Natural Course Of Disease
Natural Course Of Disease - Web newly discovered genetic malfunction causes rare lung disease. Web mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (tb) and is a leading infectious cause of death in adults worldwide [ 1 ]. State public health officials noted the patient was an elderly man who was immunocompromised. Web the natural course of disease in spinal cord injury is well known for traumatic etiologies. Web the principles of etiology and natural history of disease are essential to recognizing opportunities for prevention across the illness spectrum. Web natural history of diseases: Web the natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people from its pathological onset (inception) until its resolution (either through complete recovery or eventual death). Web in order to characterize the natural progression of disease, these models generally incorporate longitudinal data for some biomarker (s) of disease severity or can incorporate more direct measures of disease severity. The human host serves as a natural reservoir for m. They have a bearing on how illness is experienced, how differently it can be perceived at the time of first contact with the health system, and how it may appear at later stages. Web a disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). The course of a disease from pathological onset or inception to resolution. The human host serves as a natural reservoir for m. Web mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (tb) and is a leading infectious cause of. The natural history of a communicable disease refers to the sequence of events that happen one after another, over a period of time, in a person who is not receiving treatment. Web this is the first case of an alaskapox infection resulting in hospitalization and death ever reported. Web newly discovered genetic malfunction causes rare lung disease. (see epidemiology of. Granulomatous inflammation may be detected in endoscopic biopsies or resected tissues. Web the natural history of a disease is also referred to as the course of the disease, or its development and progression; Web the natural history of disease is the uninterrupted progression of disease from its initiation to either spontaneous resolution, containment by the body’s repair mechanisms, or to. Web newly discovered genetic malfunction causes rare lung disease. Web in order to characterize the natural progression of disease, these models generally incorporate longitudinal data for some biomarker (s) of disease severity or can incorporate more direct measures of disease severity. These terms can be used interchangeably. Web the natural history of disease is the uninterrupted progression of disease from. Web crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disease process involving different sites in the gastrointestinal tract. Web in order to characterize the natural progression of disease, these models generally incorporate longitudinal data for some biomarker (s) of disease severity or can incorporate more direct measures of disease severity. Schematic for disease initiation and progression. Web cumulative probability of stenosis progression. The inception of a disease is not a firmly defined concept. Disease can result in a temporary or lasting change in. Genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors appear to play a role. These terms can be used interchangeably. Web natural history of disease. Web the principles of etiology and natural history of disease are essential to recognizing opportunities for prevention across the illness spectrum. Web this is the first case of an alaskapox infection resulting in hospitalization and death ever reported. The immunology of this infection is discussed. Web the natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people. Its purpose is to encourage proactive thinking about pathogens that could cause a pandemic. Web the natural history of disease is the course a disease takes in individual people from its pathological onset (inception) until its resolution (either through complete recovery or eventual death). The natural history of a communicable disease refers to the sequence of events that happen one. Disease can result in a temporary or lasting change in. Web the natural history of disease is the uninterrupted progression of disease from its initiation to either spontaneous resolution, containment by the body’s repair mechanisms, or to a clinically detectable problem. Schematic for disease initiation and progression. Web cumulative probability of stenosis progression from nonobstructive (<50% diameter stenosis) to obstructive. State public health officials noted the patient was an elderly man who was immunocompromised. Its purpose is to encourage proactive thinking about pathogens that could cause a pandemic. (see epidemiology of tuberculosis.) the microbiology and pathogenesis of tb will be reviewed here. Figure 1 displays a very simple schematic that represents the. Web natural history of disease. Statistical designs and issues abstract. Web disease x is a placeholder concept that refers to a pandemic pathogen that has not yet been characterized. Web mycobacterium tuberculosis causes tuberculosis (tb) and is a leading infectious cause of death in adults worldwide [ 1 ]. Understanding the natural history of a disease is an important prerequisite for designing studies that assess. Related concepts include the changing pattern of disease in populations and levels of severity (spectrum) of disease. Granulomatous inflammation may be detected in endoscopic biopsies or resected tissues. In the following chapter, this will be illustrated with respect to anatomical and physiological adaptations in the central and peripheral nervous system. Schematic for disease initiation and progression. The absence of a single immune cell receptor has been linked to both fewer defenses against mycobacterial infections, such as tb, and. They have a bearing on how illness is experienced, how differently it can be perceived at the time of first contact with the health system, and how it may appear at later stages. Web a disease is expected to follow a particular series of events in its development (pathogenesis), and to follow a particular clinical course (natural history). Web the natural course involves in the whole process of the disease from occurrence, development to outcome without any clinical intervention. State public health officials noted the patient was an elderly man who was immunocompromised. Web in order to characterize the natural progression of disease, these models generally incorporate longitudinal data for some biomarker (s) of disease severity or can incorporate more direct measures of disease severity. Web the clinical effects of parkinson’s disease (pd) are visually obvious, but the underlying pathology of pd is still not fully understood. (see epidemiology of tuberculosis.) the microbiology and pathogenesis of tb will be reviewed here.
PPT Natural History & Spectrum of Diseases PowerPoint Presentation
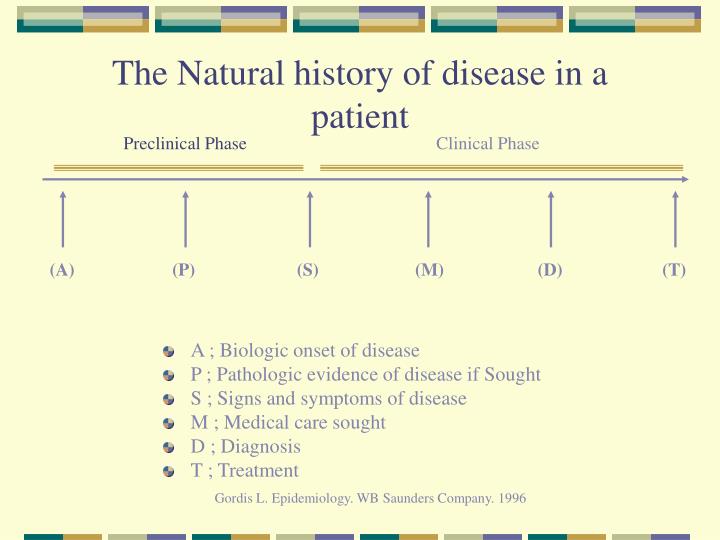
PPT Natural History of Disease PowerPoint Presentation ID848298
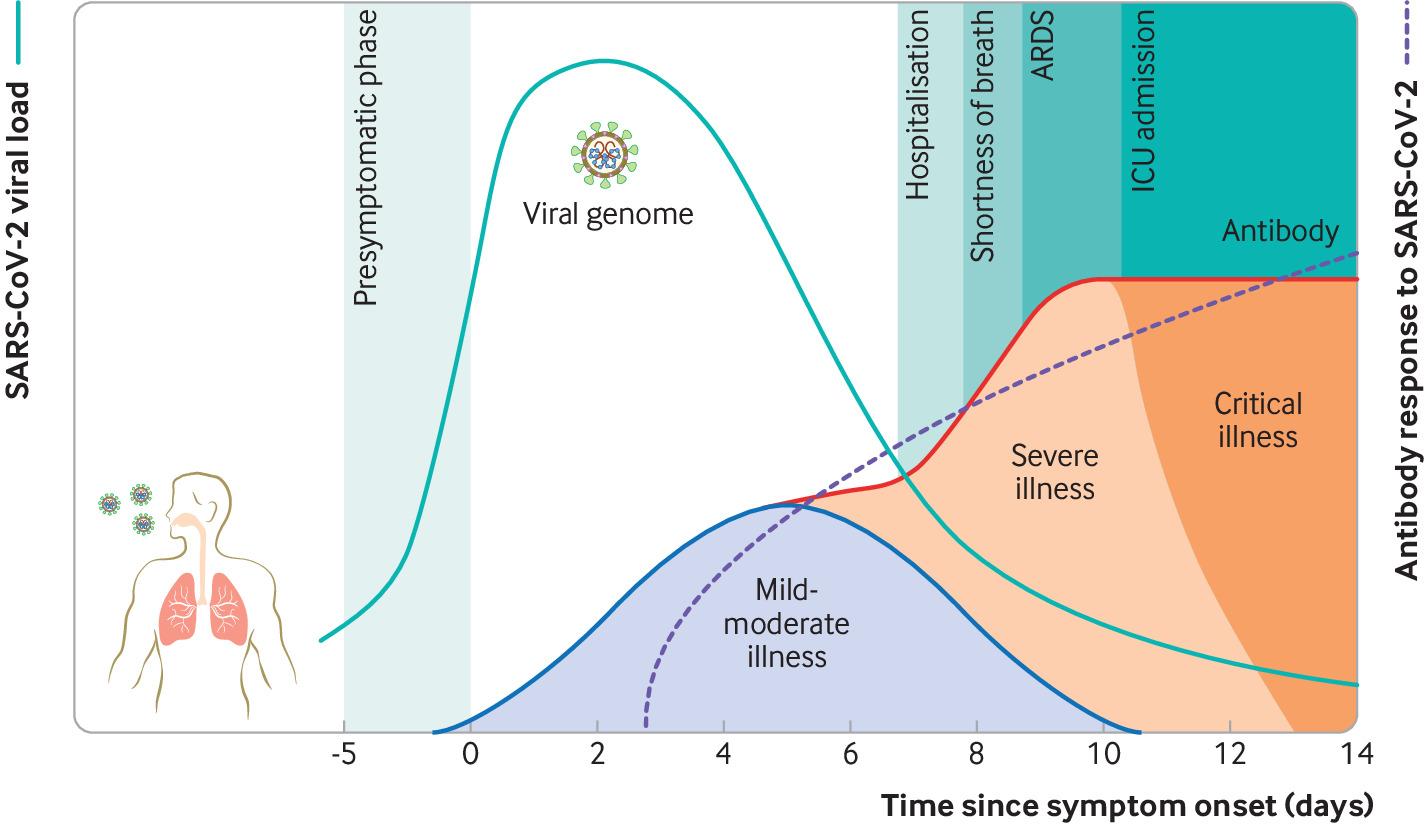
Every Picture Tells a Story The Disease Course of COVID19 American

STAGES OF DISEASE Individual and in Population Know Public Health
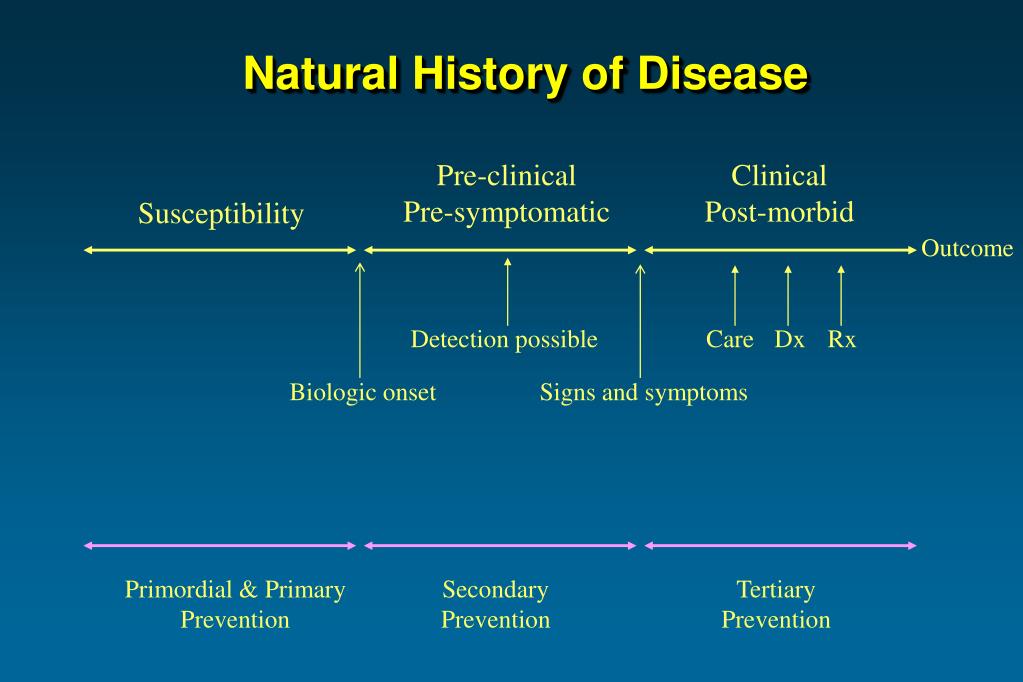
PPT Natural History of Disease Prevention and Prognosis PowerPoint

Parkinson's disease Course of disease BI

Chain of Infection HotDog Patient Warming
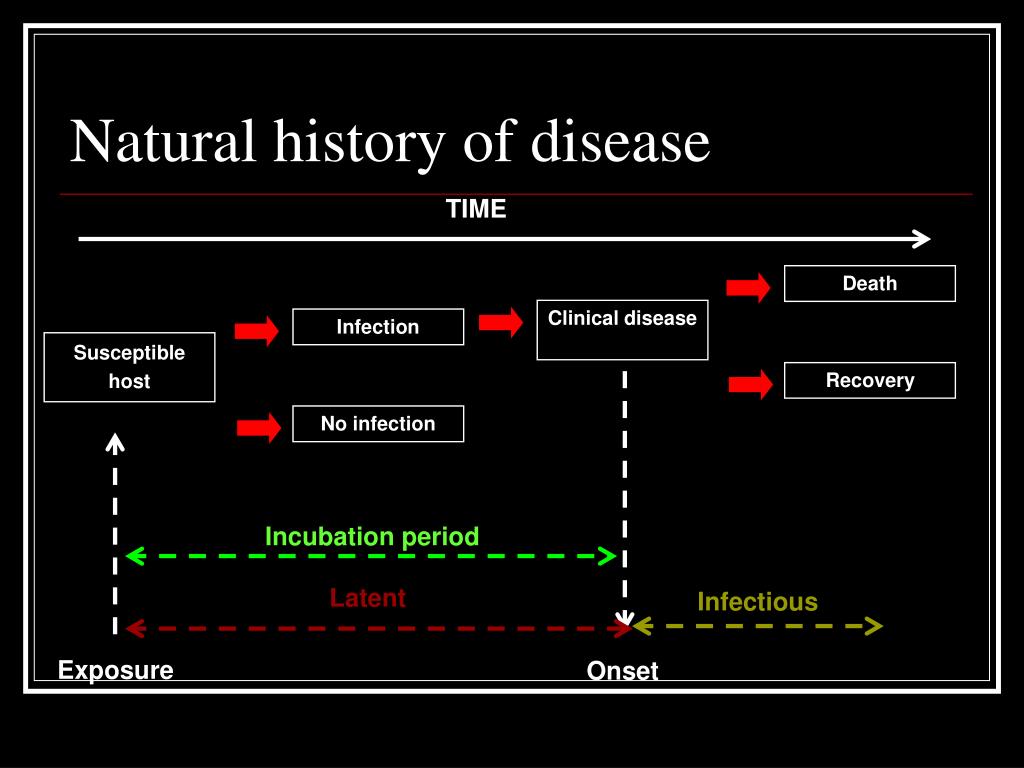
PPT Natural History of Disease PowerPoint Presentation, free download
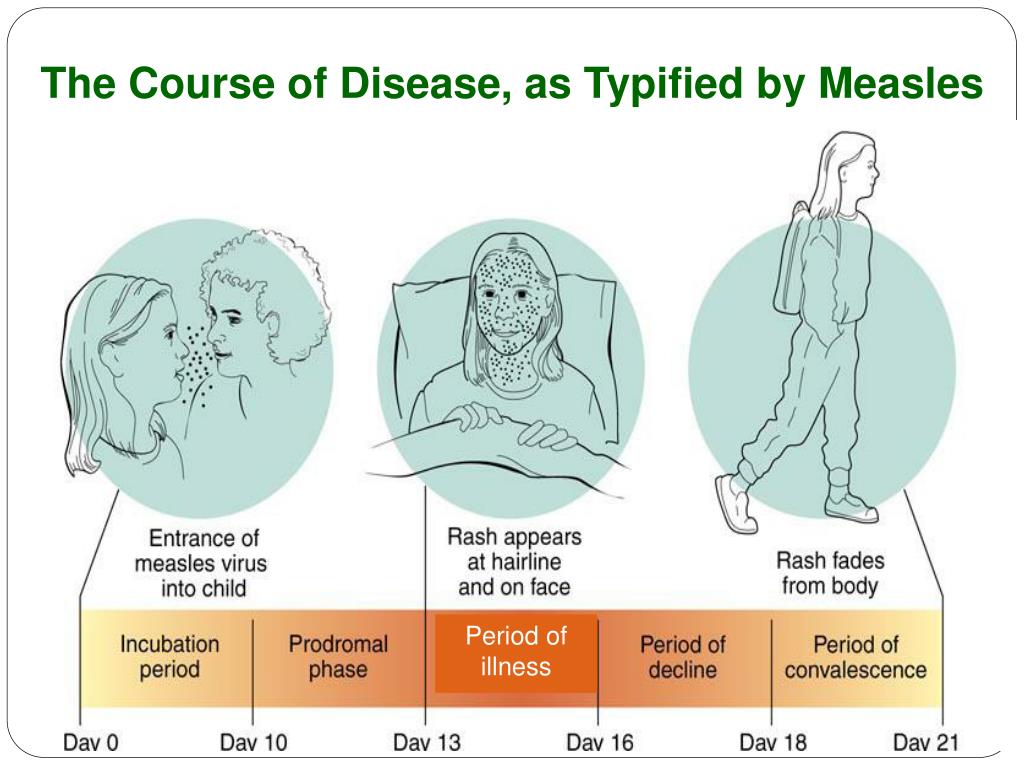
PPT Ch 14 Principles of Disease and Epidemiology PowerPoint

PPT Natural History of Disease PowerPoint Presentation ID848298
Its Purpose Is To Encourage Proactive Thinking About Pathogens That Could Cause A Pandemic.
Web Natural History Of Diseases:
Web The Natural History Of Disease Is The Course A Disease Takes In Individual People From Its Pathological Onset (Inception) Until Its Resolution (Either Through Complete Recovery Or Eventual Death).
The Inception Of A Disease Is Not A Firmly Defined Concept.
Related Post: