Paediatric Burns Chart
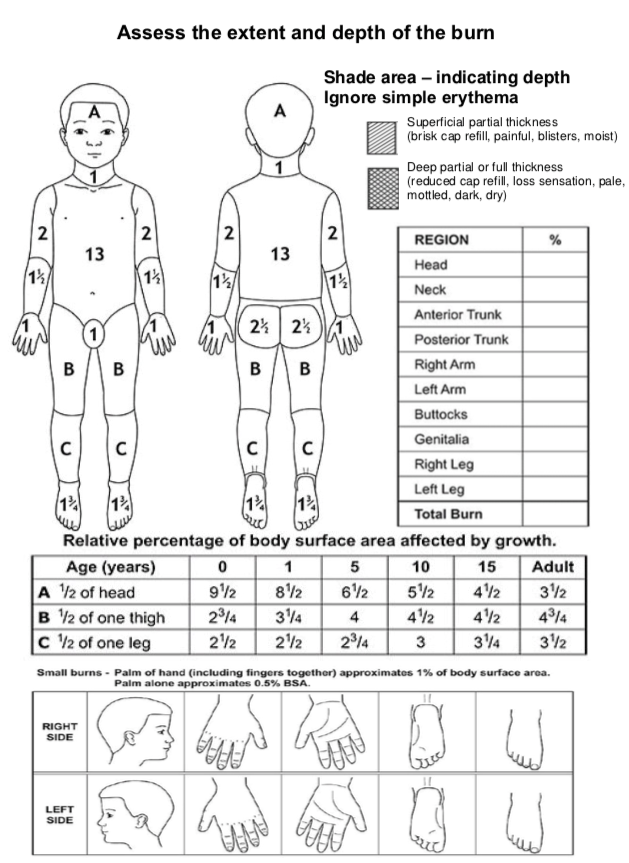
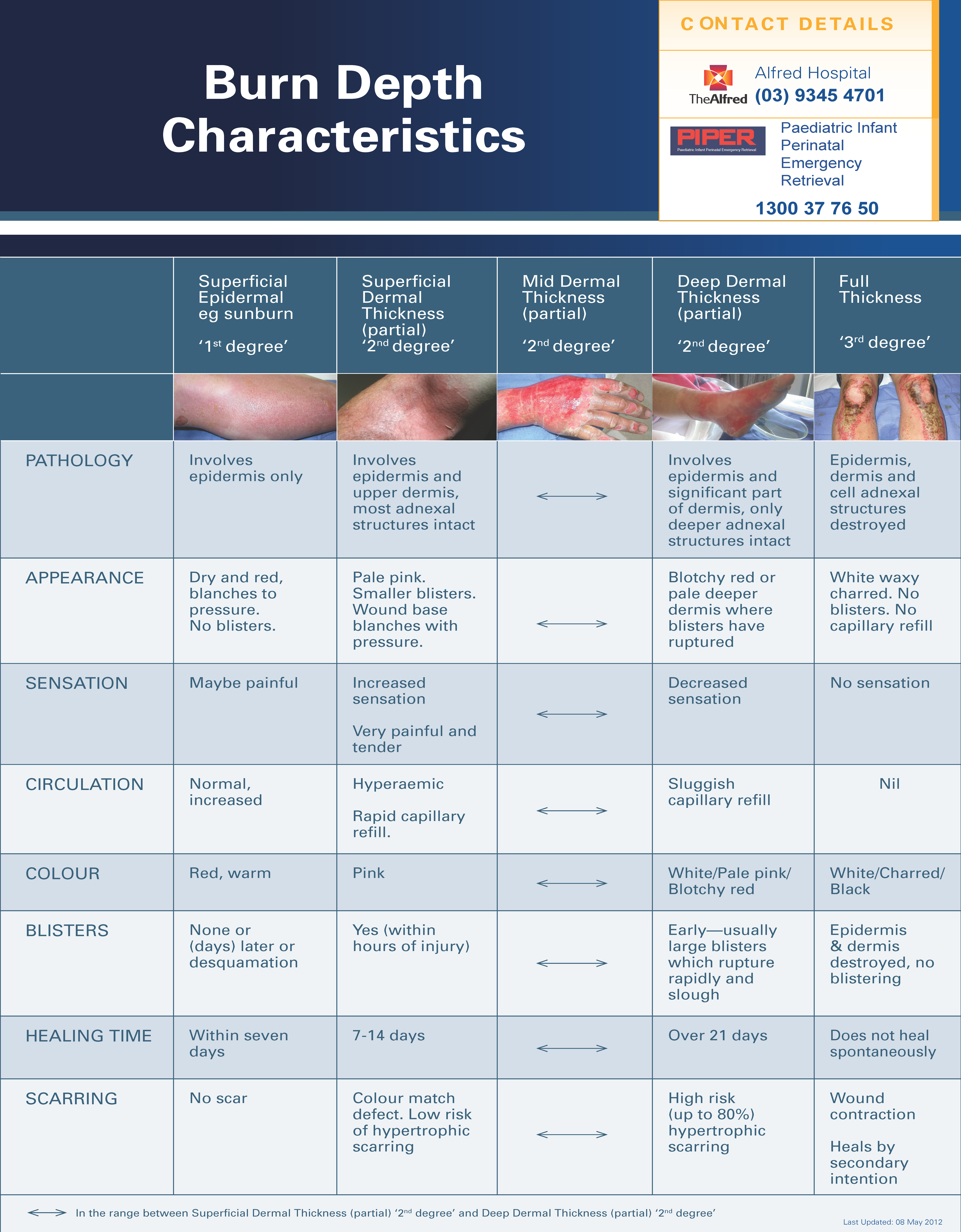
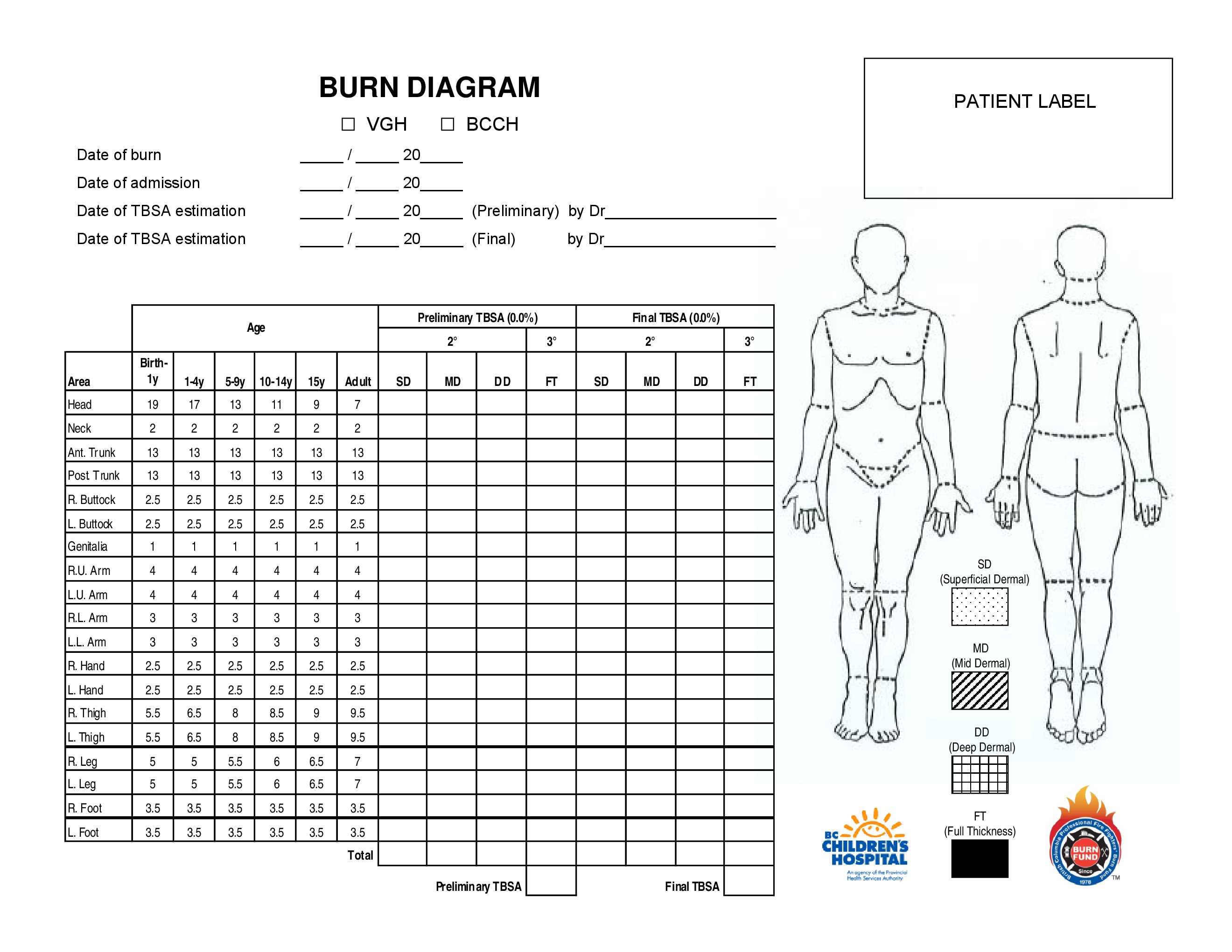
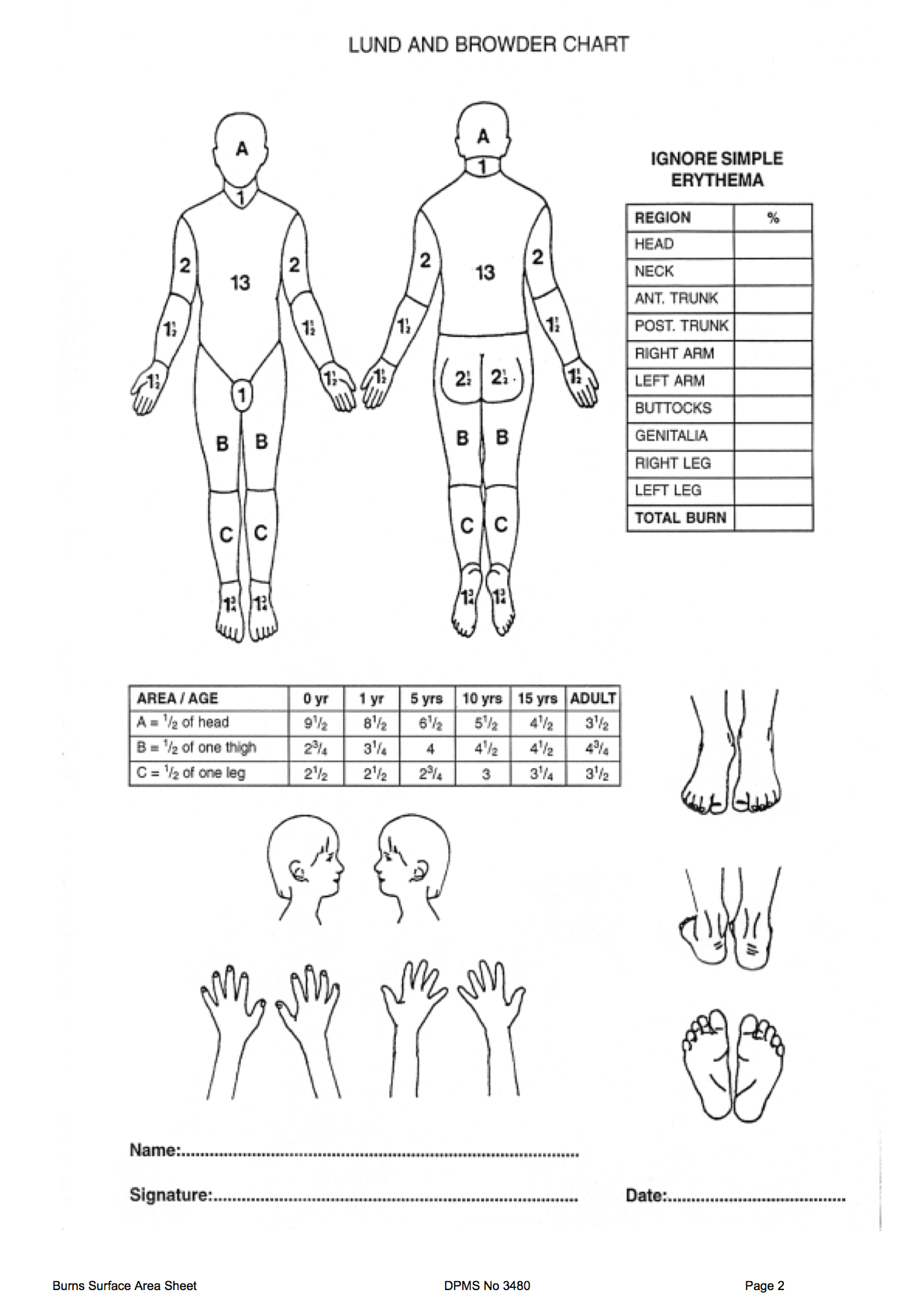
Paediatric Burns Chart - The principles of managing burns in children are similar to those for adults. Over 300 children are admitted to our lady’s children’s hospital, crumlin (olchc) burns & plastics service each year. Burns (early management) contact numbers for burn centres: Paediatric burn and scald management in a low resource setting: Look for other signs of abuse. Web eight papers mentioned the specific type of disaster, including chemical, biological, radiation, nuclear (cbrn), mass burn casualty, and mass casualty incidents involving paediatric patients. Burns + inhalation injury or need to ventilate. An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface. This pathway is intended as a guide for physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners and other healthcare providers. The service provides the majority of paediatric burn care in sa and its catchment population includes metropolitan and country sa, nt and western parts of nsw and vic. Web this app includes many different calculators including estimating tbsa and fluids resuscitation. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2). Web paediatric burns sub guideline. Children under 4 years are at highest. Stridor • change in voice. Burn + requirement for inotropic support. Feet, posterior legs, buttocks and hands. Specifically, 2 were used in the united states, 2 in germany, 1 in. Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects. Web the latest data show: Web this app includes many different calculators including estimating tbsa and fluids resuscitation. The palm (including fingers), of the patient, equates to approximately 1% of the patient’s body surface. Guidelines on the management of children with burns. Web the paediatric burns service is responsible for inpatient and outpatient treatment of children up to 16 years. Burns often associated with other trauma. Anaesthesia, intensive care, paediatric, burn injury. This pathway is intended as a guide for physicians, physician assistants, nurse practitioners and other healthcare providers. Facial burn • soot in mouth. The airway should be secured and circulation restored by controlling fluid loss and initiating fluid resuscitation to maintain global tissue perfusion. Severity of burn is determined by the temperature of the burning agent and the duration of the exposure. Burns in children < 6 months of age. Burns are thermal injuries associated with extremes of temperature, contact with chemicals or electricity. The service provides the majority of paediatric burn care in sa and its catchment population includes metropolitan and country sa,. Leading causes of accidental injury at home are burns, drowning, suffocation, choking, poisonings, falls, and firearms. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2). An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and. A reference guide and review. Leading causes of accidental injury at home are burns, drowning, suffocation, choking, poisonings, falls, and firearms. An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface. The airway should be secured and circulation restored by controlling fluid loss and initiating fluid resuscitation to maintain global tissue perfusion. The chart. The chart is shaded to show the burned area, and the tbsa is calculated by adding the numbers for each affected region. Leading causes of accidental injury at home are burns, drowning, suffocation, choking, poisonings, falls, and firearms. Discuss the anaesthetic management of a. Specifically, 2 were used in the united states, 2 in germany, 1 in. Only 10 papers. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2). Unintentional injury is a leading cause of death among children under age 14. Has appropriate first aid been given? Severity of burn is determined by. Leading causes of accidental injury at home are burns, drowning, suffocation, choking, poisonings, falls, and firearms. Look for other signs of abuse. Discuss the anaesthetic management of a. Specifically, 2 were used in the united states, 2 in germany, 1 in. Calculate requirements from time of. Web eight papers mentioned the specific type of disaster, including chemical, biological, radiation, nuclear (cbrn), mass burn casualty, and mass casualty incidents involving paediatric patients. The airway should be secured and circulation restored by controlling fluid loss and initiating fluid resuscitation to maintain global tissue perfusion. A reference guide and review. Severity of burn is determined by the temperature of the burning agent and the duration of the exposure. Scalds in straight line suggest immersion. Only 10 papers revealed the country or region to which the charts were applied; Specifically, 2 were used in the united states, 2 in germany, 1 in. The care requirements of burns Discuss the anaesthetic management of a. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child. Local injury, systemic response, and metabolic changes combine to determine the severity of a burn injury as follows: Paracetamol (age based dosing) and/or ibuprofen (age based dosing) in fentanyl 1.5 mcg/kg. Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2). Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects. Different percentages are used in paediatrics because the surface area of the head and neck relative to the surface area of the limbs is typically larger in children than adults. The chart is shaded to show the burned area, and the tbsa is calculated by adding the numbers for each affected region.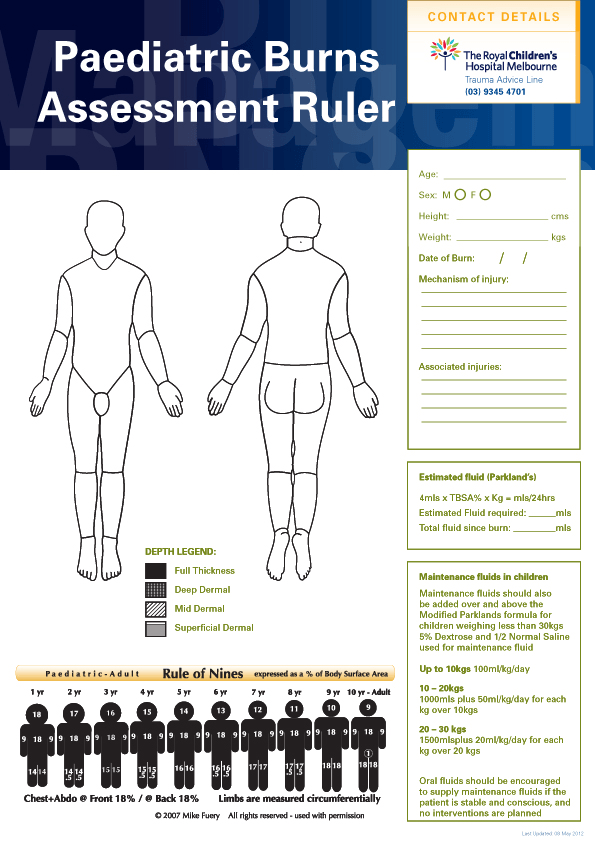
CME 11/2/16 Burns Management Charlie's ED

Major Burns in Children Pediatric Emergency Playbook

Burn Rule Of Nines Chart

PEDIATRIC BURNS AND SCALDSMODERN THERAPEUTIC CONCEPTS Semantic Scholar
Trauma Service Burns

Paediatric Emergency Medicine Minor Burns in Children
Paediatric TraumaPaediatric Burns Sub Guideline Trauma Victoria
Pediatric Burn Diagram
CME 11/2/16 Burns Management Charlie's ED

CME Burns Management Charlie's ED
Web Paediatric Burns Sub Guideline.
Anaesthesia, Intensive Care, Paediatric, Burn Injury.
Feet, Posterior Legs, Buttocks And Hands.
Web Burns Range From Minor Wounds That Can Be Managed In An Outpatient Setting To Moderate Wounds, Requiring Transfer To Paediatric Burns Unit And Surgical Management, Through To Major Wounds With Associated Traumatic Injuries Requiring Retrieval To Paediatric Intensive Care And Burns Unit.
Related Post: