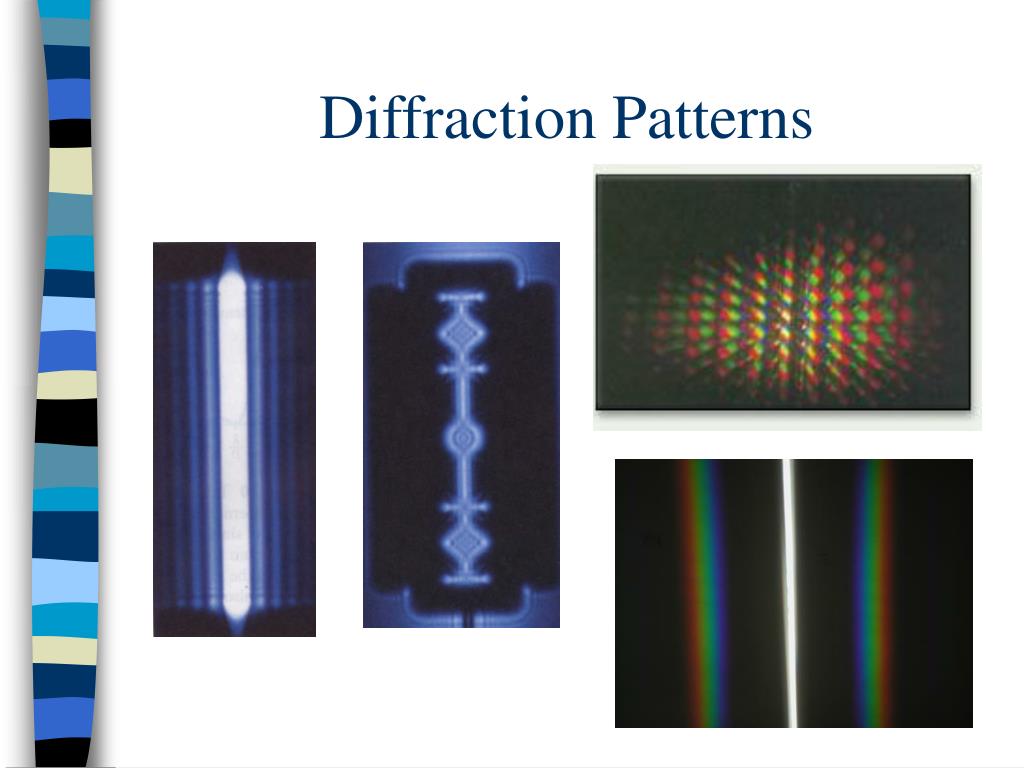
Single Slit Diffraction Pattern
Single Slit Diffraction Pattern - The numerical simulations are performed with grating wall size a s = 100 nm, grating thickness l g =100 nm, c 3 = 5.04 mev nm 3 and a propagation time from the grating to the detector t = 21 ms. Web single slit interference pattern. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. After passing through a narrow aperture (opening), a wave propagating in a specific direction tends to spread out. Web a fraunhofer diffraction pattern is produced on a screen located 1.00 m from a single slit. (a) single slit diffraction pattern. the wavelength of the light is 600 nm, and the screen is 2.0 m from the slit. Subsidiary maxima equally spaced, successively smaller in intensity and half the width of the central maximum. Web a diffraction pattern of a red laser beam projected onto a plate after passing through a small circular aperture in another plate. Describe diffraction through a single slit. Web light passing through a single slit forms a diffraction pattern somewhat different from that formed by double slits. (a) 0.010 0 mm (b) 0.100 mm (c) 0.200 mm (d) 1.00 mm (e) 0.005 00 mm As the slit width a increases from a = λ to 5 λ a = λ to 5 λ and then to 10λ 10λ. Describe diffraction through a single slit. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. I think that's because the waves are getting reinforcement so they don't go so. By the end of this section, you will be able to: After passing through a narrow aperture (opening), a wave propagating in a specific direction tends to spread out. Web the intensity pattern for diffraction due to a single slit can be calculated using phasors as \ (i = i_0 \left (\frac {sin \space \beta} {\beta}\right)^2,\) where \ (\beta = \frac {\phi} {2} = \frac {\…. A central maximum with a high intensity. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. Subsidiary maxima equally spaced, successively smaller in intensity and half the width of the central maximum. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum. Web single slit diffraction pattern all the waves passing through the slit interfere to produce a diffraction pattern consisting of bright and dark fringes. Explore the concept of single slit interference in light waves. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer. the wavelength of the light is 600 nm, and the screen is 2.0 m from the slit. In contrast, a diffraction grating produces evenly spaced lines that dim slowly on either side of the center. What is the width of the slit? As the slit width a increases from a = λ to 5 λ a = λ to 5. (b) the diagram shows the bright central maximum, and the dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. The numerical simulations are performed with grating wall size a s = 100 nm, grating thickness l g =100 nm, c 3 = 5.04 mev nm 3 and a propagation time from the grating to the detector t = 21 ms. Web the. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. A central maximum with a high intensity. (a) monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. Web a diffraction pattern of a red laser beam projected onto a. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. The numerical simulations are performed with grating wall size a s = 100 nm, grating thickness l g =100 nm, c 3 = 5.04 mev nm 3 and a propagation time from the grating to the detector t = 21 ms. With a general. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. Note that the central maximum is larger than maxima on either side and that the intensity decreases rapidly on either side. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either. (b) the drawing shows the bright central maximum and dimmer and thinner maxima on either side. As the waves spread out, they interfere with each other, resulting in an interference pattern on a screen placed some distance away. Web figure 27.21 shows a single slit diffraction pattern. Note that the central maximum is larger than those on either side,. Describe diffraction through a single slit. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a. Monochromatic light passing through a single slit has a central maximum and many smaller and dimmer maxima on either side. Note that the central maximum is larger than maxima on either side and that the intensity decreases rapidly on either side. Web a fraunhofer diffraction pattern is produced on a screen located 1.00 m from a single slit. Explain the phenomenon of diffraction and the conditions under which it is observed. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. The central maximum is six times higher than shown. What happens when there's only one hole? Explore the concept of single slit interference in light waves.
Single Slit Diffraction Wize University Physics Textbook Wizeprep

Diffraction

Photon

Diffraction Through a Single Slit

Single slit diffraction equation drugbinger
PPT Diffraction through a single slit PowerPoint Presentation, free

Schematic of the farfield single slit diffraction pattern for a fused
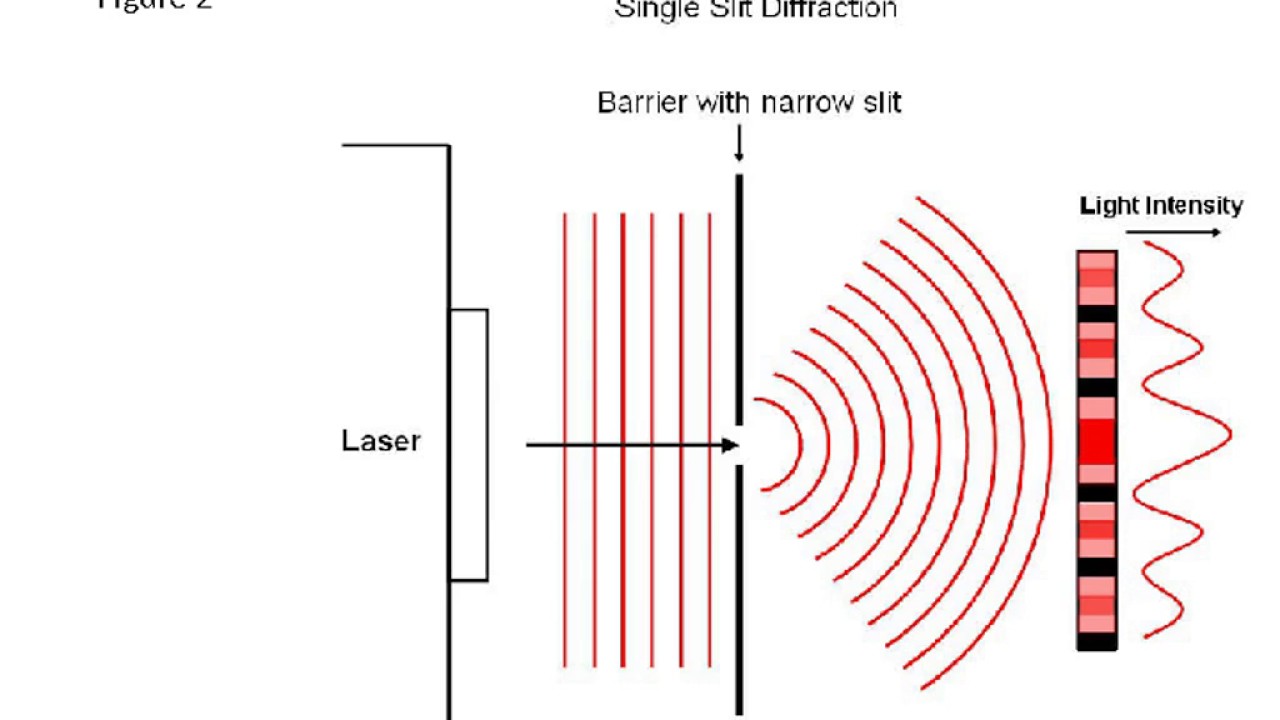
single slit diffraction Experiment YouTube
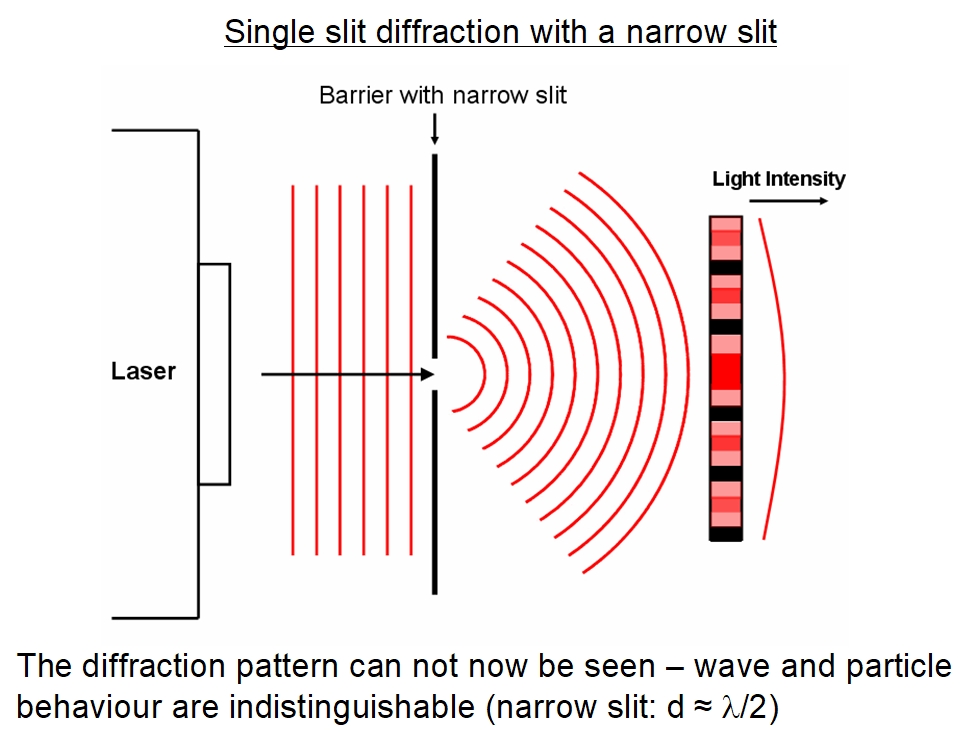
Diffraction Pattern Single Slit
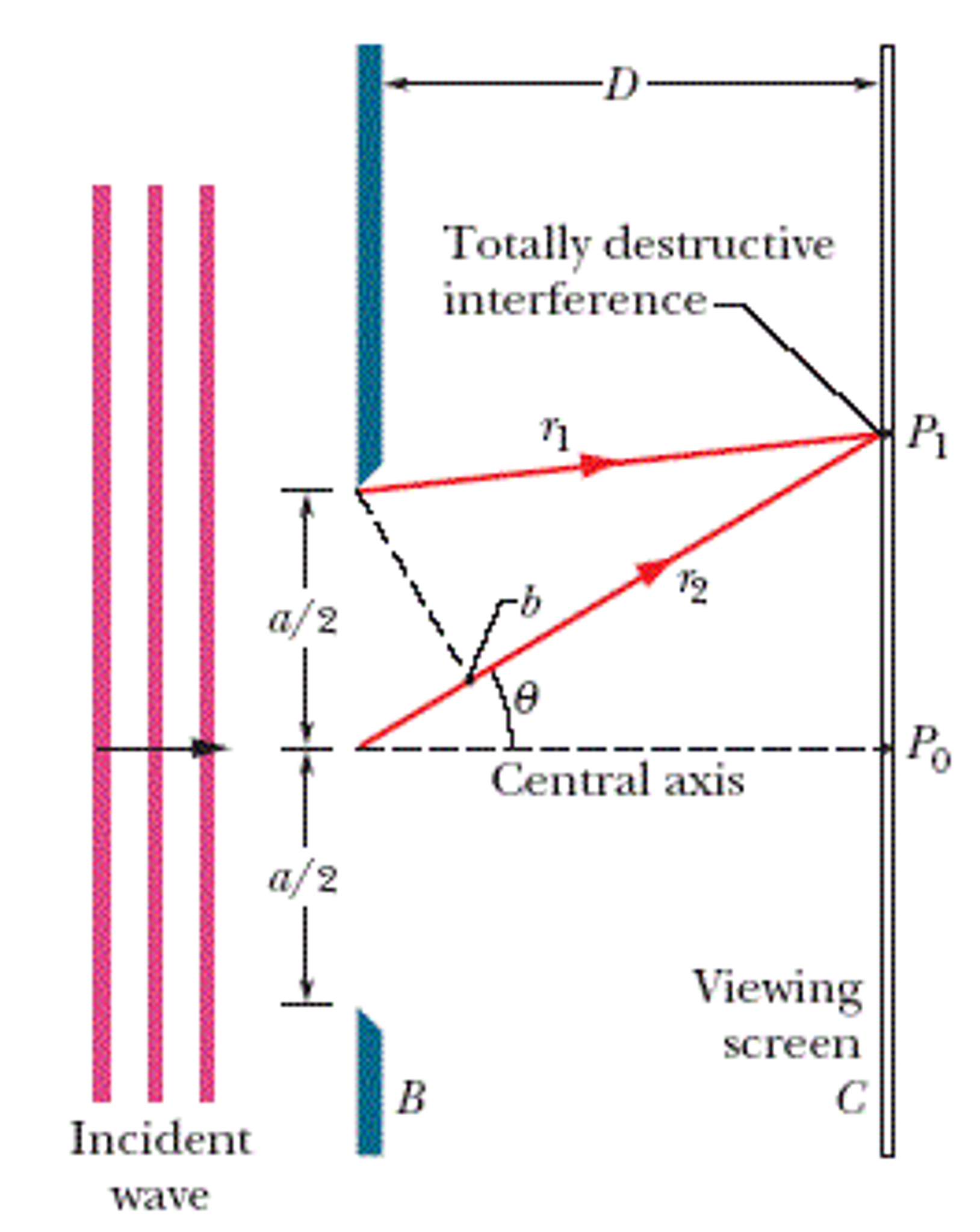
Solved In the singleslit diffraction experiment of the
Note That The Central Maximum Is Larger Than Those On Either Side, And That The Intensity Decreases Rapidly On Either Side.
A Mathematical Representation Of Huygens' Principle Can Be Used To Start An Equation.
Let's Call The Gap Width Of The Aperture A A, And Assume That This Is Much Smaller Than The Distance To The Screen, As In The Figure Below.
When Light Passes Through A Single Slit Whose Width W Is On The Order Of The Wavelength Of The Light, Then We Can Observe A Single Slit Diffraction Pattern On A Screen That Is A Distance L >> W Away From The Slit.
Related Post: