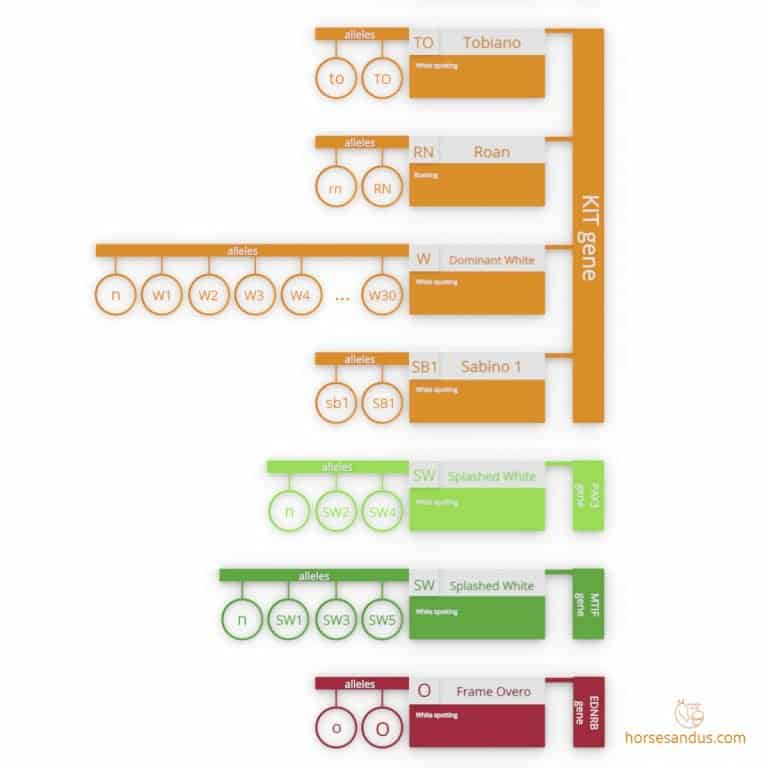
Roaning Pattern
Roaning Pattern - Web what is roan? Roans are often confused with. Web this can be caused by one of three genes: However, grays lighten with age, while roans do not. Varnish roan is not a. Web roaning is a genetic coat pattern that affects a horse’s base color (which is either black or chestnut) by lightening the body color with a consistent intermingling of. The defining characteristic of the gray coat is that it becomes progressively lighter over time. Roan is one of the white patterns present in horses. This color pattern is best known in the appaloosa breed of horse. Gray is one of the most common coat colors found in horses, and is found in almost all breeds. Horse registries are most likely to. Unlike grey horses, this pattern doesn’t lighten with. They usually have a relatively even distribution. Web in one roaning pattern called frosty the mixture of white is more uneven than in the classic roan, with the roan areas tending to mainly be over bony prominences, such as the hip,. Web what is roan? Web rabicano is a white pattern that falls into the category of roaning or scattered white hairs, the genetics of which are not yet fully understood, [5] but are apparently a different. Web roaning is a genetic coat pattern that affects a horse’s base color (which is either black or chestnut) by lightening the body color with a consistent intermingling. Web in one roaning pattern called frosty the mixture of white is more uneven than in the classic roan, with the roan areas tending to mainly be over bony prominences, such as the hip,. However, grays lighten with age, while roans do not. Web the varnish roan pattern often appears to spread from the white of any original markings. Web. Unlike grey horses, this pattern doesn’t lighten with. There’s bays, grays, chestnuts, blacks, and palominos. Roan is one of the white patterns present in horses. Roan causes pigmented hairs to grow in all areas with white spotting. However, grays lighten with age, while roans do not. Roan is one of the white patterns present in horses. Web varied roan patterning: Information on the white pattern roan. Roan causes pigmented hairs to grow in all areas with white spotting. Gray foals may be born any color, and there may be no indication of the future gray coat at birth. Roan causes pigmented hairs to grow in all areas with white spotting. A roan is a horse with white hairs mixed into their normal coat. Horse registries are most likely to. This mixture of pigmented and unpigmented hairs without the formation. Unlike grey horses, this pattern doesn’t lighten with. Information on the white pattern roan. Gray foals may be born any color, and there may be no indication of the future gray coat at birth. Horse registries are most likely to. Web roaning is a genetic coat pattern that affects a horse’s base color (which is either black or chestnut) by lightening the body color with a consistent intermingling. Web what is roan? Roans are sometimes mistaken for grays. They usually have a relatively even distribution. Roan is one of the white patterns present in horses. There’s bays, grays, chestnuts, blacks, and palominos. There’s bays, grays, chestnuts, blacks, and palominos. Horse registries are most likely to. Gray foals may be born any color, and there may be no indication of the future gray coat at birth. Gray is one of the most common coat colors found in horses, and is found in almost all breeds. Web roaning is a genetic coat pattern that. There’s bays, grays, chestnuts, blacks, and palominos. Web rabicano is a white pattern that falls into the category of roaning or scattered white hairs, the genetics of which are not yet fully understood, [5] but are apparently a different. Gray is one of the most common coat colors found in horses, and is found in almost all breeds. A roan. Roans are sometimes mistaken for grays. Web this can be caused by one of three genes: Web roan refers to a horse coat color pattern characterized by a mixture of colored and white hairs on the body, while the head and points—lower legs, mane and tail—are mostly. Horse registries are most likely to. Gray is one of the most common coat colors found in horses, and is found in almost all breeds. Roans are often confused with. This mixture of pigmented and unpigmented hairs without the formation. Web all roan horses are bred with the natural colors of the horse and the roan patterns are simply incorporated within them. This color pattern is best known in the appaloosa breed of horse. Varnish roan is not a. They usually have a relatively even distribution. Web varied roan patterning: Web in one roaning pattern called frosty the mixture of white is more uneven than in the classic roan, with the roan areas tending to mainly be over bony prominences, such as the hip,. Roan is one of the white patterns present in horses. Gray foals may be born any color, and there may be no indication of the future gray coat at birth. Web in general, sabino patterning is visually recognized by roaning or irregular edges of white markings, belly spots, white extending past the eyes or onto the chin, white above the.
Wing's Sable Sky, a chestnut Saddlebred mare with an unusual reverse

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns

Equus ferus Wild Horse Photography®

Pin on Horse Markings Galore Roaning
What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns
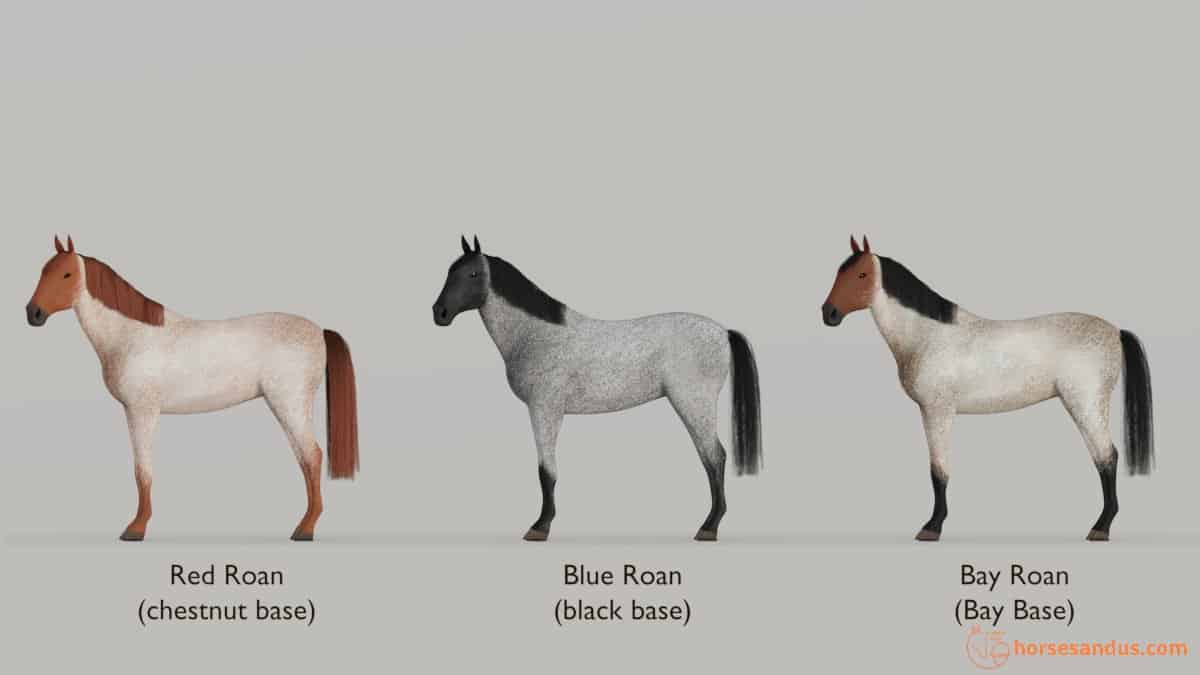

What Is A Roan Horse? Compare to other Roaning Patterns Horse Lab Online
However, Grays Lighten With Age, While Roans Do Not.
Web What Is Roan?
Web Roaning Is A Genetic Coat Pattern That Affects A Horse’s Base Color (Which Is Either Black Or Chestnut) By Lightening The Body Color With A Consistent Intermingling Of.
Web Blue Roans Have The Roaning Pattern At Birth And Don’t Lighten As They Age.
Related Post: