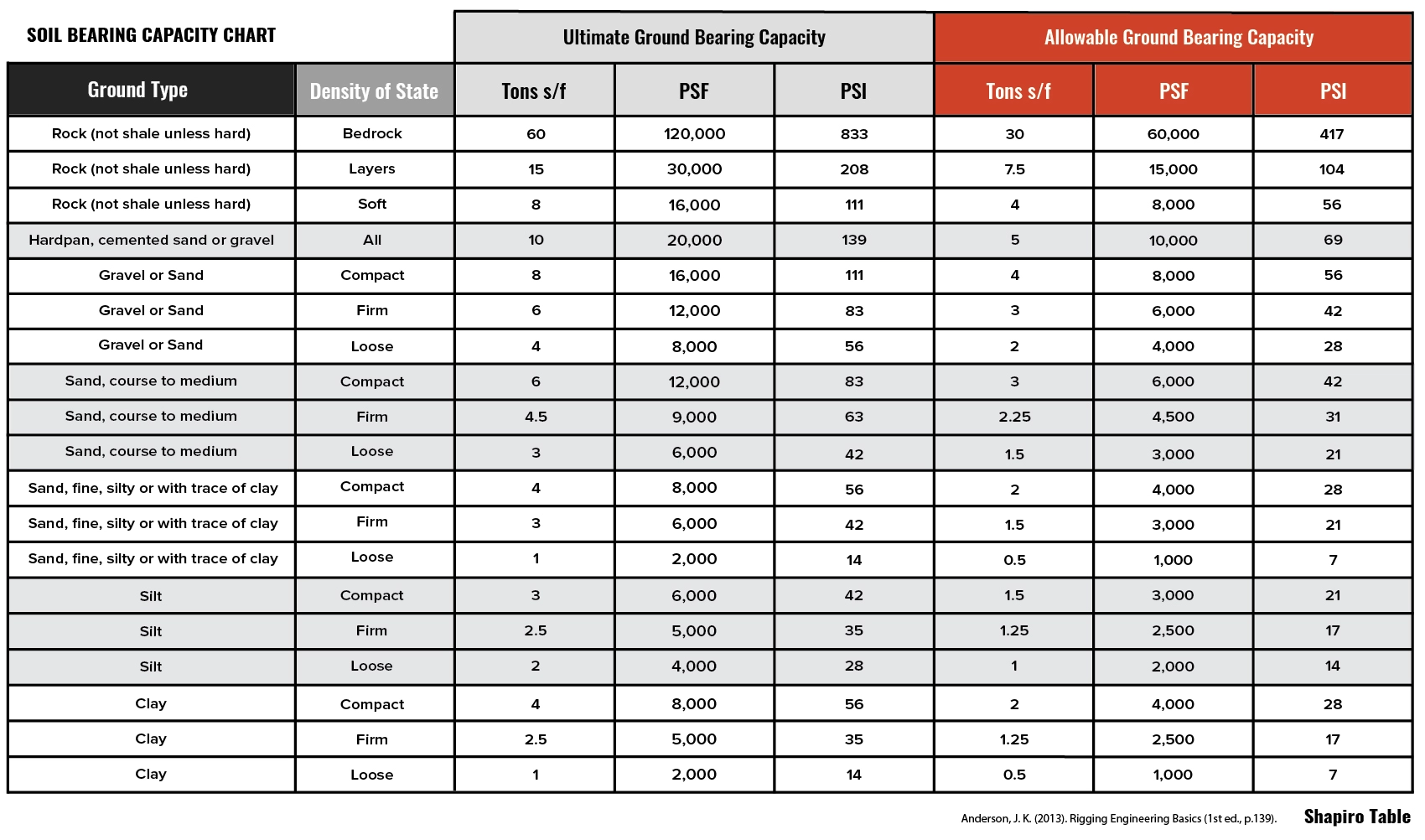
Soil Bearing Capacity Chart Ultimate Ground Bearing Capacity DICA
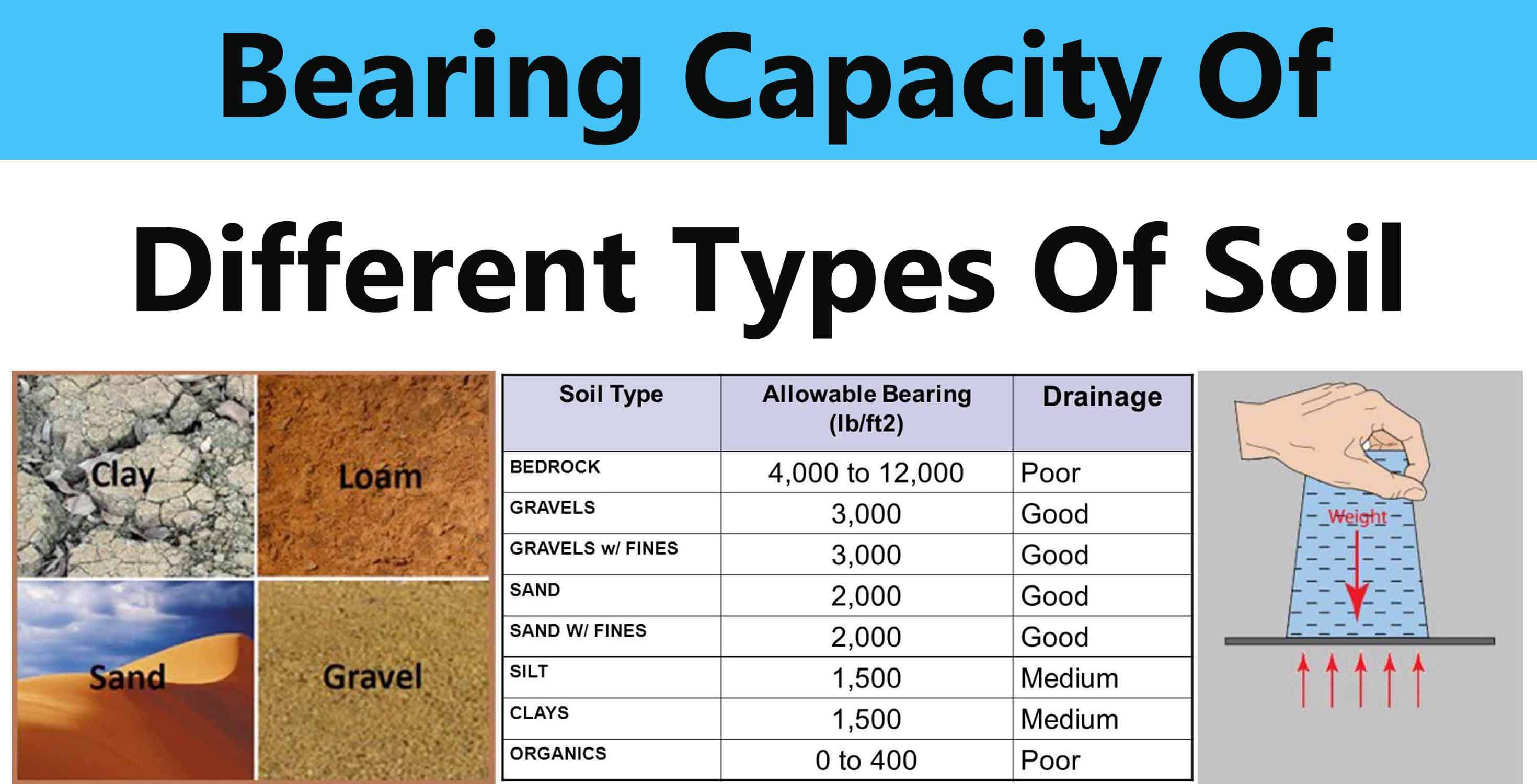
Bearing Capacity Of Different Types Of Soil Engineering Discoveries
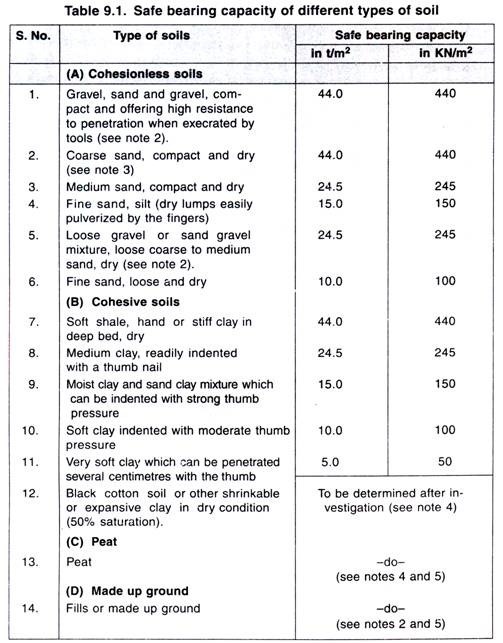
Safe Bearing Capacity of different types of soil Civilology
In Simpler Terms, It Gauges The Soil’s Strength And Stability As A Foundation Material.
Web Bearing Capacity Is The Ability Of Soil To Safely Carry The Pressure Placed On The Soil From Any Engineered Structure Without Undergoing A Shear Failure With Accompanying Large Settlements.
Web Soil Bearing Capacities Chart.
For Soils Classified As Ch Or Mh, Without Either Torque Probe Values Or Blow Count Test Results, Selected Anchors Must Be Rated For A.
Related Post: