Microtubules Drawing
Microtubules Drawing - Like microfilaments, microtubules are also dependent on a nucleotide triphosphate for polymerization, but in this case, it is gtp. Web microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. The microtubule polymer is largely viewed as a passive building block during the organization process. To begin with, the outside diameter of a microtubule (usually about 25 nm) is much greater than that of microfilaments. Furthermore, microtubules are hollow, containing a central lumen about 15 nm in diameter. Tubulin dimers can depolymerize as well as polymerize, and microtubules can undergo rapid cycles of assembly and disassembly. Microtubules are usually discussed with microfilaments. “microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.” microtubules extend throughout the cell providing it with proper shape and keeping the organelles in place. Web despite the “micro” in their name, microtubules are the largest of the three types of cytoskeletal fibers, with a diameter of about 25 nm. The aster is an array of microtubules that radiates out from the centrosome towards the cell edge. Learn how microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments organize the cell. To begin with, the outside diameter of a microtubule (usually about 25 nm) is much greater than that of microfilaments. Of the three main cytoskeletal fibers, intermediate filaments serve a mainly structural role in cells. Web dynamic networks of protein filaments give shape to cells and power cell movement.. The microtubules are cytoplasmic tubules that serve as structural components of cytoskeleton, cilia, and eukaryotic flagella. Microtubules are essential, multitasking protein polymers that serve as structural elements in most eukaryotic cells. They are formed by the lateral association of between 12 and 17 protofilaments into a regular helical lattice [2], [3]. Web dynamic networks of protein filaments give shape to. “microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.” microtubules extend throughout the cell providing it with proper shape and keeping the organelles in place. Web despite the “micro” in their name, microtubules are the largest of the three types of cytoskeletal fibers, with a diameter of about 25 nm.. 32k views 3 years ago. Web despite the “micro” in their name, microtubules are the largest of the three types of cytoskeletal fibers, with a diameter of about 25 nm. Microtubules are hollow cylinders [1] that are approximately 25nm in diameter [2] and vary in length from 200 nm to 25 μm. Kinesin and dynein, the prototypes of microtubule motor. Microtubules have many features that distinguish them from microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Kinesin and dynein, the prototypes of microtubule motor proteins, move along microtubules in opposite directions— kinesin toward the plus end and dynein toward the minus end ( figure 11.45 ). 32k views 3 years ago. Each microtubule subunit comprises two closely related polypeptides: Web microtubules are polymers of. Microtubules are hollow cylinders [1] that are approximately 25nm in diameter [2] and vary in length from 200 nm to 25 μm. This tutorial demonstrates how to draw microtubule for research publication, conference. The microtubule polymer is largely viewed as a passive building block during the organization process. While microfilaments are thin, microtubules are thick, strong spirals of thousands of. They are formed by the lateral association of between 12 and 17 protofilaments into a regular helical lattice [2], [3]. The microtubules are cytoplasmic tubules that serve as structural components of cytoskeleton, cilia, and eukaryotic flagella. Microtubules are the proteins of the cytoskeleton. Web more specifically, in the first part of anaphase — sometimes called anaphase a — the kinetochore. Tubulin dimers can depolymerize as well as polymerize, and microtubules can undergo rapid cycles of assembly and disassembly. Diagram indicating kinetochore microtubules (bound to kinetochores) and the aster. They play a massive role in various cellular functions like cell movement and spindle. They form a network within neurons for internal transport. While microfilaments are thin, microtubules are thick, strong spirals. Microtubules are the largest structures in the cytoskeleton at about 24 nanometers thick. The microtubule polymer is largely viewed as a passive building block during the organization process. “microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.” microtubules extend throughout the cell providing it with proper shape and keeping the. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Although they are both proteins that help define cell structure and movement, they are very different molecules. Web despite the “micro” in their name, microtubules are the largest of the three types of cytoskeletal fibers, with a diameter of about 25 nm. Tubulin dimers can depolymerize as well as polymerize, and microtubules can undergo. Microtubules are essential, multitasking protein polymers that serve as structural elements in most eukaryotic cells. Identification of microtubule motor proteins. The microtubule polymer is largely viewed as a passive building block during the organization process. Web dynamic networks of protein filaments give shape to cells and power cell movement. Microtubules are hollow cylinders [1] that are approximately 25nm in diameter [2] and vary in length from 200 nm to 25 μm. Furthermore, microtubules are hollow, containing a central lumen about 15 nm in diameter. Microtubules have many features that distinguish them from microfilaments and intermediate filaments. Web microtubules and microfilaments have dual functions, dynamically maintaining cell shape and. “microtubules are microscopic, hollow tubes made of alpha and beta tubulin that are a part of the cell’s cytoskeleton.” microtubules extend throughout the cell providing it with proper shape and keeping the organelles in place. Learn how microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments organize the cell. The microtubules are cytoplasmic tubules that serve as structural components of cytoskeleton, cilia, and eukaryotic flagella. They are dynamic, and their dynamics. Microtubules are usually discussed with microfilaments. Kinesin and dynein, the prototypes of microtubule motor proteins, move along microtubules in opposite directions— kinesin toward the plus end and dynein toward the minus end ( figure 11.45 ). The aster is an array of microtubules that radiates out from the centrosome towards the cell edge. Web more specifically, in the first part of anaphase — sometimes called anaphase a — the kinetochore microtubules shorten and draw the chromosomes toward the spindle poles.
Structure of a microtubule, illustration Stock Image F020/1416
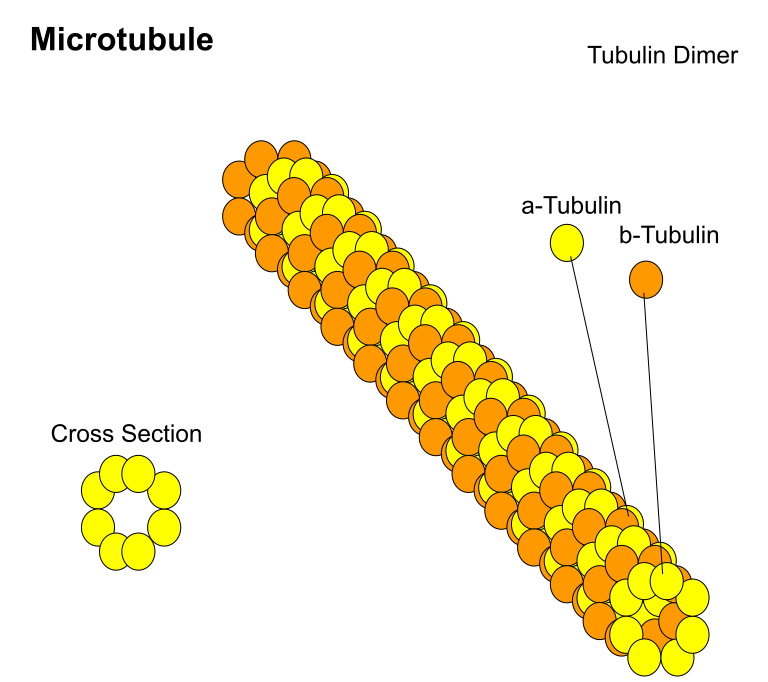
Microtubules are constituents ofA) Centrosome, nucleosome, and

Microtubuli Il citoscheletro BioPills
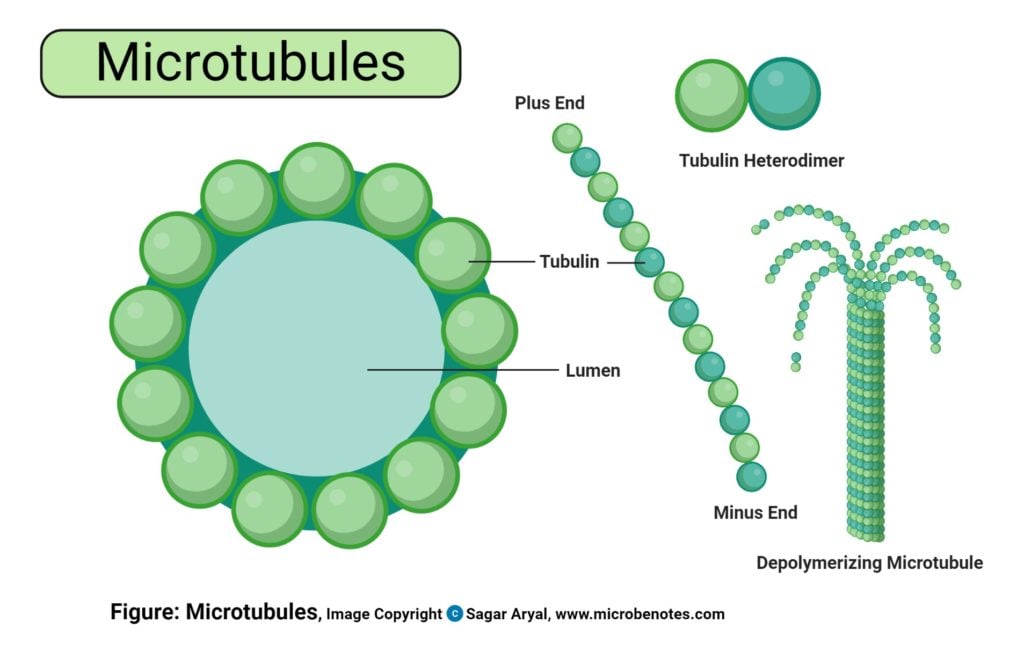
Cell Organelles Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram

Microtubules Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1

Microtubules In A Cell Diagram

Microtubules, illustration Stock Image F020/1405 Science Photo
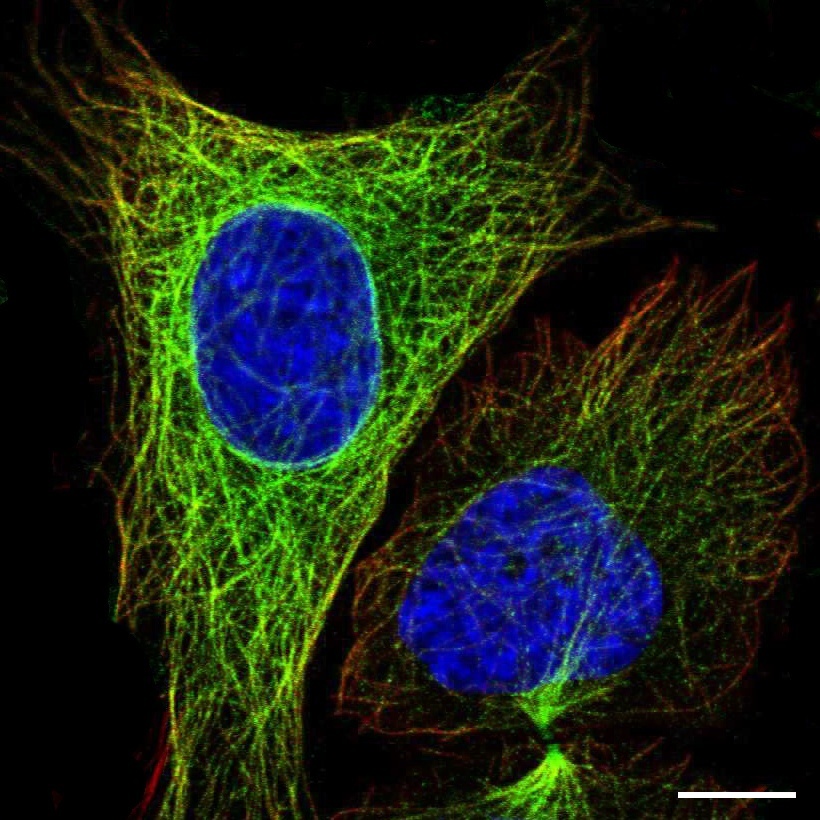
Dictionary Cell Microtubules The Human Protein Atlas

Elements of the microtubule cytoskeleton within the cilium. Download

Microtubules, artwork Stock Image C029/7073 Science Photo Library
Each Microtubule Subunit Comprises Two Closely Related Polypeptides:
Web Despite The “Micro” In Their Name, Microtubules Are The Largest Of The Three Types Of Cytoskeletal Fibers, With A Diameter Of About 25 Nm.
Web Anatomy Of The Mitotic Spindle.
Microtubules Are The Proteins Of The Cytoskeleton.
Related Post: