Neck Trigger Point Referral Patterns
Neck Trigger Point Referral Patterns - Fifty children (14 boys, 36 girls, mean age: Web cervicogenic headache (cgh) is caused primarily by dysfunction in the upper cervical spine. Several areas along the fibers, all radiating superiorly into head and skull and toward frontal region. These points can be painful and may. It is characterized by a the presence of a taught band, tender or painful nodules, a positive stretch sign and a referred pain pattern. Don’t forget to map trigger points and referral patterns. These maps are handy for narrowing down the prospect of locating pain sources. Web trigger points in these muscles can cause referred pain into the neck and shoulders. Fifty children (14 boys, 36 girls, mean age: Web our aim was to describe the referred pain pattern and areas from trigger points (trps) in head, neck, and shoulder muscles in children with chronic tension type headache (ctth). Advantage is gained in looking at tp referral pattern maps because the practitioner can use the map in either direction. On a head and neck diagram indicate: Web medical literature suggests that pain felt from trigger points may spread in a familiar referral pattern. Web in the effort to identify which musculoskeletal structures (intervertebral disc, zygophophyseal joints, and muscles) are. Web in the sternal head of scm, there are usually 4 tps which can give issues as ptosis, blurred vision, sinus headaches and referred pain pattern. Left scm (sternocleidomastoid) and right scm. Here are two exercises that can help relieve some types of trigger point pain: Web compress points in the taut band for at least 3 seconds to ask. Left temporalis trigger points may produce pain that radiates to the left side of the neck and upper shoulder, while right temporalis trigger points can refer pain to the right neck and shoulder regions. If the pain in your neck extends to other areas in predictable ways, this can signal the location of trigger points. Web in the sternal head. Fifty children (14 boys, 36 girls, mean age: Left scm (sternocleidomastoid) and right scm. Web our aim was to describe the referred pain pattern and areas from trigger points (trps) in head, neck, and shoulder muscles in children with chronic tension type headache (ctth). Direct compression or muscle contraction can elicit jump sign, local tenderness, local twitch response and referred. These maps are handy for narrowing down the prospect of locating pain sources. Trigger points (trps) or muscle “knots” are sore spots in soft tissue that cause deep aching. Web each section contains trigger point (trp) pain referral patterns that may cause or be associated with a clinical condition commonly seen in clinical practice. Web trigger points in these muscles. Web trapezius trigger points are raised parts of the trapezius muscle, which is the large band of muscles that spans your upper back, shoulders, and neck. Doctors look for specific referred pain patterns that align with known trigger points. Behind the ear, interscapular region, posterolateral neck, suprascapular region. It is characterized by a the presence of a taught band, tender. Web dizziness or balance problems, nausea, fainting, lacrimation (excess tear production,) blurred vision, eyelid jerking or droopy eyelid and visual disturbances have all been claimed to be a possible result of trigger points along the sternocleidomastoid. Fifty children (14 boys, 36 girls, mean age: Myofascial pain syndrome (mps) is a chronic pain disorder of too many trigger points. Web we. Web a trigger point is a contractile knot in skeletal muscle that is cause by a muscle being over shortened, over lengthened or over loaded. Left scm (sternocleidomastoid) and right scm. Web myofascial trigger point referred pain is well mapped and documented into referral patterns. Web if you’re experiencing neck pain, it’s important to identify the trigger points that may. Web dizziness or balance problems, nausea, fainting, lacrimation (excess tear production,) blurred vision, eyelid jerking or droopy eyelid and visual disturbances have all been claimed to be a possible result of trigger points along the sternocleidomastoid. Web a trigger point (trp) is a hyperirritable spot, a palpable nodule in the taut bands of the skeletal muscles' fascia. It is characterized. Web a trigger point (trp) is a hyperirritable spot, a palpable nodule in the taut bands of the skeletal muscles' fascia. They produce pain locally and in a referred pattern and often accompany chronic musculoskeletal. Trigger point therapy for neck pain, head pain, and face pain. Web we use our knowledge of joint open and closing patterns, of ivd loading. Trigger point therapy for neck pain, head pain, and face pain. Web in the sternal head of scm, there are usually 4 tps which can give issues as ptosis, blurred vision, sinus headaches and referred pain pattern. Fifty children (14 boys, 36 girls, mean age: Trigger point pain patterns in neck, head, and face. They produce pain locally and in a referred pattern and often accompany chronic musculoskeletal. Web an extremely detailed guide to the unfinished science of muscle pain, with reviews of every theory and treatment option. Myofascial pain syndrome (mps) is a chronic pain disorder of too many trigger points. Left temporalis trigger points may produce pain that radiates to the left side of the neck and upper shoulder, while right temporalis trigger points can refer pain to the right neck and shoulder regions. Web a trigger point (trp) is a hyperirritable spot, a palpable nodule in the taut bands of the skeletal muscles' fascia. Web dizziness or balance problems, nausea, fainting, lacrimation (excess tear production,) blurred vision, eyelid jerking or droopy eyelid and visual disturbances have all been claimed to be a possible result of trigger points along the sternocleidomastoid. Advantage is gained in looking at tp referral pattern maps because the practitioner can use the map in either direction. Abductor digiti minimi (foot) abductor digiti minimi (hand) abductor hallucis. Web trigger points are discrete, focal, hyperirritable spots located in a taut band of skeletal muscle. The direction/pattern of all referred pain phenomena. Web we use our knowledge of joint open and closing patterns, of ivd loading positions, aggravating and easing positions for each structure, and of the pain referral patterns to determine which structure is most likely responsible for the. However, patients with cgh are also highly likely to have myofascial trigger point pain from overactivity in their anterior neck muscles (including sternocleidomastoid) and weakness of their deep neck flexors.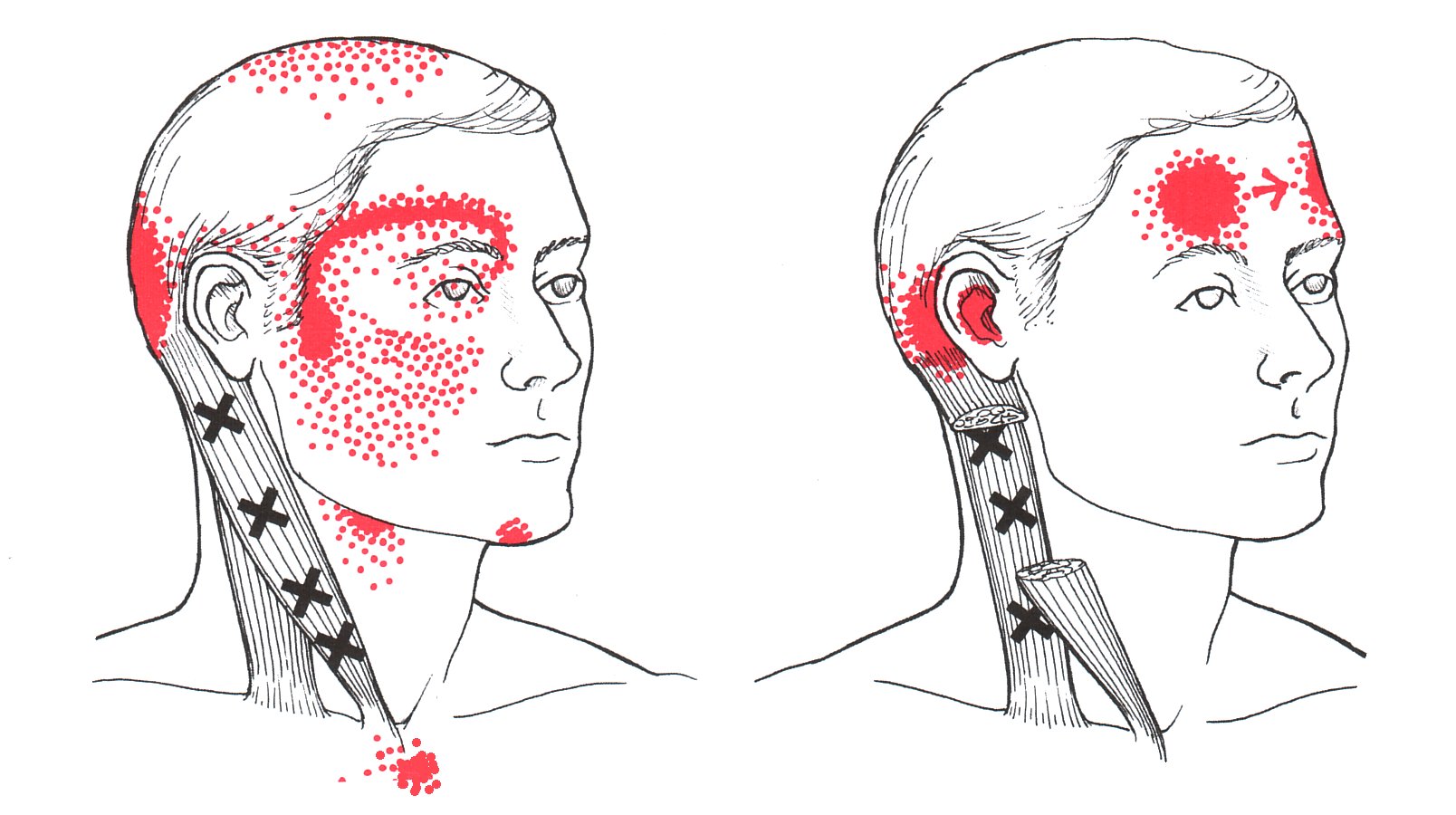
Sternocleidomastoid The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide

Myofascial Trigger Point Therapy PalmLeaf Massage Clinic — Buffalo
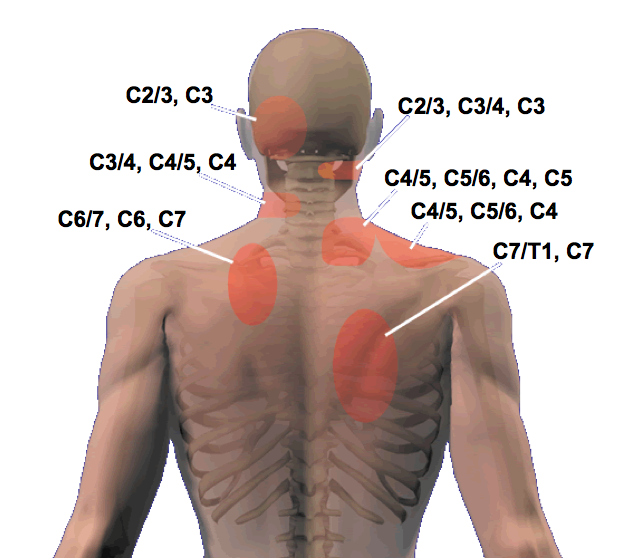
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Trigger Point Pain Patterns Charts byTravell and Simons Physio Needs
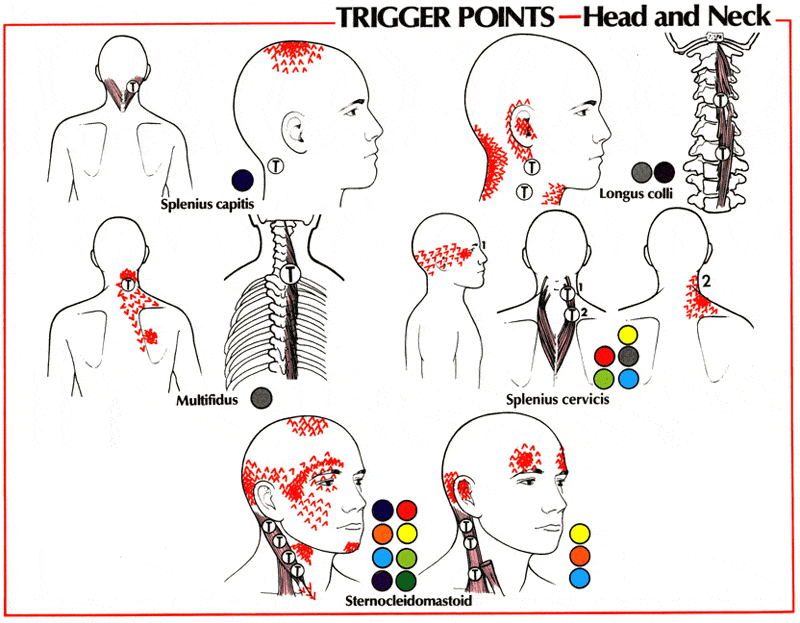
What Is a Proper Diagnostic Block Headache Workup? Regenexx
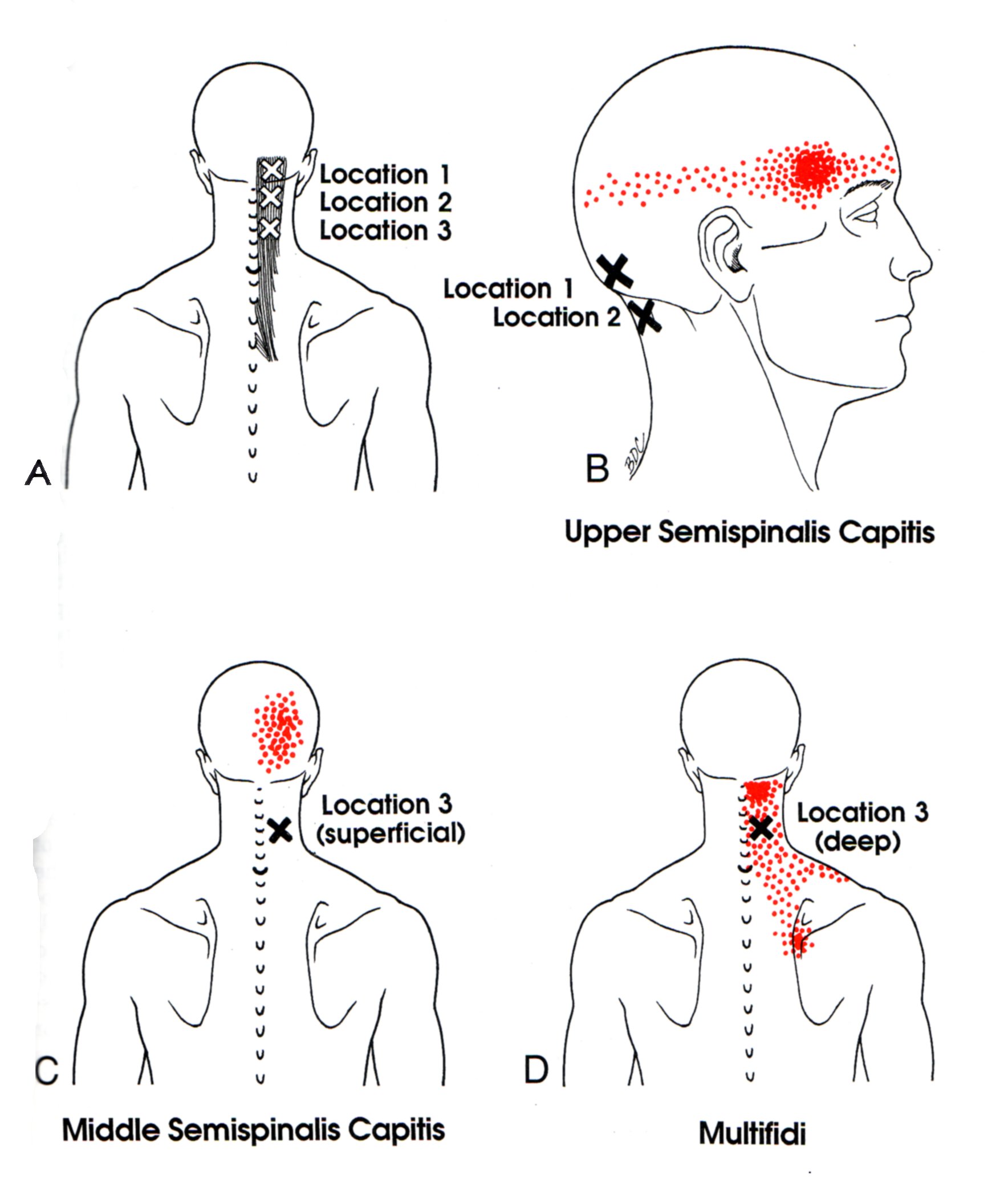
Semispinalis Capitis The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide
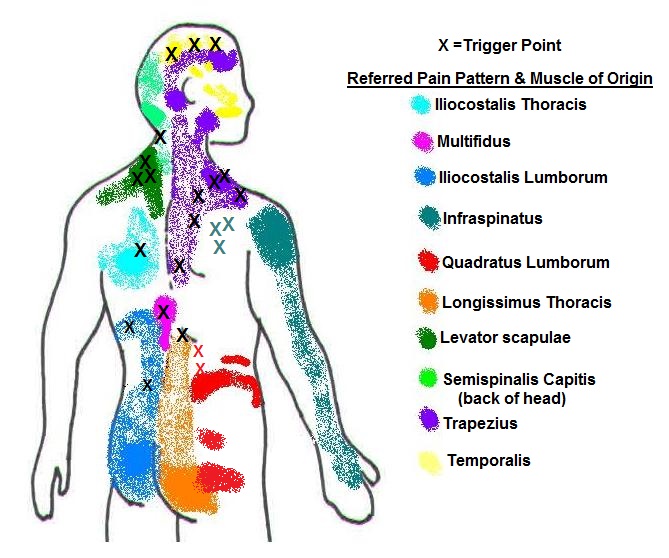
Myofascial Pain & Trigger Points Spine Plus
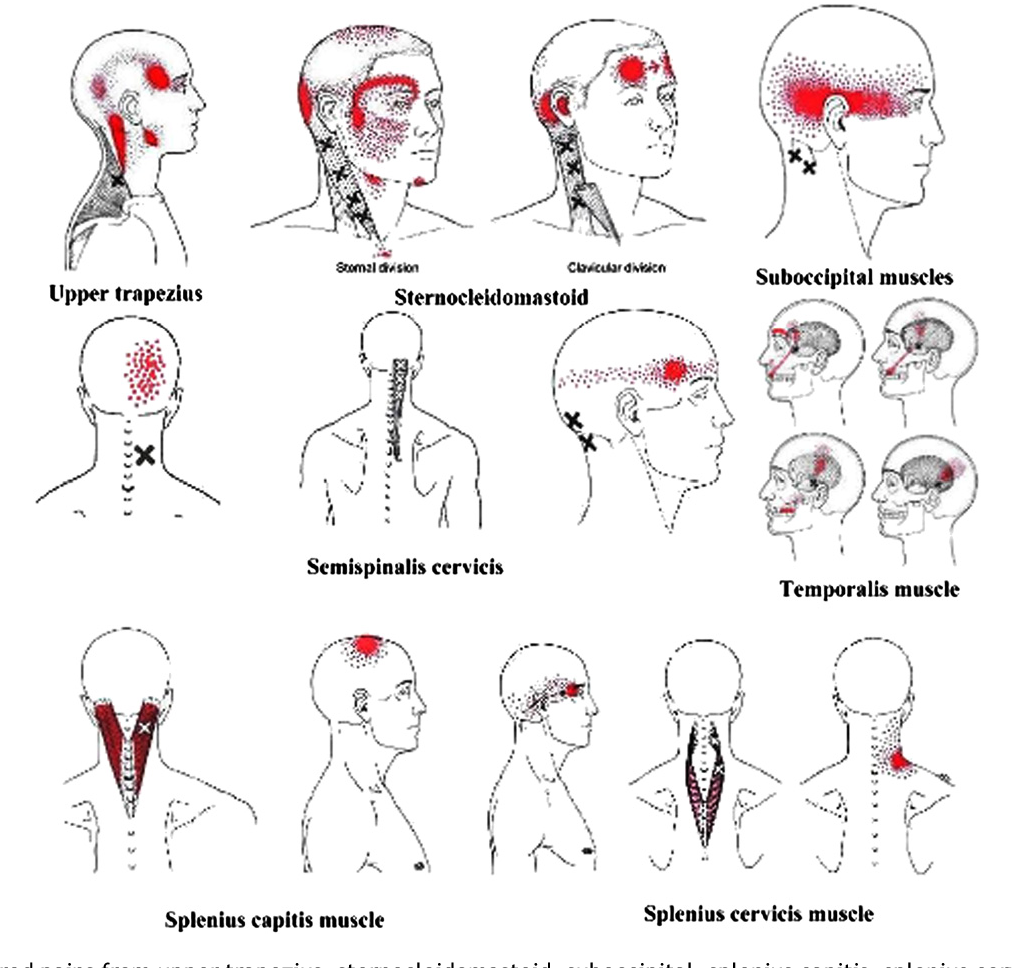
Figure 1 from Referred pain areas of active myofascial trigger points

Myofascial trigger points in subjects presenting with mechanical neck

Pin on Health and Beauty
Left Scm (Sternocleidomastoid) And Right Scm.
Doctors Look For Specific Referred Pain Patterns That Align With Known Trigger Points.
Web Trigger Points In These Muscles Can Cause Referred Pain Into The Neck And Shoulders.
Web Compress Points In The Taut Band For At Least 3 Seconds To Ask About Referral.
Related Post: