Ophiasis Pattern Alopecia Areata
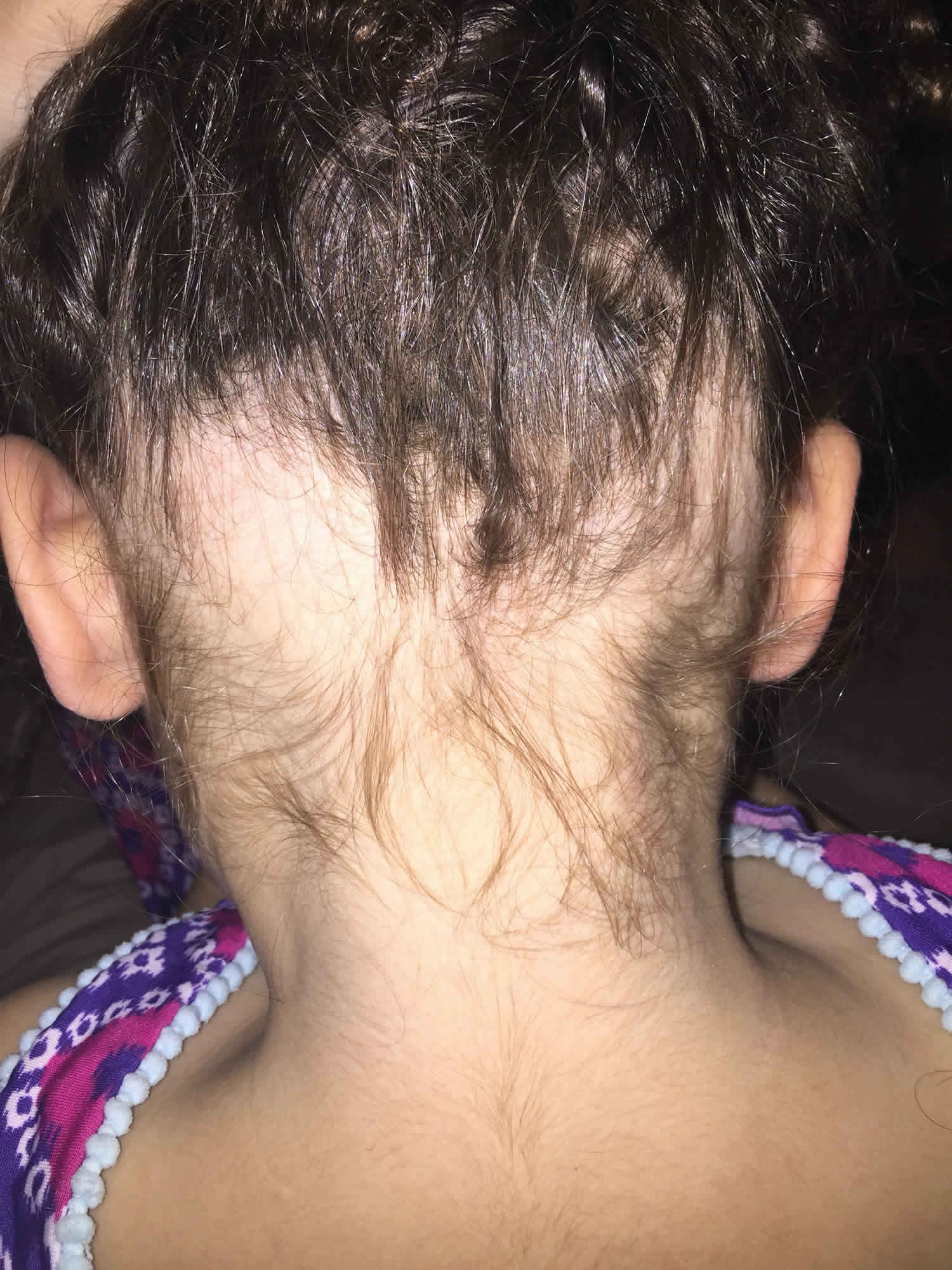
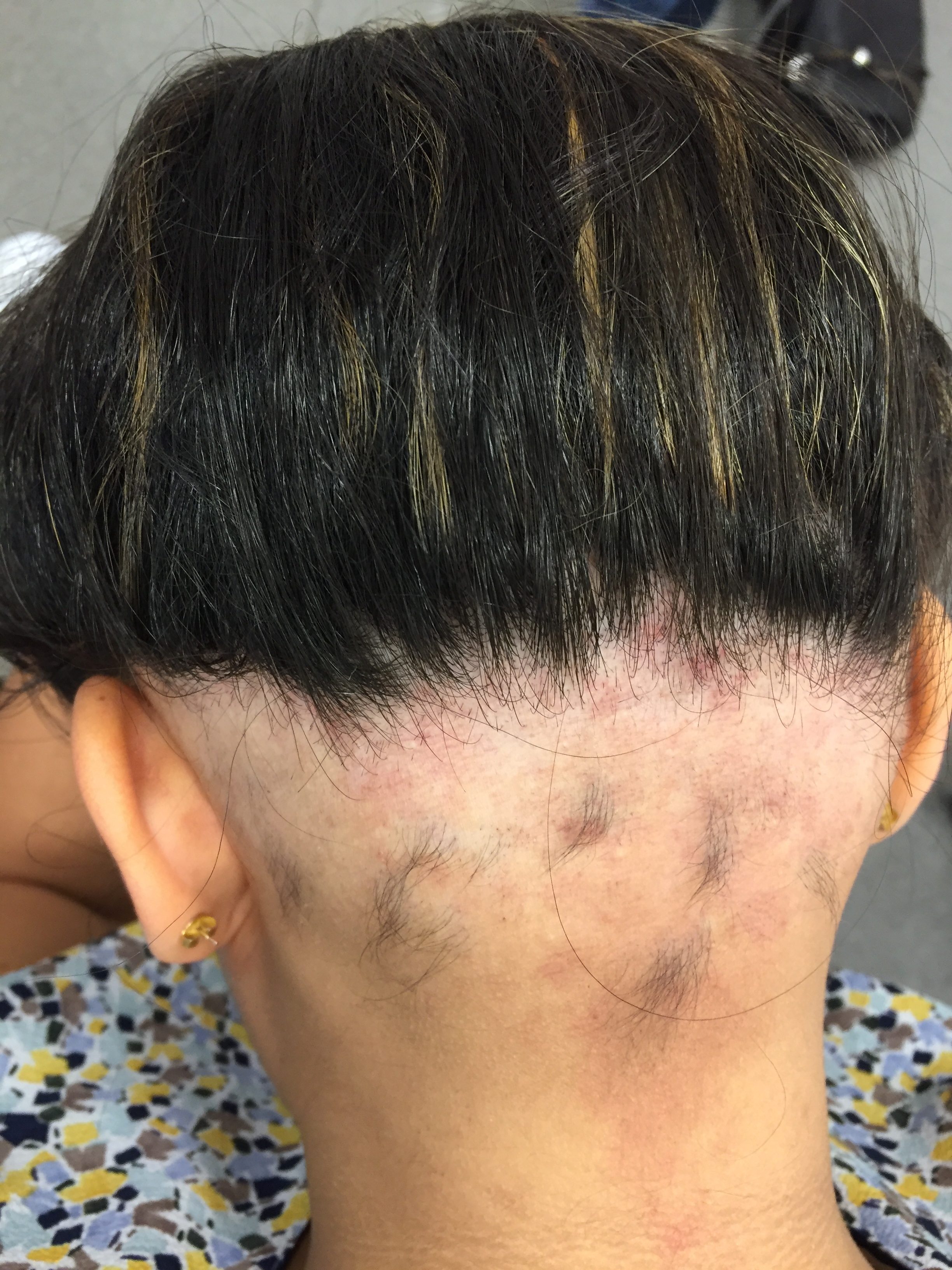
Ophiasis Pattern Alopecia Areata - 1 , 2 aa affects 2% of the global population 3 and may occur at any age and peaks between the second and fourth decades of life with no sex predominance. Temporal and occipital scalp hair clearance usually involving vertex and avoiding ophiasic areas: It doesn’t damage hair follicles permanently, so regrowth is possible, though the disease can recur. Depending on its acuity and extent, hair loss is an important cause of anxiety and disability. 1 c), sisaipho (opposite of ophiasis, central hair loss resembling androgenetic alopecia) and alopecia reticularis (active, stable and resolving patches present at the same moment) [ 6 ]. Ophiasis [1] is a form of alopecia areata characterized by the loss of hair in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. Web ophiasis — bandlike hair loss on the occipital and temporal scalp margins. Patches that unite to form one mass). Alopecia universalis (less than 1% of cases) all or the majority of hair on the scalp and body is lost. 4 , 5 the complex interplay between underlying. Tips scalp psoriasis stop damaging your hair. Androgenic alopecia, also known as. What are the signs and symptoms of alopecia areata? This condition results from the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles, leading to hair loss without permanent damage to the follicles. Androgenic alopecia, also known as. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune form of hair loss seen regularly in primary care. Extensive hair loss is experienced in coalescent patches (i.e. What are the signs and symptoms of alopecia areata? Self care hair loss or shedding? With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). What are the signs and symptoms of alopecia areata? “alopecia” is a medical term for hair loss or baldness, and “areata” means that it occurs in small, random areas. Web alopecia totalis (5% of cases) all or the majority of. This condition results from the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles, leading to hair loss without permanent damage to the follicles. Extensive hair loss is experienced in coalescent patches (i.e. Ophiasis [1] is a form of alopecia areata characterized by the loss of hair in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head. 1 , 2 aa. 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). Web the most common pattern is a small round or patchy bald lesion (patchy alopecia areata), usually on the scalp, that can progress to total loss of scalp hair only (alopecia.. 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). Extensive hair loss is experienced in coalescent patches (i.e. Depending on its acuity and extent, hair loss is an important cause of anxiety and disability. Diffuse alopecia areata (alopecia areata incognita). 1, 2 one subtype, the ophiasis form, affects the occipital and parietal scalp and is often more resistant to treatment than aa monolocularis and aa multilocularis (ie, patchy aa). Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that can cause round bald patches at any age. (b) evolution after 9 months of treatment: Web alopecia areata of the scalp can also occur. Sisaipho (ophiasis inversus) — hair loss on the frontal, temporal, and parietal scalp which may mimic male pattern hair loss. It doesn’t damage hair follicles permanently, so regrowth is possible, though the disease can recur. Pattern of alopecia areata affecting the occipital and lateral scalp in which a bald area encircles the scalp. Ophiasis [1] is a form of alopecia. Diffuse alopecia areata (alopecia areata incognita) — rapid and widespread hair loss. Self care hair loss or shedding? This disease causes sudden hair loss, which often begins as a round or oval, smooth balding patch that develops on the scalp or beard. Web clinical patterns of hair loss in alopecia areata are usually very distinct. It doesn’t damage hair follicles. Temporal and occipital scalp hair clearance usually involving vertex and avoiding ophiasic areas: Web aa can present in several patterns, which are often more therapeutically challenging: Depending on its acuity and extent, hair loss is an important cause of anxiety and disability. This condition results from the immune system mistakenly attacking hair follicles, leading to hair loss without permanent damage. Web ophiasis — bandlike hair loss on the occipital and temporal scalp margins. What are the signs and symptoms of alopecia areata? There are many different classifications of alopecia. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that can cause round bald patches at any age. Web alopecia totalis (5% of cases) all or the majority of scalp hair is lost. Overall, there is approximately a 2% risk of developing aa over one’s lifetime [ 2 ]. With all types of alopecia areata, hair loss and regrowth can be very unpredictable and cyclical (happen over and over). Self care hair loss or shedding? Web clinical patterns of hair loss in alopecia areata are usually very distinct. Androgenic alopecia, also known as. The hair loss occurs in a band along the sides and back of the head. This disease causes sudden hair loss, which often begins as a round or oval, smooth balding patch that develops on the scalp or beard. It doesn’t damage hair follicles permanently, so regrowth is possible, though the disease can recur. In this pattern, hair loss is localised and presents on the lower back and sides of the scalp (similar to that of an undercut). Diffuse alopecia areata (alopecia areata incognita) — rapid and widespread hair loss. Alopecia areata (aa) is the most prevalent autoimmune disorder characterized by nonscaring patchy hair loss.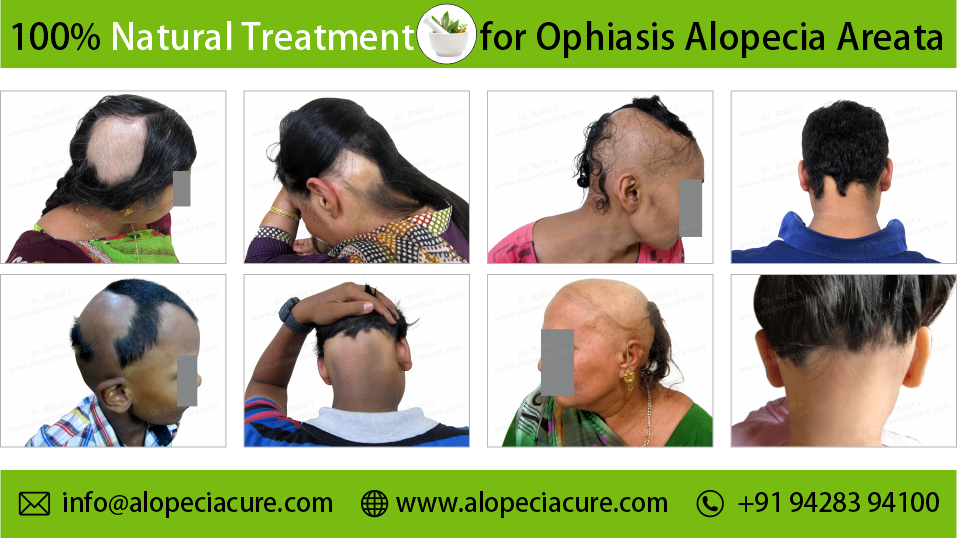
Ophiasis Alopecia Areata

Comparing Ophiasis Alopecia Areata to Occipital Frontal Fibrosing
Ophiasis, definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
Sisaipho Alopecia Areata An variant of alopecia areata

Management of alopecia areata The BMJ
Contour Dermatology Ophiasis pattern of halo hairloss
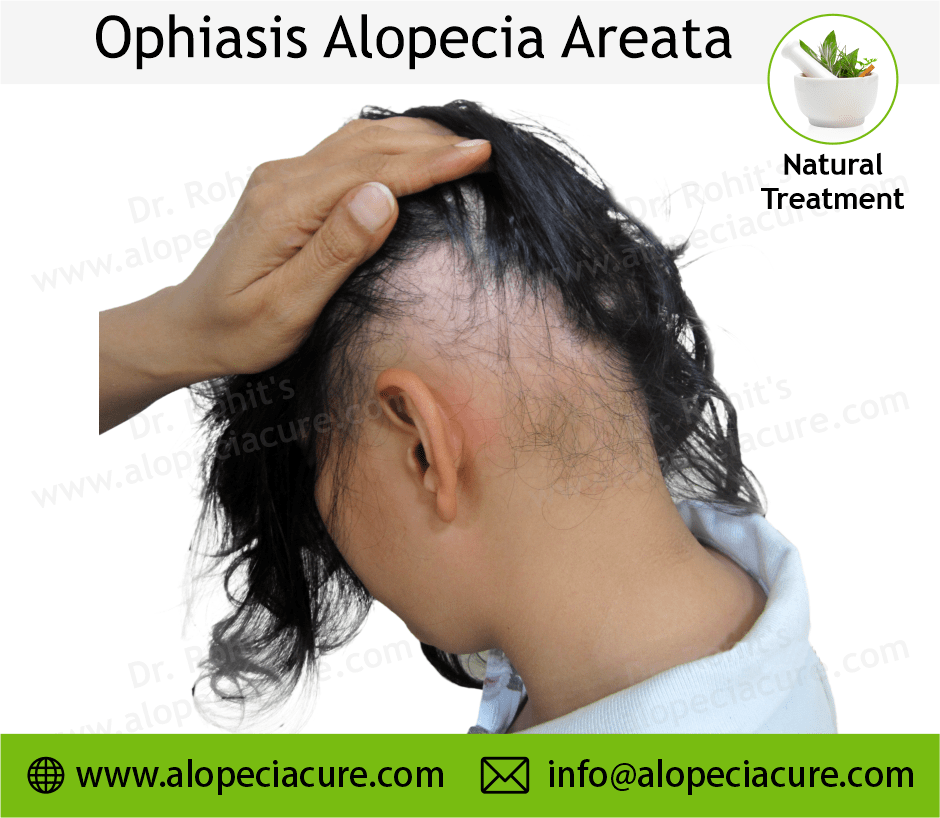
Ophiasis Alopecia Areata

Alopecia areata update Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology

Alopecia Areata Causes, Treatments, Breakthroughs 2020 Guide
Alopecia areata Primary Care Dermatology Society UK
This Condition Results From The Immune System Mistakenly Attacking Hair Follicles, Leading To Hair Loss Without Permanent Damage To The Follicles.
1, 2 One Subtype, The Ophiasis Form, Affects The Occipital And Parietal Scalp And Is Often More Resistant To Treatment Than Aa Monolocularis And Aa Multilocularis (Ie, Patchy Aa).
Web Alopecia Areata Is A Common Nonscarring Hair Loss On The Scalp Or Other Areas Of The Body.
4 , 5 The Complex Interplay Between Underlying.
Related Post:

