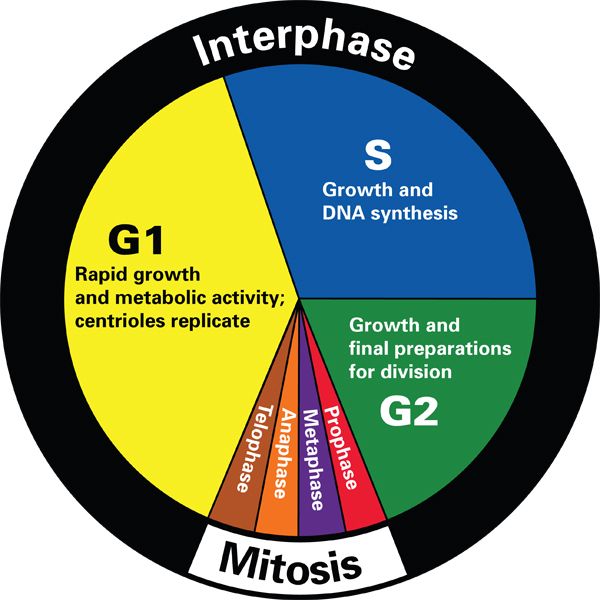
Pie Chart Of Cell Cycle
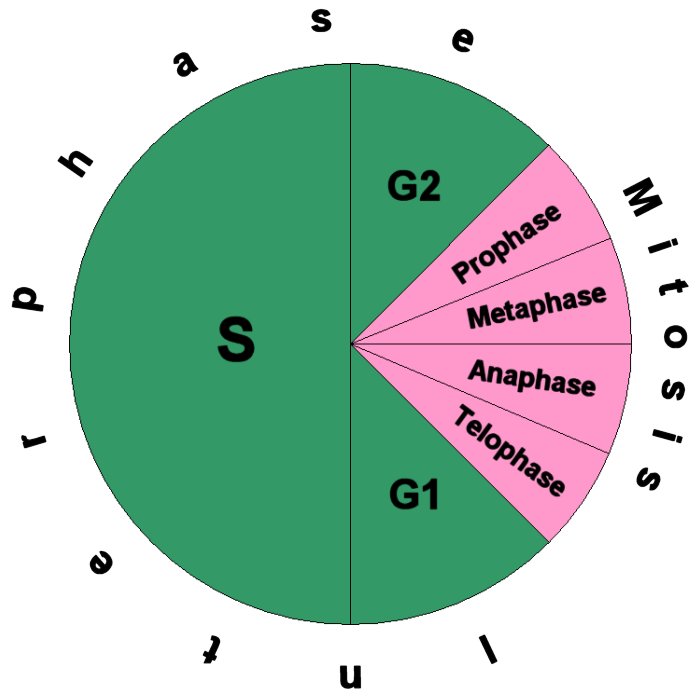
Pie Chart Of Cell Cycle - Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains the potential to cycle; The second sector is labeled. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. Web why do cells divide? Use your data from part 1. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. What are the two major steps of cell division in a eukaryotic cell? At each checkpoint the cell is assessed. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Web stages of the cell cycle. The second sector is labeled. Interphase (g1, s and g2) nuclear. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells via mitosis. The second sector is labeled. At each checkpoint the cell is assessed. Web the figure shows the pie chart of the cell cycle, which consists of two parts. To divide, a cell must complete several important. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells via mitosis. Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events.. These events include duplication of its genome and. The cycle begins at the end of each nuclear division and. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains the potential to cycle; Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Various methods can be used for. Interphase (g1, s and g2) nuclear. This process is vital for the growth, development, repair, and maintenance of. Web the cell cycle describes an orderly sequence of events that are highly regulated. Your paper plate represents 24 hours in the cell cycle. The second sector is labeled. It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. G 1 = growth and preparation of the chromosomes for replication, s = synthesis of dna and duplication of the centrosome, g. Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: Web measuring the cell cycle can include probing many aspects: Cells on. The cycle begins at the end of each nuclear division and. Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through. The area of each chart is proportional to the overall cell cycle duration. Web the cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. Web the figure shows the pie chart of the cell cycle, which consists of two parts. Web most of the cell cycle is the period. Various methods can be used for. These events include duplication of its genome and. The second sector is labeled. Which cell cycle phase a cell is in,. Web the cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. Web why do cells divide? Web the cell cycle is a series of events that cells go through to grow, replicate their dna, and divide. Web revise mitosis, the cell cycle and how stem cells work in humans and plants for gcse biology, aqa. Web each pie chart shows the fraction of the cell cycle devoted to each of the primary stages of the cell cycle. The length of the cell cycle is highly. This process is vital for the growth, development, repair, and maintenance of. Web measuring the cell cycle can include probing many aspects: The second sector is labeled. If all is well the cell is allowed to. Web the cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. Whether or not a cell is cycling or whether it retains the potential to cycle; Web the cell cycle is the regulated sequence of events that occurs between one cell division and the next. Web the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints: It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. The bigger part of this pie chart, labeled c, divides into three sectors. Control of the cell cycle.17 Magnificent Activities To Teach Mitosis Teaching Expertise

Cell Cycle Graph
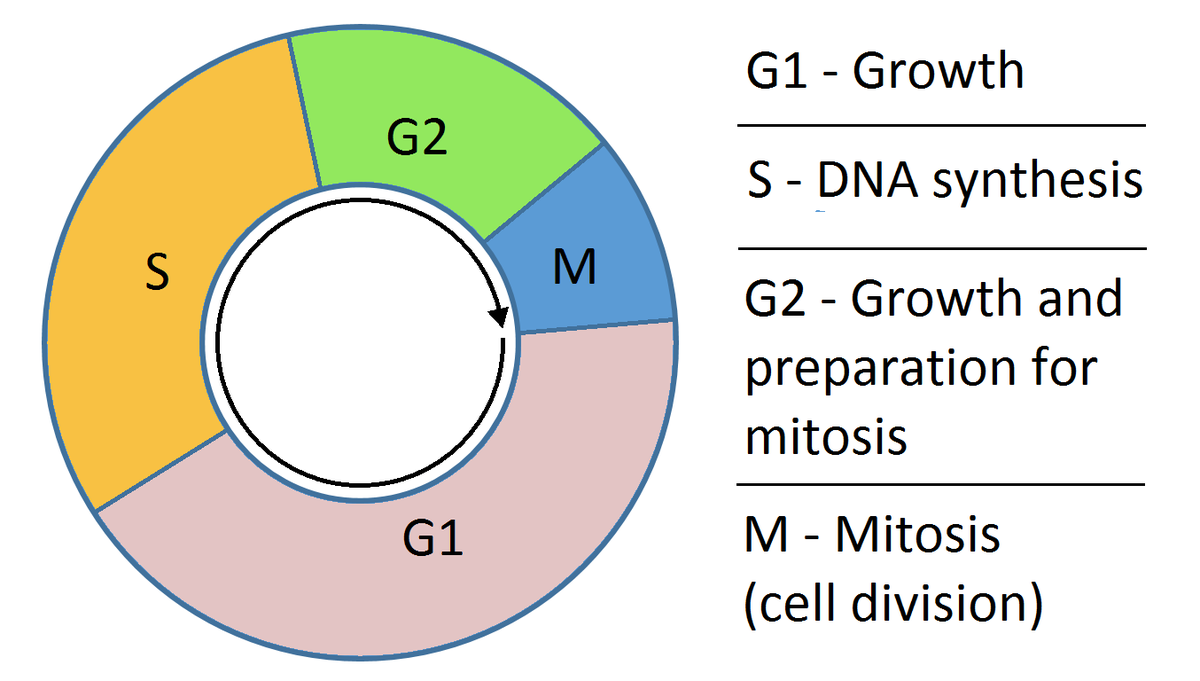
Draw a neat labelled diagram of cell cycle.

cell cycle pie chart Diagram Quizlet

Cell cycle pie chart
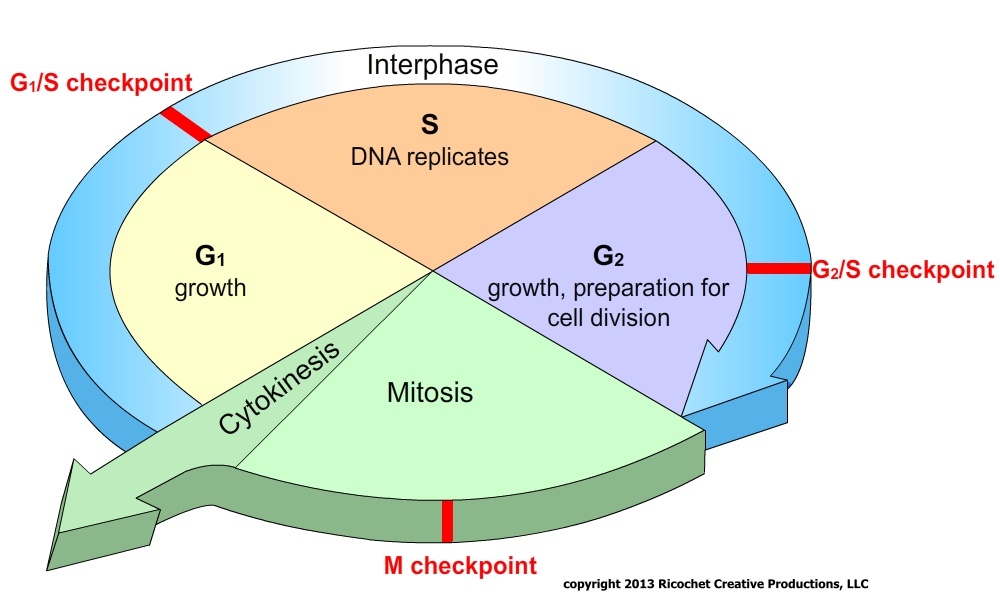
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
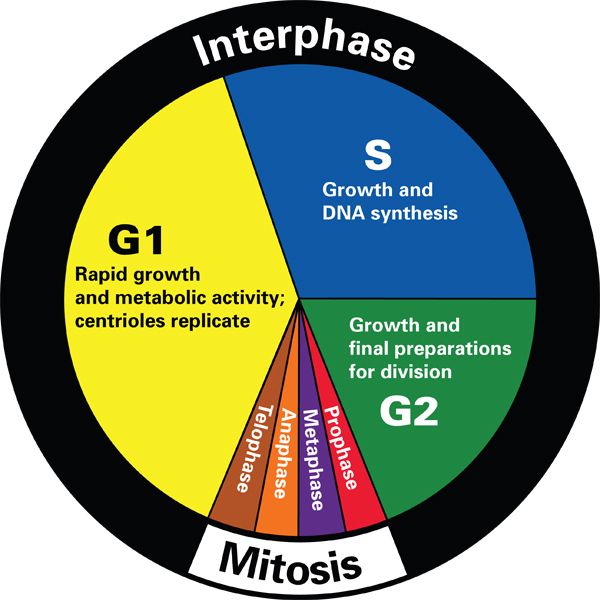
Teaching the Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Cell Cycle Diagram ClipArt Best

Cell Cycle Graph
Use Your Data From Part 1.
G 1 = Growth And Preparation Of The Chromosomes For Replication, S = Synthesis Of Dna And Duplication Of The Centrosome, G.
Web The Cell Cycle Is The Repeating Pattern Of Cell Growth (Increase In Size), Followed By Nuclear And Then Cytoplasmic Division (Splitting Of One Cell To Produce Identical Daughter Cells In.
Your Paper Plate Represents 24 Hours In The Cell Cycle.
Related Post: