Select The Patterns Of Indirect Transmission Of Infectious Disease
Select The Patterns Of Indirect Transmission Of Infectious Disease - 14 14 15 select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease. Web the scheme below categorizes transmission as direct transmission, if the infective form of the agent is transferred directly from a reservoir to an infected. Web please select the patterns of direct (contact) transmission of infectious disease. Infectious organisms may be transmitted either by direct or indirect contact. (examples of direct contact transmission) kissing, touching mother to fetus (vertical). Web three things are necessary for an infection to occur: Web we developed a novel statistical tool, inods (identifying contact networks of infectious disease spread) that estimates the transmission rate of an infectious disease. Web describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Food, water kissing, touching fomites air. Mathematical models describing indirect contact transmission are an important component of infectious disease mitigation and risk assessment. Food, water kissing, touching fomites air. Web select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease food, water fomites air soil please choose the best definition of virulence factors. Web how are diseases transmitted? Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission. Web the scheme below categorizes transmission as direct transmission, if the infective form of the agent is. Web flu (influenza) whooping cough (petrussis) rsv (respiratory syncytial virus) common colds (rhinovirus, adenovirus) formite (surface) formite transmission involves. 14 14 15 select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease. Infectious organisms may be transmitted either by direct or indirect contact. (examples of direct contact transmission) kissing, touching mother to fetus (vertical). Web the scheme below categorizes transmission. Web given these direct and indirect mitigating impacts at various levels to different infectious diseases and their burdens, we must consider an integrated. Describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Infectious diseases are transmitted from person to. Web indirect contact transmission involves inanimate objects called fomites that become contaminated by pathogens from an infected individual or reservoir (figure 16.10). Web. 14 14 15 select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease. Web describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission. In this mode of transmission, the pathogen or virus is passed on through an intermediary object or surface. Web how are diseases transmitted? Web indirect contact transmission infectious agent must pass from infected host to an intermediate conveyor, and from there to another host infected individuals contaminate. Web please select the patterns of direct (contact) transmission of infectious disease. Mathematical models describing indirect contact transmission are an important component of infectious disease mitigation and risk assessment. Transmission may occur through several different mechanisms.. Infectious organisms may be transmitted either by direct or indirect contact. Web given these direct and indirect mitigating impacts at various levels to different infectious diseases and their burdens, we must consider an integrated. Web select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease food, water fomites air soil please choose the best definition of virulence factors. Web the. Examples include air, water, food, soil, and inanimate objects known as fomites. Web flu (influenza) whooping cough (petrussis) rsv (respiratory syncytial virus) common colds (rhinovirus, adenovirus) formite (surface) formite transmission involves. Food, water kissing, touching fomites air. Web describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission. Places where infectious agents (germs) live (e.g., sinks, surfaces, human skin) susceptible person with a way. Examples include air, water, food, soil, and inanimate objects known as fomites. Web flu (influenza) whooping cough (petrussis) rsv (respiratory syncytial virus) common colds (rhinovirus, adenovirus) formite (surface) formite transmission involves. In this mode of transmission, the pathogen or virus is passed on through. Web given these direct and indirect mitigating impacts at various levels to different infectious diseases and their burdens, we must consider an integrated. Mathematical models describing indirect contact transmission are an important component of infectious disease mitigation and risk assessment. Web how are diseases transmitted? Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission. Examples include air, water, food, soil, and. Web select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease. Web how are diseases transmitted? Transmission may occur through several different mechanisms. Web given these direct and indirect mitigating impacts at various levels to different infectious diseases and their burdens, we must consider an integrated. Mathematical models describing indirect contact transmission are an important component of infectious disease mitigation. Mathematical models describing indirect contact transmission are an important component of infectious disease mitigation and risk assessment. Infectious diseases are transmitted from person to. Web flu (influenza) whooping cough (petrussis) rsv (respiratory syncytial virus) common colds (rhinovirus, adenovirus) formite (surface) formite transmission involves. Web indirect contact transmission infectious agent must pass from infected host to an intermediate conveyor, and from there to another host infected individuals contaminate. Web the scheme below categorizes transmission as direct transmission, if the infective form of the agent is transferred directly from a reservoir to an infected. Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission. Web please select the patterns of direct (contact) transmission of infectious disease. Web select the patterns of indirect (vehicle) transmission of infectious disease. Web three things are necessary for an infection to occur: Infectious organisms may be transmitted either by direct or indirect contact. Web how are diseases transmitted? Describe the different types of disease reservoirs. Web indirect contact transmission involves inanimate objects called fomites that become contaminated by pathogens from an infected individual or reservoir (figure 16.10). Examples include air, water, food, soil, and inanimate objects known as fomites. Web there, a fourth specific feature often intervenes, namely the direct and indirect action of immunity, and a fifth specific trait, already described in sect. Compare contact, vector, and vehicle modes of transmission.
Pathophysiology Global Overview Of Select Infectious Diseases E6D

Infectious disease transmission Royalty Free Vector Image
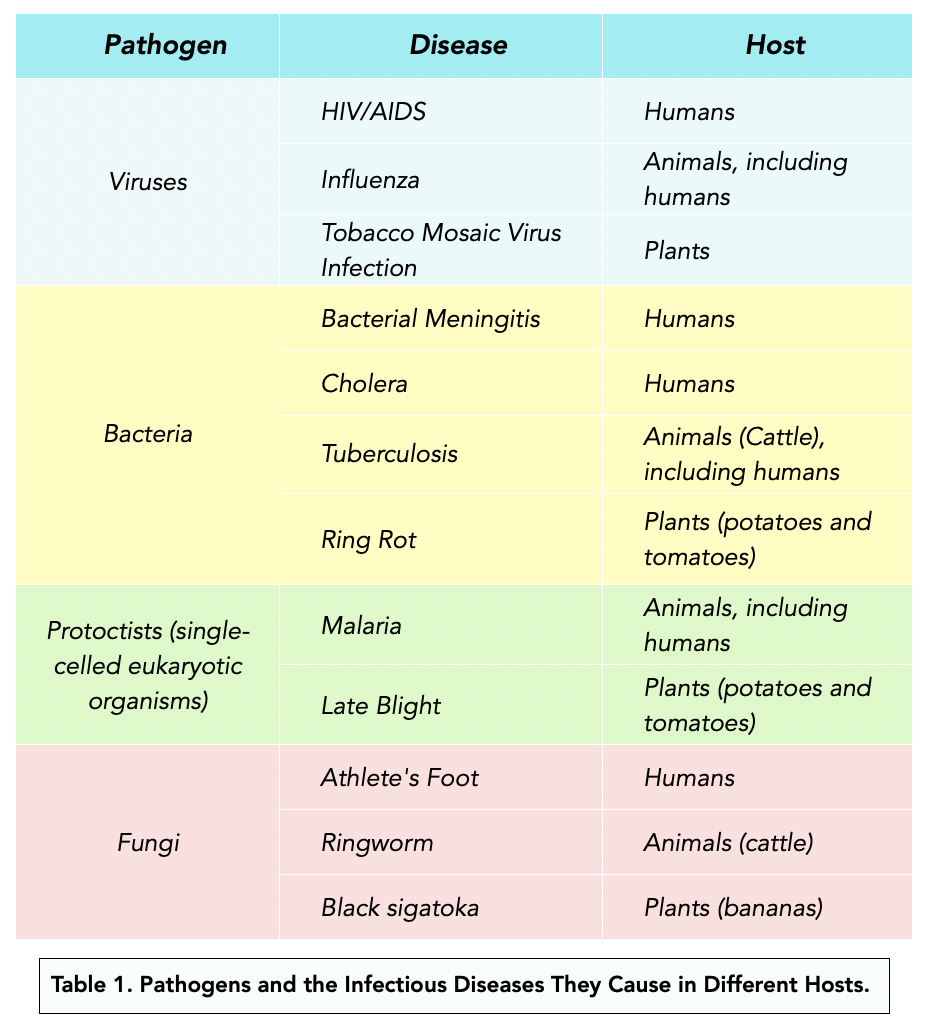
Pathogens and Infectious Diseases (Alevel Biology) Study Mind

Staphylococcus Presentation

Nurse Aide Infection Control

An Introduction to Infectious Disease Science in the News

Types Of Disease Transmission Concept Map Answers Map
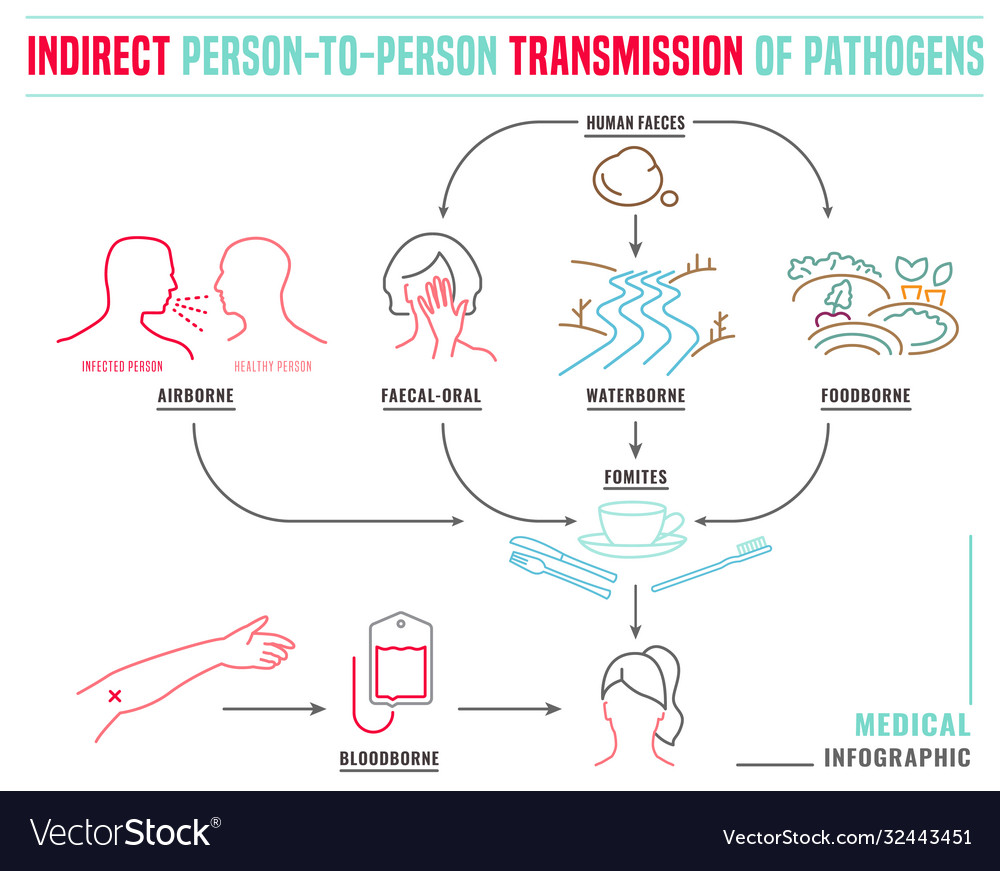
Indirect disease transmission Royalty Free Vector Image

This image of the mode of disease transmission clearly shows the

Infection and immunity 1.6 Indirect persontoperson transmission of
Web Select The Patterns Of Indirect (Vehicle) Transmission Of Infectious Disease Food, Water Fomites Air Soil Please Choose The Best Definition Of Virulence Factors.
Transmission May Occur Through Several Different Mechanisms.
For Example, Touching A Contaminated Surface And Then Touching The Face Can.
Web We Developed A Novel Statistical Tool, Inods (Identifying Contact Networks Of Infectious Disease Spread) That Estimates The Transmission Rate Of An Infectious Disease.
Related Post: