Mvp Amniotic Fluid Chart
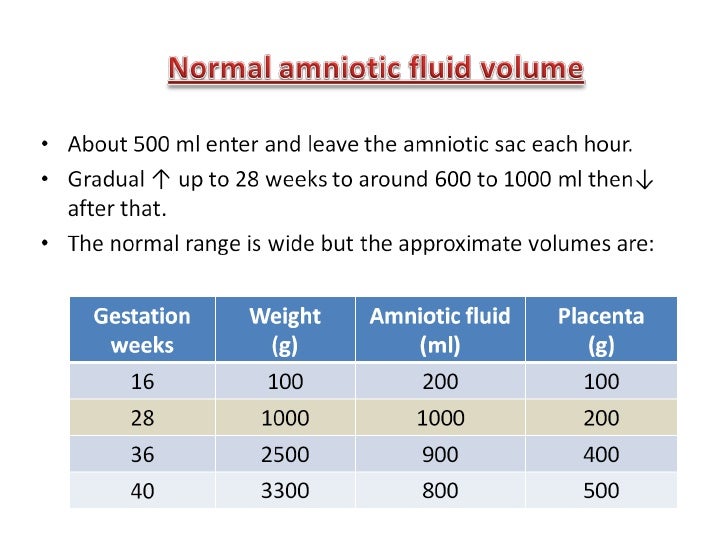
Mvp Amniotic Fluid Chart - Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. But what does this mean for a mother and her unborn baby? Some women are told they have too little or too much amniotic fluid. Web last updated october 3, 2023. Web it is performed by assessing a pocket of a maximal depth of amniotic fluid which is free of an umbilical cord and fetal parts. Web qualitative or semiquantitative assessment of amniotic fluid volume (afv) is a standard component of every obstetric ultrasound examination, regardless of indication, because it is an indicator of fetoplacental health and thus useful for identifying, monitoring, and managing complicated pregnancies [ 1,2 ]. Web the normal amniotic fluid level range is between 8 to 18 cm. Fluid volume abnormalities can directly interfere with fetal development, causing structural anomalies such as pulmonary hypoplasia. Most pregnant women don’t even think about their baby’s amniotic fluid levels, until their healthcare provider tells them it could be a problem. Web the single deepest vertical pocket is described as the preferred method of assessing amniotic fluid volume based on fewer oligohydramnios diagnoses and labor inductions with no demonstrable difference in pregnancy outcomes compared with the amniotic fluid index. Web amniotic fluid index, afi, is the sum total measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest pocket of amniotic fluid in each of the four quadrants of the uterus. Accurately diagnosing an amniotic fluid abnormality can aid in the proper management of a pregnancy at risk for an adverse outcome. Most pregnant women don’t even think about their baby’s amniotic fluid. Web amniotic fluid index, afi, is the sum total measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest pocket of amniotic fluid in each of the four quadrants of the uterus. Web amniotic fluid volume (afv) is a function both of the amount of water transferred to the gestation across the placental membrane, and the flux of water across the amnion. Some women. The afv undergoes characteristic changes with gestation. Normal but should be taken in the context of subjective volume. The afi is normally 7 to 25 cm. Most pregnant women don’t even think about their baby’s amniotic fluid levels, until their healthcare provider tells them it could be a problem. Sdp stands for single deepest pocket and it is the measurement,. Web it is performed by assessing a pocket of a maximal depth of amniotic fluid which is free of an umbilical cord and fetal parts. Web the amniotic fluid index is a standardized way to assess the sufficiency of amniotic fluid quantity in pregnancy. Sdp stands for single deepest pocket and it is the measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest. But what does this mean for a mother and her unborn baby? Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. The afv undergoes characteristic changes with gestation. The afi is normally 7 to 25 cm. Some women are told they. Sdp stands for single deepest pocket and it is the measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest pocket in. Web the normal amniotic fluid level range is between 8 to 18 cm. Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. The. Sdp stands for single deepest pocket and it is the measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest pocket in. Web it is performed by assessing a pocket of a maximal depth of amniotic fluid which is free of an umbilical cord and fetal parts. Some women are told they have too little or too much amniotic fluid. The usually accepted values. Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. Fluid volume abnormalities can directly interfere with fetal development, causing structural anomalies such as pulmonary hypoplasia. But what does this mean for a mother and her unborn baby? How that’s measured differs. Web it is performed by assessing a pocket of a maximal depth of amniotic fluid which is free of an umbilical cord and fetal parts. Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. Web last updated october 3, 2023. Change. Change in volume through gestation. Web qualitative or semiquantitative assessment of amniotic fluid volume (afv) is a standard component of every obstetric ultrasound examination, regardless of indication, because it is an indicator of fetoplacental health and thus useful for identifying, monitoring, and managing complicated pregnancies [ 1,2 ]. Web last updated october 3, 2023. The amniotic fluid index is used. Web amniotic fluid index, afi, is the sum total measurement, in centimeters, of the deepest pocket of amniotic fluid in each of the four quadrants of the uterus. The afv undergoes characteristic changes with gestation. But what does this mean for a mother and her unborn baby? Most pregnant women don’t even think about their baby’s amniotic fluid levels, until their healthcare provider tells them it could be a problem. Then add them as if stacked top to bottom. The first method is to estimate the depth of volume in each of the four quadrants within the placenta. Some women are told they have too little or too much amniotic fluid. Web to estimate the association of polyhydramnios detected by either maximum vertical pocket (mvp) or amniotic fluid index (afi) or both and adverse maternal, fetal and neonatal outcomes. Accurately diagnosing an amniotic fluid abnormality can aid in the proper management of a pregnancy at risk for an adverse outcome. Web the single deepest vertical pocket measurement in the assessment of amniotic fluid volume during fetal surveillance seems a better choice since the use of the amniotic fluid index increases the rate of diagnosis of oligohydramnios and the rate of induction of labor without improvement in peripartum outcomes. Web amniotic fluid volume (afv) is a function both of the amount of water transferred to the gestation across the placental membrane, and the flux of water across the amnion. Web the amniotic fluid index is a standardized way to assess the sufficiency of amniotic fluid quantity in pregnancy. Web qualitative or semiquantitative assessment of amniotic fluid volume (afv) is a standard component of every obstetric ultrasound examination, regardless of indication, because it is an indicator of fetoplacental health and thus useful for identifying, monitoring, and managing complicated pregnancies [ 1,2 ]. Web the normal amniotic fluid level range is between 8 to 18 cm. Web last updated october 3, 2023. The afi is normally 7 to 25 cm.
Amniotic Fluid Level Chart

Levels Of Amniotic Fluid Chart
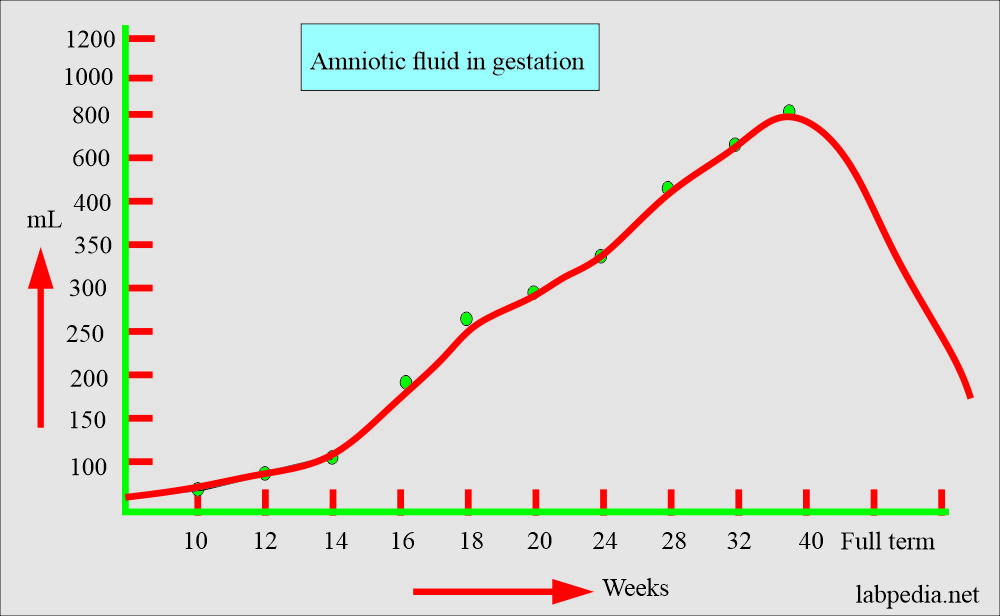
Amniotic Fluid Levels Chart
Normal Amniotic Fluid Index Chart 018

Amniotic Fluid Index Chart For Ultrasound

Amniotic Fluid Levels Chart
Normal Amniotic Fluid Index Chart 018

Normal Amniotic Fluid Index Chart 018

Amniotic Fluid Levels Chart

Amniotic Fluid Measurement Chart
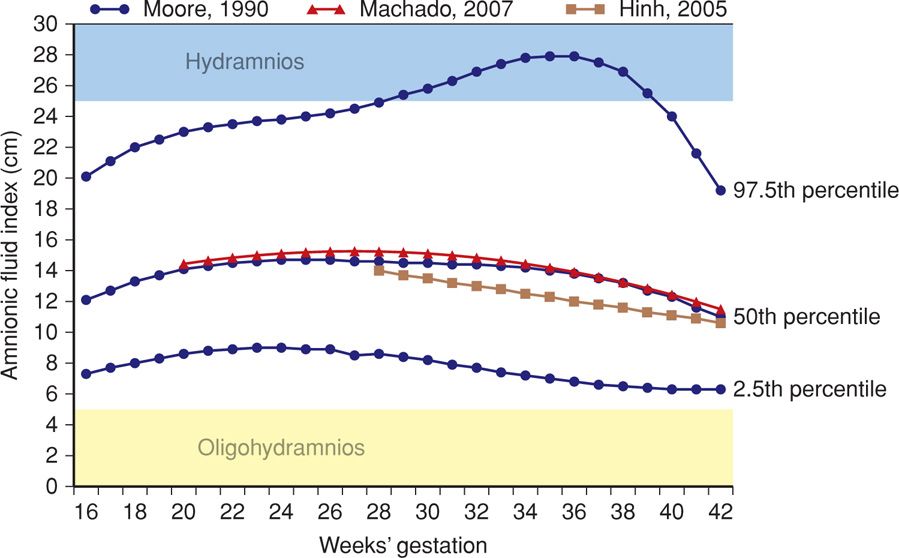
The Maximum Vertical Pocket (Mvp) And Amniotic Fluid Index (Afi) Are Both Used To Assess Amniotic Fluid Volume By Ultrasound.
The Amniotic Fluid Index Is Used In Patients Who Are At Least 24 Weeks Pregnant With A Singleton Gestation.
Web The Single Maximal Vertical Pocket (Mvp) Technique Involves Finding The Single Largest Pocket Of Amniotic Fluid On Ultrasound, Free Of Cord And Fetal Parts, And Then Measuring The Greatest Vertical Dimension With The Ultrasound Transducer Perpendicular To The Floor (Figures.
The Usually Accepted Values Are:
Related Post: