Lymph Flow Chart
Lymph Flow Chart - The immune and lymphatic systems. Lymphatic vessels, ducts and tracts; Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. The lymph not only flows through the lymph node, but some of it is reabsorbed into. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. Contains mainly water, with suspended proteins and immune cells. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. Web summary of basic concepts. Web this animation shows normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. Web the lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid around the body. First is the maintenance of fluid balance, second is the facilitation of the absorption of dietary fats from the gastrointestinal tract to the bloodstream for metabolism or storage, and third is the enhancement and facilitation of the immune system. Web there are three primary functions of the lymphatic system: Web the lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid around the body. The. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. Web compiled by howie baum. Lymph from peripheral tissues is pumped into lymph nodes by afferent collecting lymphatic vessels. Pathogens are then filtered and. The immune and lymphatic systems. Here, let us discuss the circulation of lymph with the help of a flowchart. In most people the thoracic duct drains into the subclavian vein on. Protects the body from invasion by bacteria or other germs. Lymphatic vessels, ducts and tracts; Web quick overview of the lymphatic system and how lymph flows through the body 3d models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. Learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and ducts of the lymphatic system. Web • lymph. Pathogens are then filtered and. Web this animation shows normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. First is the maintenance of fluid balance, second is the facilitation of the absorption of dietary fats from the gastrointestinal tract to the bloodstream for metabolism or storage, and third is the enhancement and facilitation of the immune system. 3d models help you explore the anatomy. As a vital part of your immune system, your lymphatic system protects you from infection and destroys old or abnormal cells your body doesn’t need. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. Find out how the body's mysterious second circulatory system works, and how it can move fluid even when it has no heart of its own. Lymphatic. The immune and lymphatic systems. Web to return to the venous circulation, the lymph is collected by the major lymphatic ducts: The process starts with the extravasation of fluid from the blood capillaries. Web there are three primary functions of the lymphatic system: Web summary of basic concepts. The specialized structure of the lymphatic vasculature enables it to propel lymph through the body and back into blood circulation. The fluid that flows through lymphatic vessels. Web • lymph returns the excess fluid filtered from the blood vessel capillaries, as well as the protein that leaks out of the blood vessel capillaries. Web quick overview of the lymphatic system. Contains mainly water, with suspended proteins and immune cells. 3d models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. The lymphatic system is responsible for picking up excess interstitial water and protein as well as other cells, including bacteria, which can enter the tissue through small cuts or breaks in the skin. Web how lymphatic vessels move fluid (video) | khan. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells and have a thin layer of smooth muscles and adventitia that bind the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and nodes which acts to drain lymphatic fluid from the tissues and return it to the circulation. Learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and. Web your lymphatic system is a network of organs, vessels and tissues that work together to move a colorless, watery fluid ( lymph) back into your circulatory system (your bloodstream). Web to return to the venous circulation, the lymph is collected by the major lymphatic ducts: Learn about lymph itself, bone marrow, and the different types of immunity. Pathogens are then filtered and. The lymphatic system is responsible for picking up excess interstitial water and protein as well as other cells, including bacteria, which can enter the tissue through small cuts or breaks in the skin. The active part of the system is lymph fluid. Web this animation shows normal lymphatic anatomy and flow. Web summary of basic concepts. The lymphatic system cleverly returns fluid to the circulatory system without a pump. Web there are three primary functions of the lymphatic system: Web lymph flows from the lymphatic capillaries, through lymphatic vessels, and then is dumped into the circulatory system via the lymphatic ducts located at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins in the neck. 3d models help you explore the anatomy and physiology. Find out how the body's mysterious second circulatory system works, and how it can move fluid even when it has no heart of its own. Lymphatic vessels, ducts and tracts; Protects the body from invasion by bacteria or other germs. Here, let us discuss the circulation of lymph with the help of a flowchart.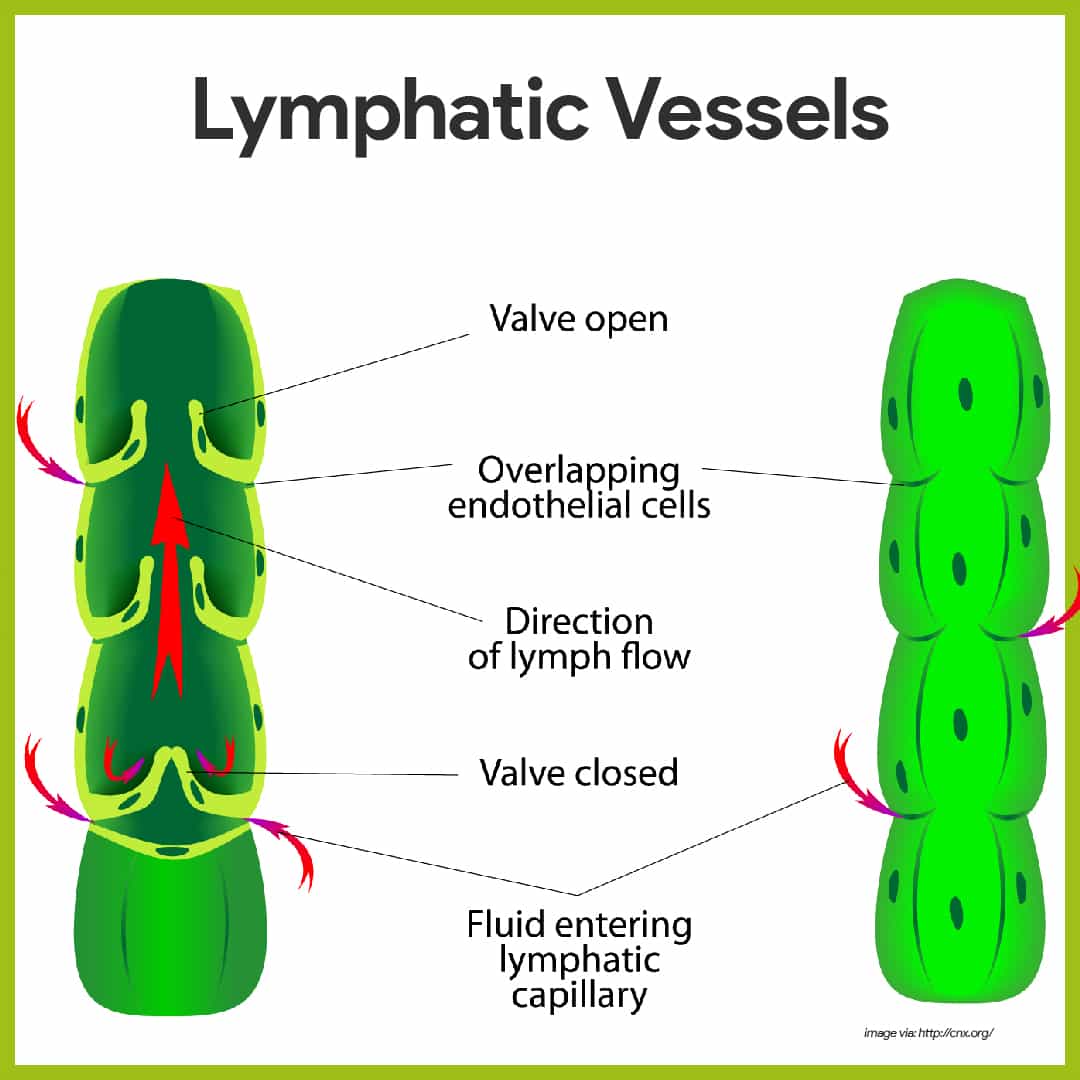
Lymphatic System Anatomy and Physiology Nurseslabs
![What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute](http://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/7367-Lymphatic-System-Infographic.png)
What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute
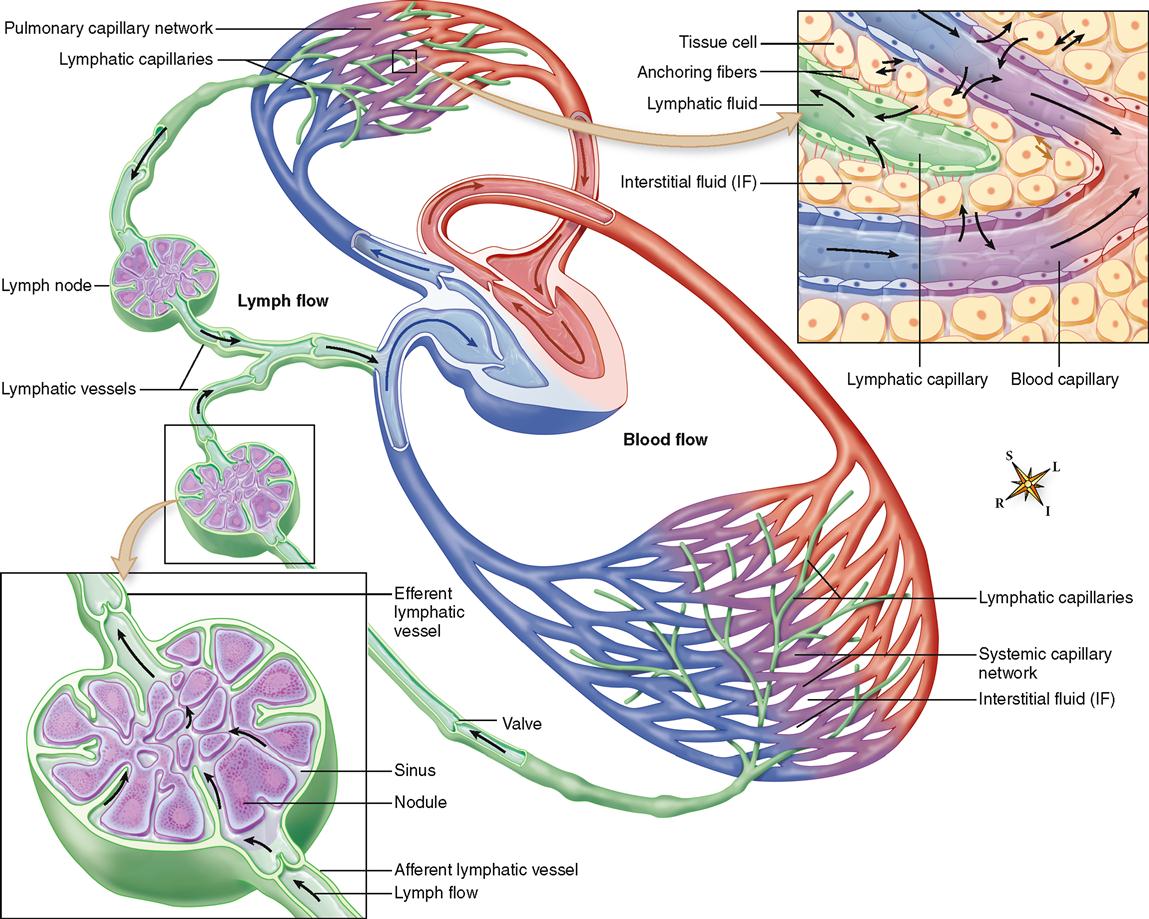
Lymphatic System Basicmedical Key
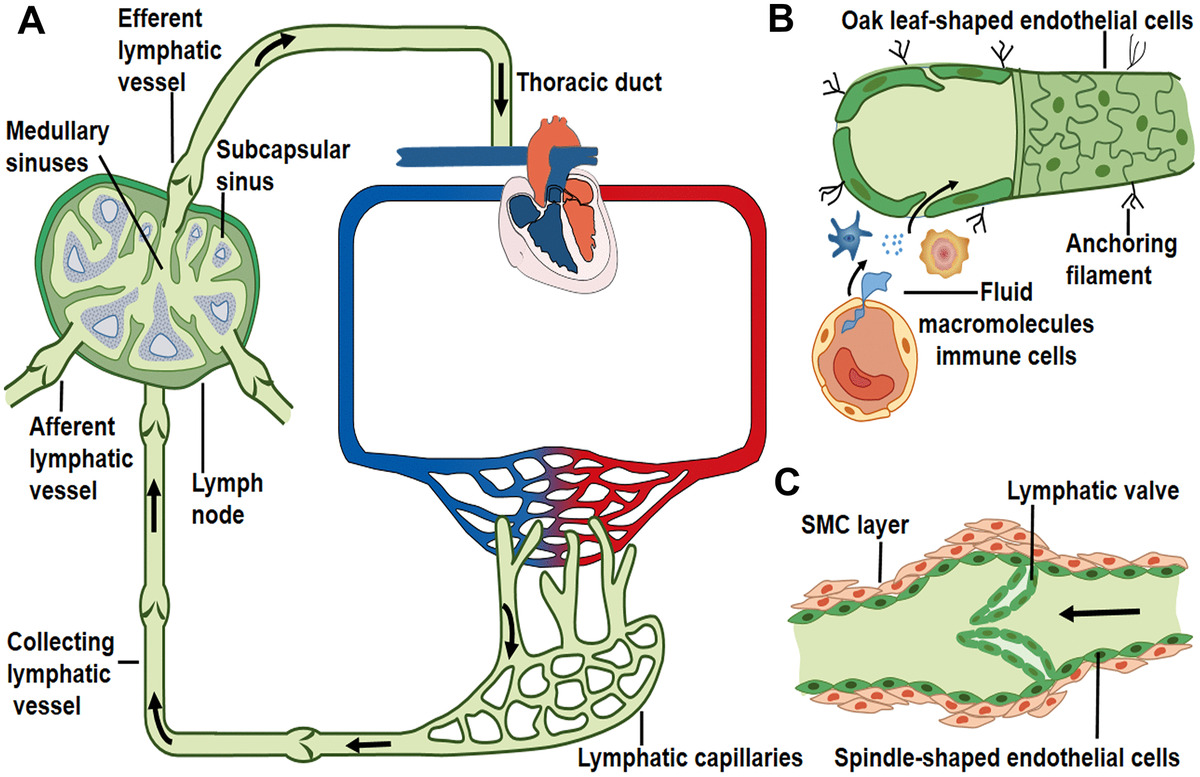
Lymphatic Drainage System Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
/lymphatic_system_2-58110f0c5f9b58564c6e31cb.jpg)
Lymphatic System Components Spleen, Thymus, Nodes

Holistic Wellness / Body of Health & Life » Lymph Drainage
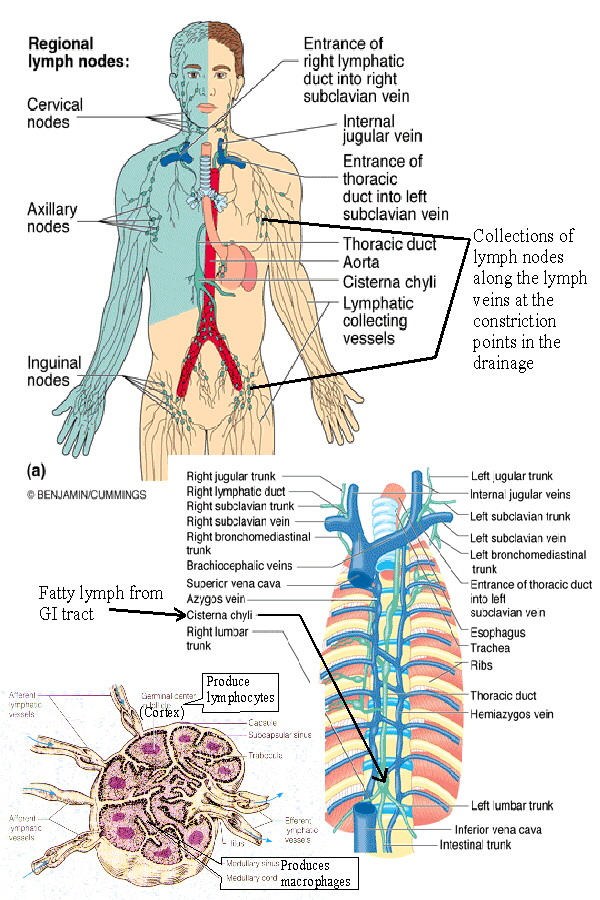
Understanding the Lymphatic System
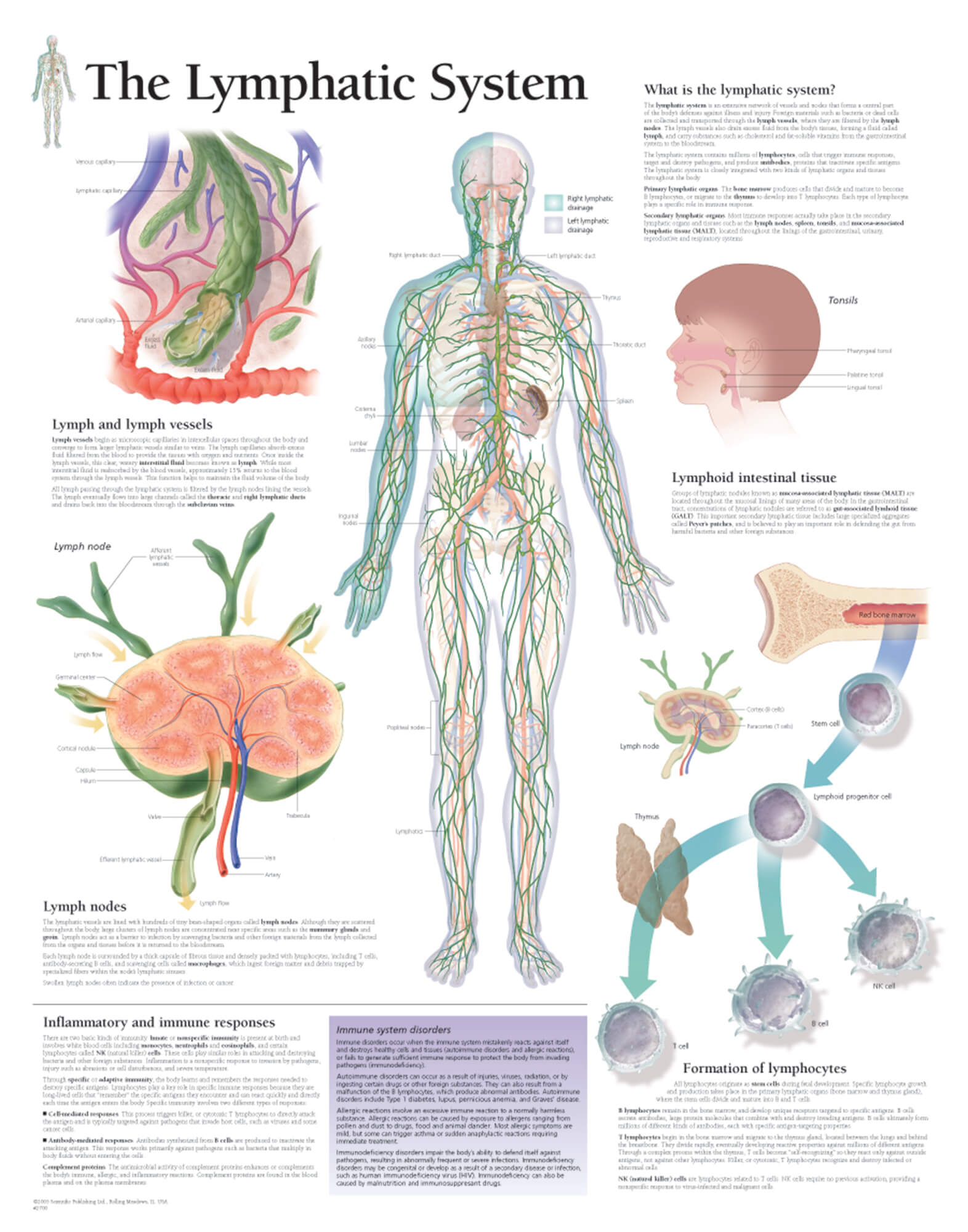
The Lymphatic System Scientific Publishing

What You Didn't Know About Your Lymphatic System VIVA Wellness
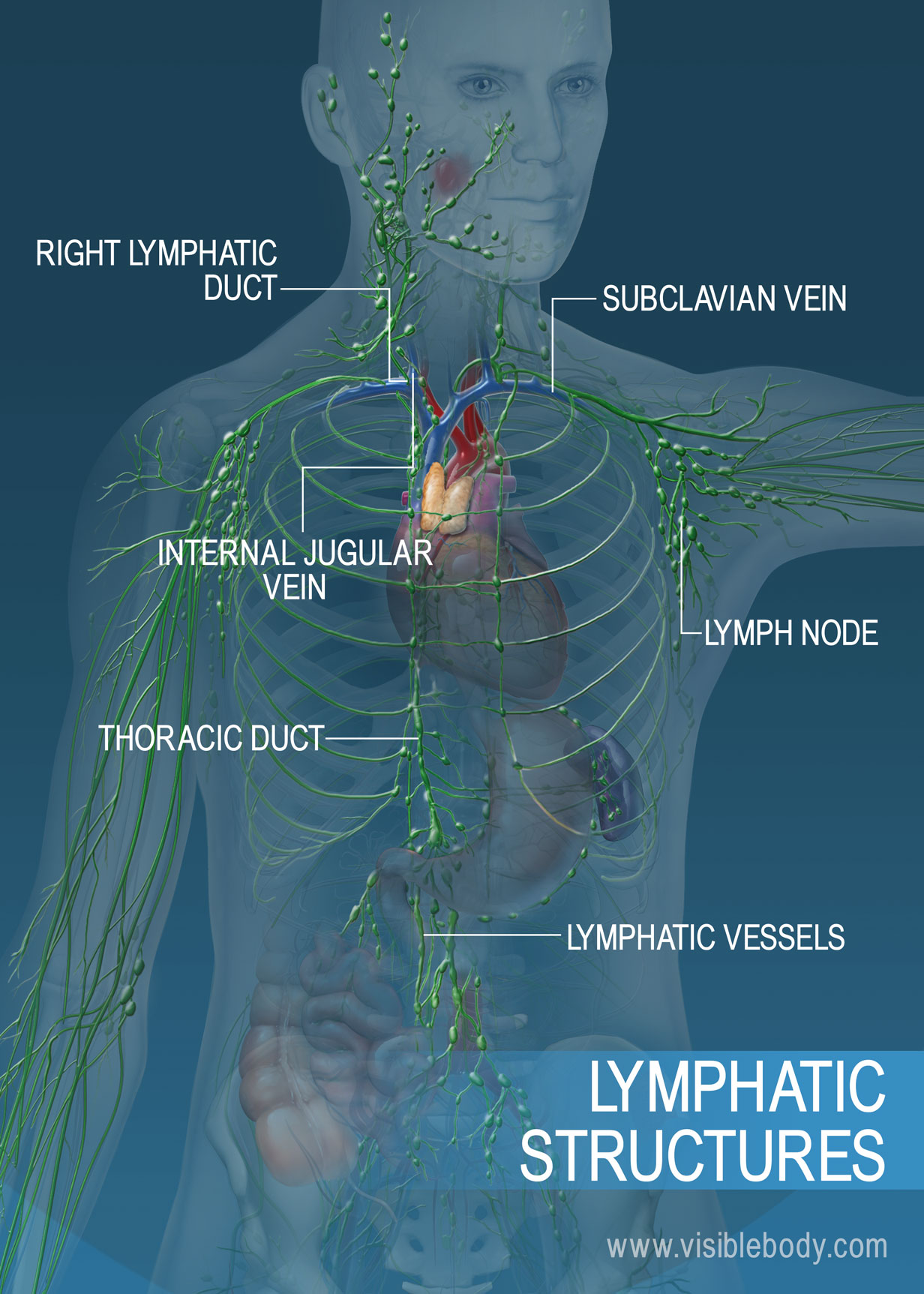
Lymphatic System
Web How Lymphatic Vessels Move Fluid (Video) | Khan Academy.
Contains Mainly Water, With Suspended Proteins And Immune Cells.
Lymph From Peripheral Tissues Is Pumped Into Lymph Nodes By Afferent Collecting Lymphatic Vessels.
The Fluid That Flows Through Lymphatic Vessels.
Related Post: