Mpc V Common Law Chart
Mpc V Common Law Chart - 1) a specific provocation is not required in mpc, aggregation is okay. Defendant enters into contract requiring 2. Common law chart from polsci 101 at university of michigan. Web five instances where you have a legal duty to act: You'll also see questions that invoke the mpc standards vs. Web model penal code (mpc) standards are important. In this chapter, we will distinguish between states that are common law jurisdictions and states that are model penal. Web a note on common law v. (iii) provisions governing treatment and correction; Web common types are intentionally, knowingly, recklessly, and negligently. 2) extreme emotional disturbance allows for more subjectivity. 1) a specific provocation is not required in mpc, aggregation is okay. Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: A person is guilty of conspiracy with. (ii) definitions of specific offenses; Requires a voluntary and a social harm an act is voluntary if willed the action or if she was sufficiently free that she could be blamed for. Defendant enters into contract requiring 2. (i) general principles of liability; Web common types are intentionally, knowingly, recklessly, and negligently. Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: Web common law mpc differences. Web common types are intentionally, knowingly, recklessly, and negligently. (i) general principles of liability; Common law chart from polsci 101 at university of michigan. Web the model penal code (typically abbreviated as “mpc”) is a code created in the 1950s and adopted in 1962 by the american law institute, a prestigious organization composed of. Web common law mpc differences. Web common law mpc differences. (iii) provisions governing treatment and correction; For a crime requiring a mens rea of: Homicide murder common law model penal code murder is killing of a. Common law chart from polsci 101 at university of michigan. Web model penal code (mpc) 5.03 criminal conspiracy. (ii) definitions of specific offenses; Web this is a chart of the mpc v the cl. Web differences between common law and mpc: Web common types are intentionally, knowingly, recklessly, and negligently. It is a chart that clearly lays. Web differences between common law and mpc: Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: Requires a voluntary and a social harm an act is voluntary if willed the action or if she was sufficiently free that she could be blamed for. The model penal code further distinguishes these categories and clarifies definitions like when. Web model penal code (mpc) standards are important. (iii) provisions governing treatment and correction; Web common law mpc differences. (ii) definitions of specific offenses; Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: For a crime requiring a mens rea of: Suppose that hill had opened the window and hayes had climbed through? Requires a voluntary and a social harm an act is voluntary if willed the action or if she was sufficiently free that she could be blamed for. At common law the rule. Web differences between common law and mpc: A person is guilty of conspiracy with. Web common types are intentionally, knowingly, recklessly, and negligently. (ii) definitions of specific offenses; The model penal code further distinguishes these categories and clarifies definitions like when. Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: For a crime requiring a mens rea of: Web differences between common law and mpc: Web this note compares the purpose, knowledge, recklessness, and negligence (pkrn) mens rea regime laid out in the model penal code (mpc) and dominant in american. Defendant enters into contract requiring 2. You'll also see questions that invoke the mpc standards vs. Web this note compares the purpose, knowledge, recklessness, and negligence (pkrn) mens rea regime laid out in the model penal code (mpc) and dominant in american. In this chapter, we will distinguish between states that are common law jurisdictions and states that are model penal. At common law the rule establishes that an agreement by two persons to commit a particular crime cannot be prosecuted as a model penal code § 210(1): Web common law mpc differences. Web the mpc is comprised of four parts: Requires a voluntary and a social harm an act is voluntary if willed the action or if she was sufficiently free that she could be blamed for. (ii) definitions of specific offenses; The model penal code further distinguishes these categories and clarifies definitions like when. For a crime requiring a mens rea of: A person may not be convicted of an offense unless he acted purposefully, knowingly, recklessly, or. Web mens rea culpability terms mpc common law rule: Web common law mpc differences. Web this is a chart of the mpc v the cl. Web differences between common law and mpc: Web model penal code (mpc) standards are important.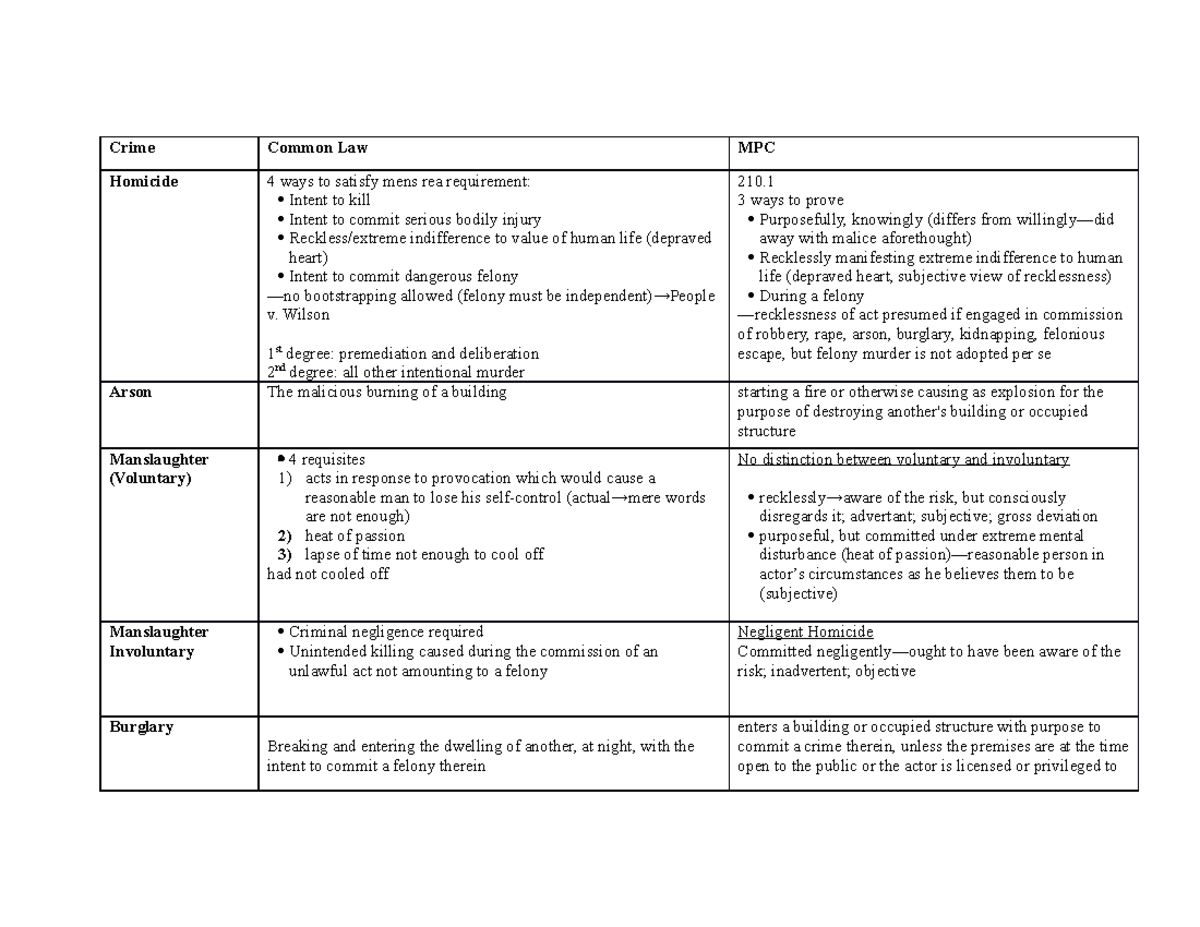
Common law versus model penal code Crime Common Law MPC Homicide 4
Common Law V MPC PDF Intention (Criminal Law) Mens Rea
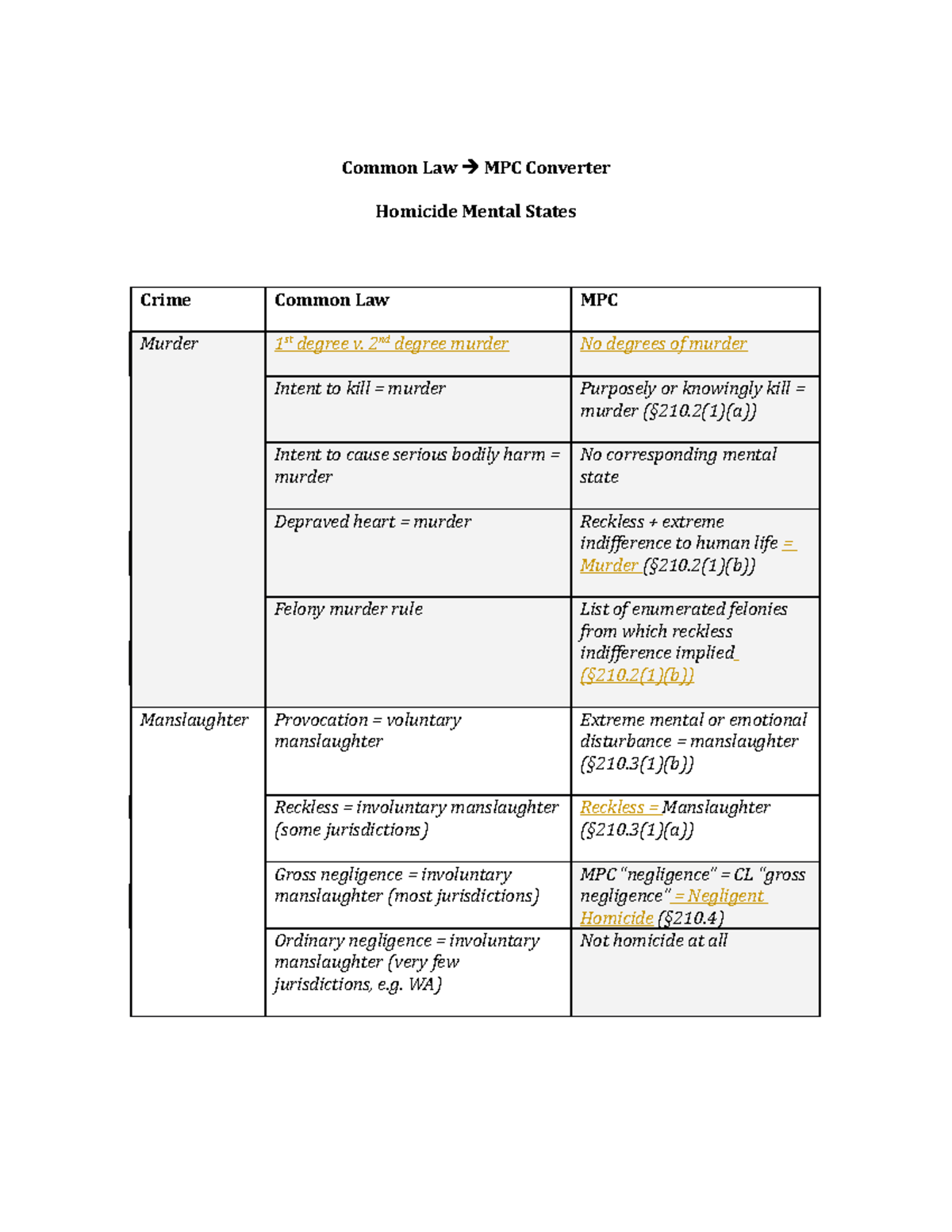
Common Law MPC Converter Common Law MPC Converter Homicide Mental
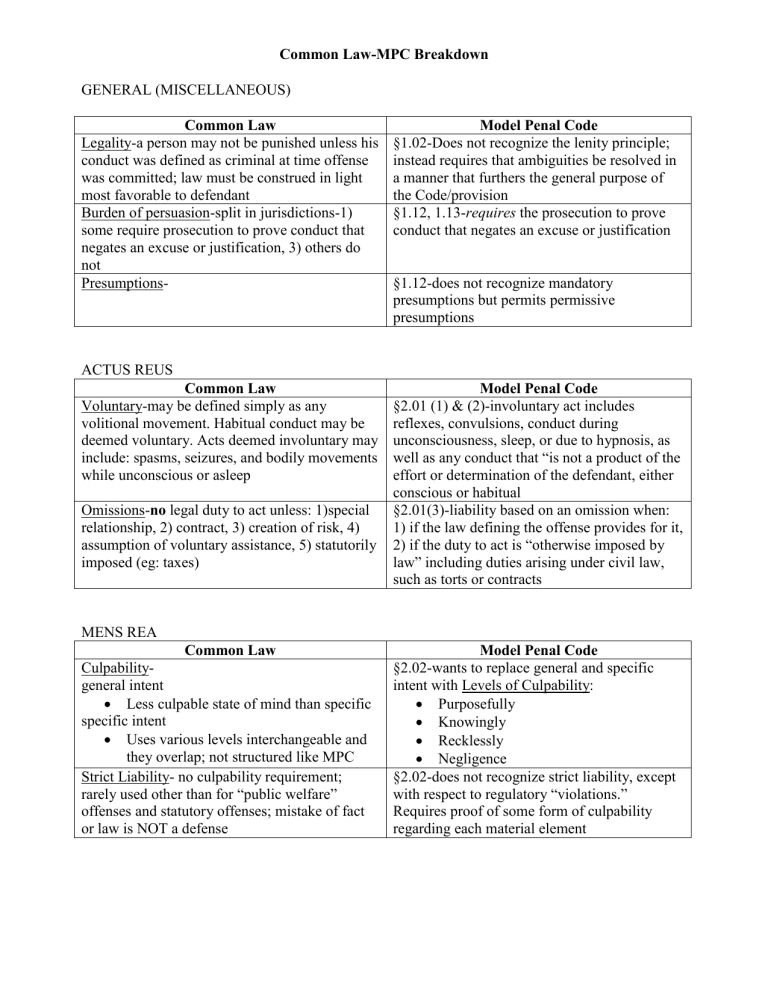
Common Law MPC Breakdown
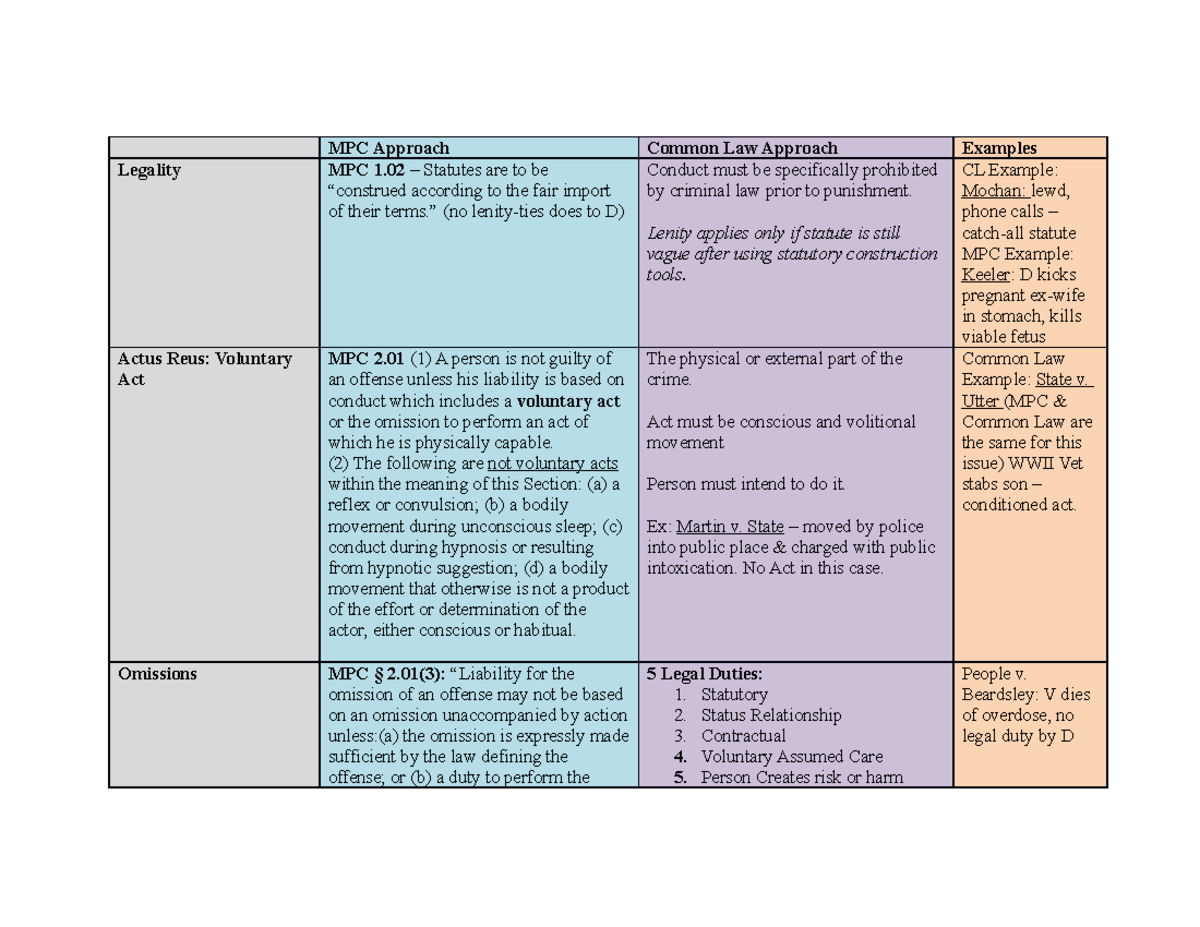
MPC and Common Law Table MPC Approach Common Law Approach Examples
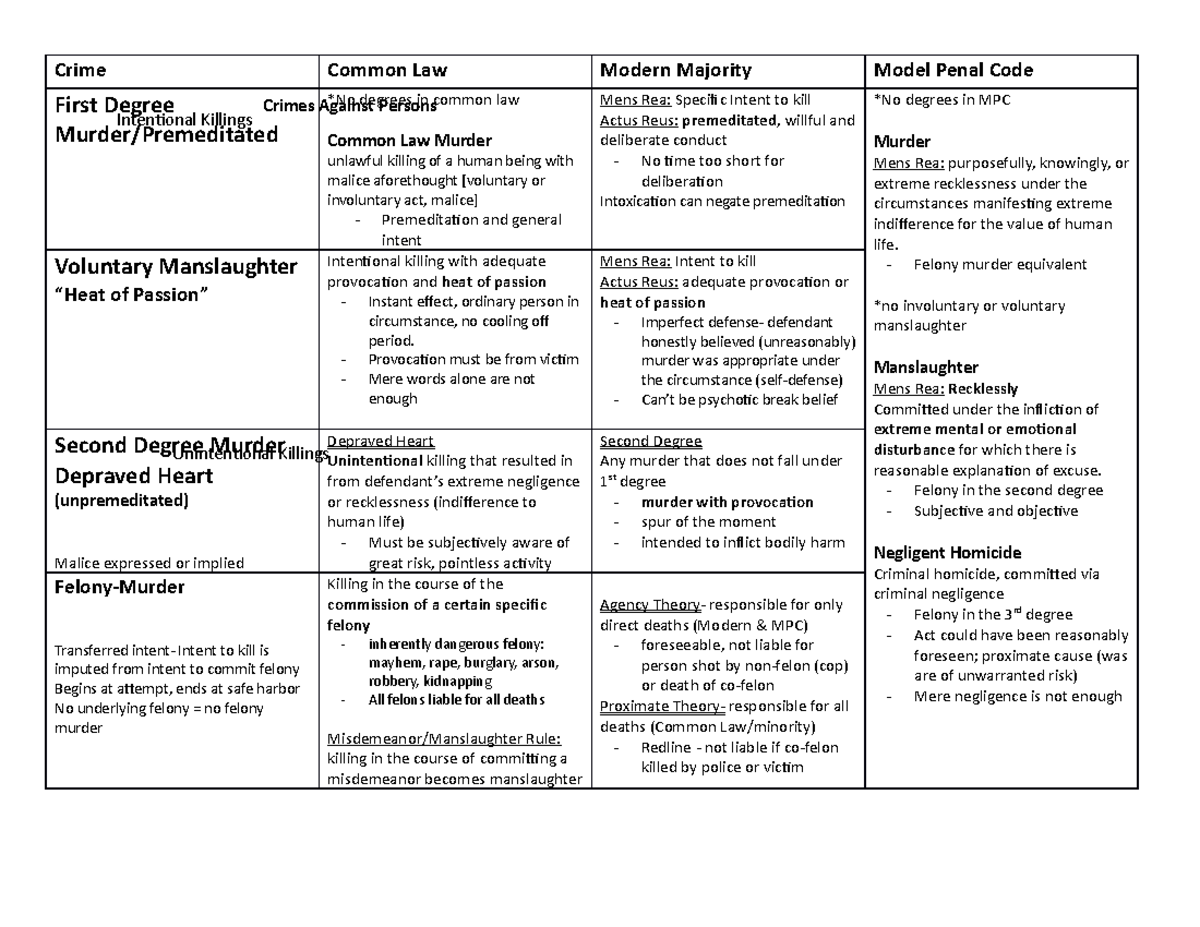
CRIM LAW Charts Crime Common Law Modern Majority Model Penal Code
MPC and NYPL Chart Criminal Law Mens Rea Insanity Defense
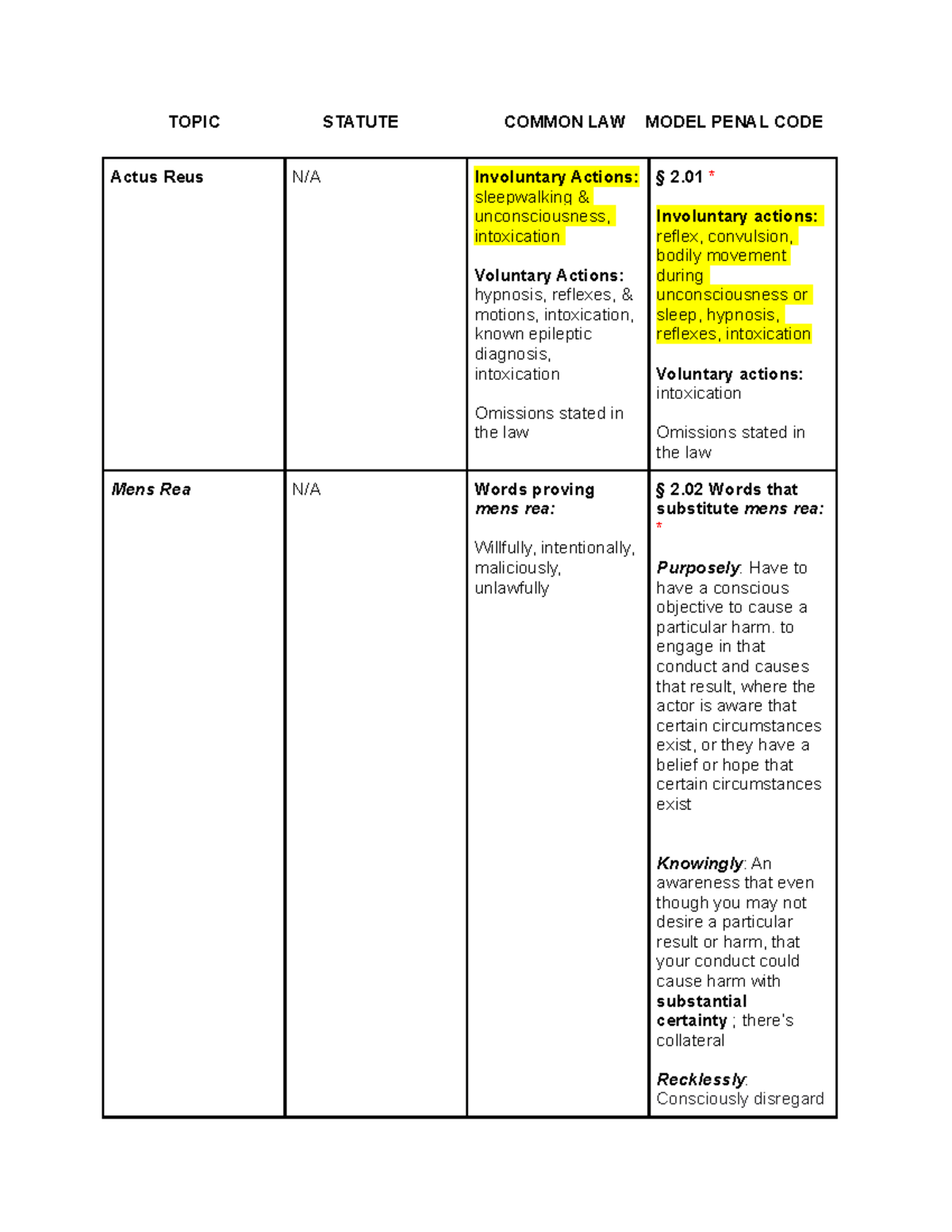
Statute v. Common Law v. MPC Chart TOPIC STATUTE COMMON LAW MODEL

Criminal Law Homicide Chart Docsity
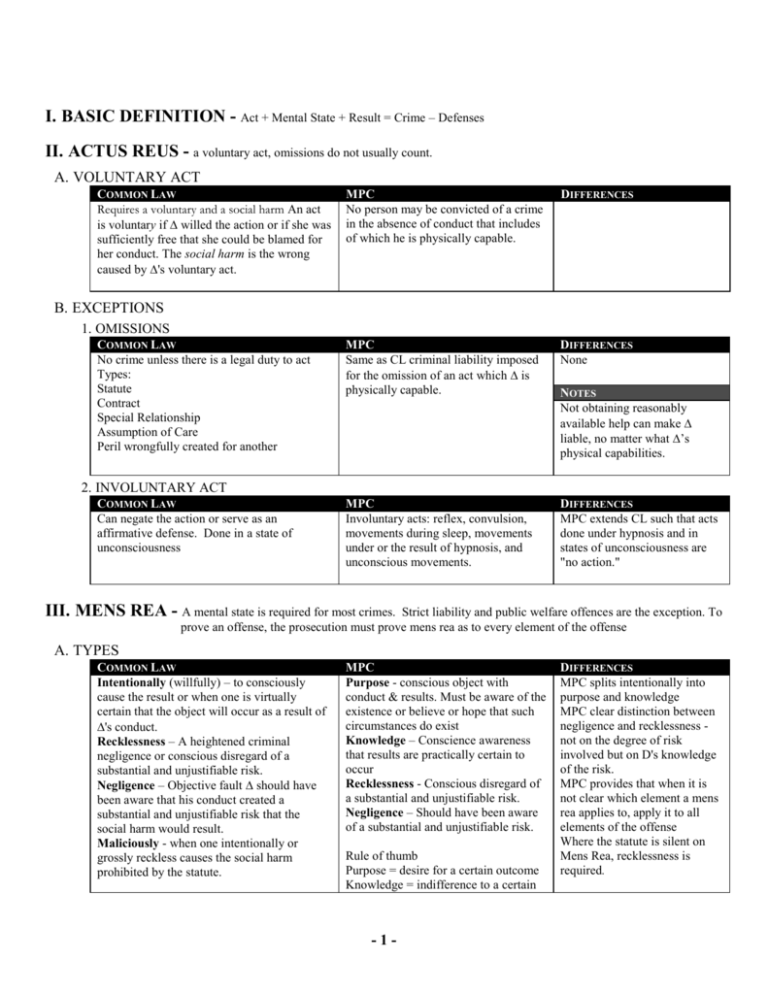
Common Law Versus MPC Chart Wikispaces
Web Common Law Mpc Differences.
This Isn't A Hugely Tested Issue, But It Will.
Web A Note On Common Law V.
For A Crime Requiring A Mens Rea Of:
Related Post:

