Landing Pattern
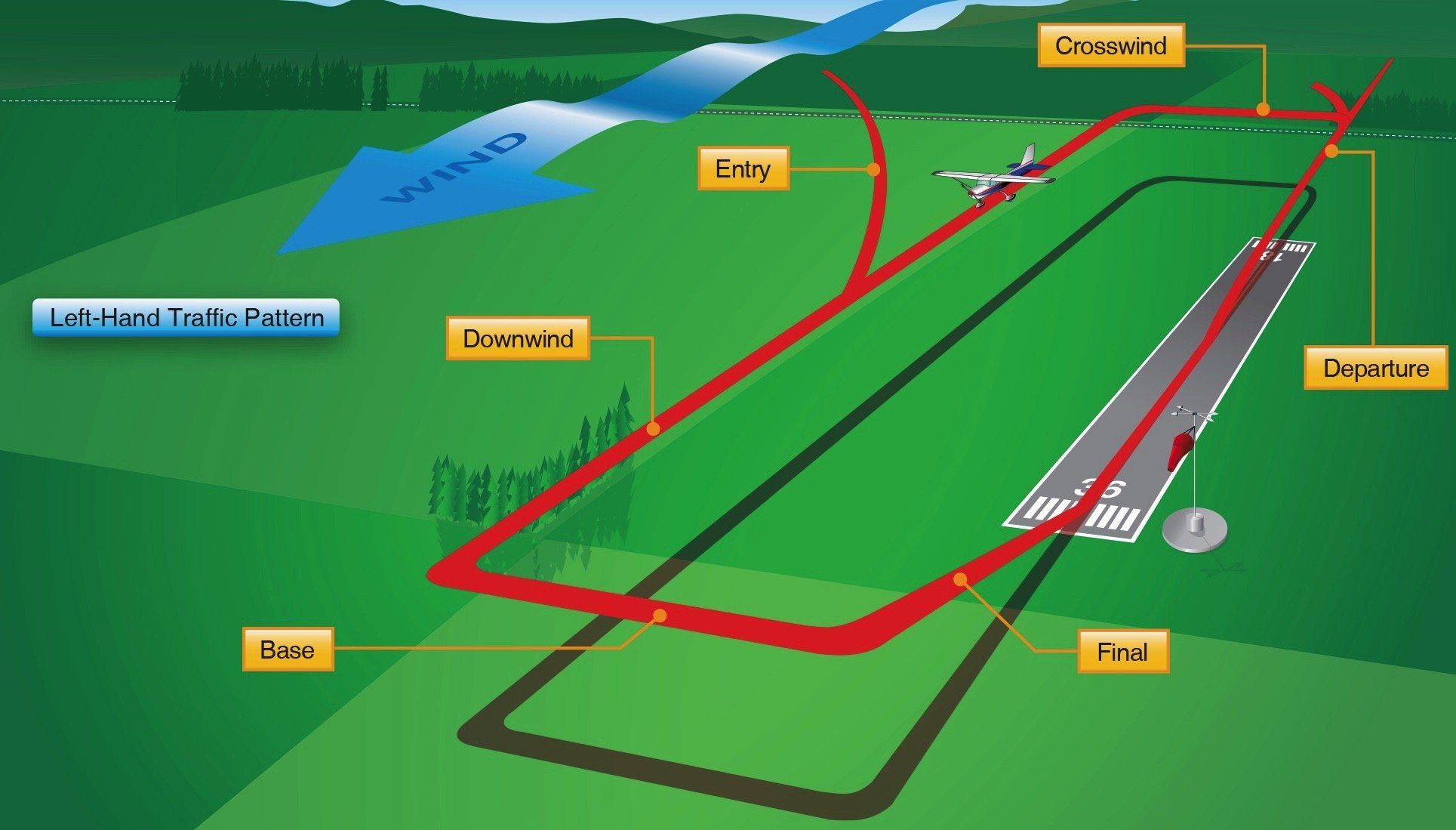
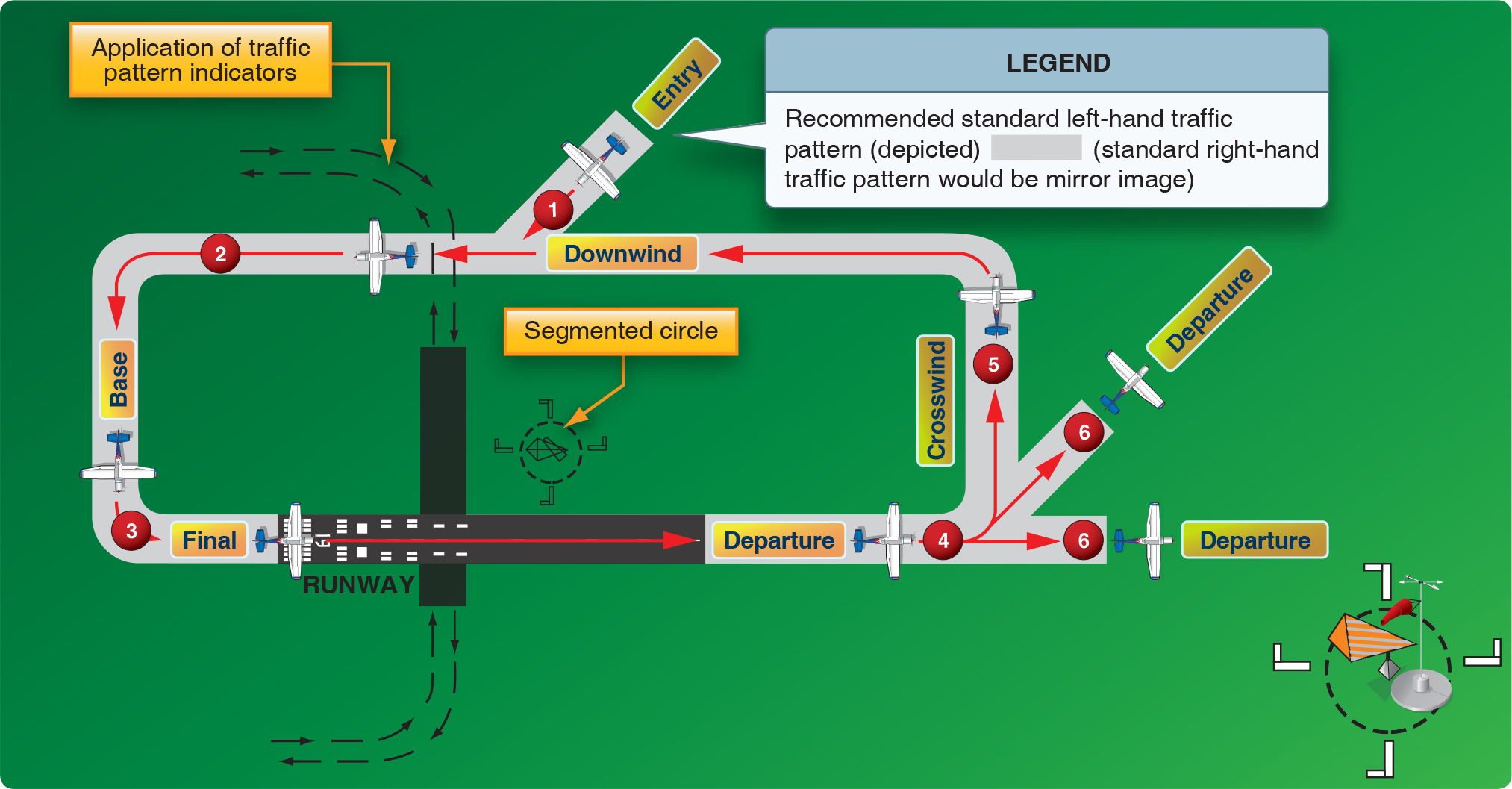
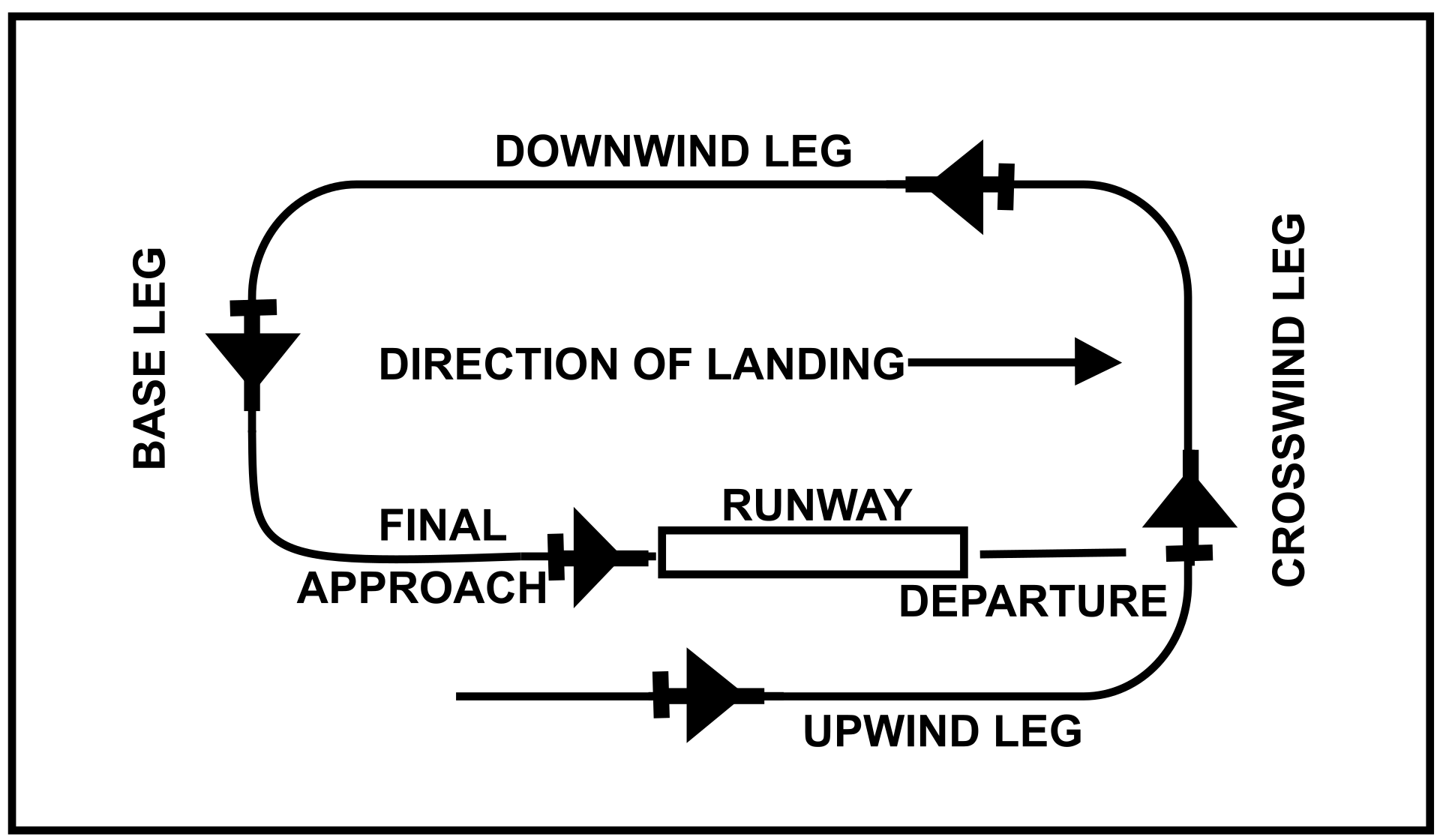
Landing Pattern - Web do you have a perfect landing every time? Losing altitude will be more difficult without the benefit of increased drag, which means you'll typically need less power. In the eliptical pattern an aircraft is both descending and changing heading to eventually align the. As the graphic shows, the downwind leg is parallel to the active runway and in the opposite direction of the landing. It finally arrived at the stand and the passengers were disembarked at 5. Web the standard traffic pattern consists of a downwind, base, and final leg. Web the traffic pattern is divided into legs which form a rectangle; Web an airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft when taking off or landing while maintaining visual contact with the airfield. Continue straight ahead until beyond departure end of runway. Web historically, these conventional metrics are measured from multiple tools on different patterns and locations; Complete turn to final at least 1 / 4 mile from the runway. However, harsh weather creates visibility hindrances, and a pilot must have a clear view of runway elements before the minimum decision altitude. On this leg you will likely have a tailwind, assuming the wind is in the direction of the runway. Web fly a consistent pattern. So. Web according to the airplane flying handbook, when you turn to your base leg, you should transition to a speed of 1.4 x vso (again, only if your manufacturer doesn't recommend a speed). Web so, what is “the pattern”? Bounces, balloons, and floats are flare entries. If remaining in the traffic pattern, commence turn to crosswind leg beyond the departure. There's a lot more guidance in the advisory circular as well. Web an airfield traffic pattern helps to “direct traffic” over an airfield. Short fields need short aim. And if they don't, the faa recommends 1.4 x v s0 for base, and 1.3 x v s0 for final. Web after the first aborted landing, the plane maintained a holding pattern. Web do you have a perfect landing every time? That is why student pilots are typically taught this information early in their training. Web the intrinsic capability to perceive depth of field and extract salient information by the human vision system (hvs) stimulates a pilot to perform manual landing over an autoland approach. The following terminology for the various components. Most patterns for piston planes were 1,000 agl (or thereabouts) but many were 800 feet and some were even lower than that. This leg is the ground path flown immediately after takeoff. As the graphic shows, the downwind leg is parallel to the active runway and in the opposite direction of the landing. To safely stay out of the pattern,. Fly the airplane through the entire flare. Web if there is a place to be overly cautious, it is in the pattern at a nontowered airport—where arriving and departing traffic mix with students making circuits for takeoff and landing practice. Web studying these interactions requires proteins with unique ptm patterns, which are challenging to obtain by recombinant methods. The following. Fly to a position that gives you a good look at the airport and the windsock. The following terminology for the various components of a traffic pattern has been adopted as standard for use by control towers and pilots [figure 1/2] Crosswind landings are normal landings with extra finesse. If you want to make your landings better, remember these 10. That is why student pilots are typically taught this information early in their training. Whenever possible, aircraft take off and land facing the wind. Web according to the airplane flying handbook, when you turn to your base leg, you should transition to a speed of 1.4 x vso (again, only if your manufacturer doesn't recommend a speed). Short fields need. Web if there is a place to be overly cautious, it is in the pattern at a nontowered airport—where arriving and departing traffic mix with students making circuits for takeoff and landing practice. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions, obstructions, and other factors. Web begins and ends at an. Crosswind landings are normal landings with extra finesse. For example, if your landing configuration stall speed (vso) was 50 knots, 1.4 x vso would be 70 knots. As the graphic shows, the downwind leg is parallel to the active runway and in the opposite direction of the landing. The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the. There's a lot more guidance in the advisory circular as well. Continue straight ahead until beyond departure end of runway. Web maintain pattern altitude until abeam approach end of the landing runway on downwind leg. At an airport, the pattern (or circuit) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic. Most patterns for piston planes were 1,000 agl (or thereabouts) but many were 800 feet and some were even lower than that. Web the traffic pattern is divided into legs which form a rectangle; If you want to make your landings better, remember these 10 tips. This leg is the ground path flown immediately after takeoff. 1) fly your pattern speeds. The following terminology for the various components of a traffic pattern has been adopted as standard for use by control towers and pilots [figure 1/2] On this leg you will likely have a tailwind, assuming the wind is in the direction of the runway. Web legs define a phase of flight associated with takeoff, landing, or closed pattern touch and go operations. As the graphic shows, the downwind leg is parallel to the active runway and in the opposite direction of the landing. Web so, what is “the pattern”? Web begins and ends at an airport or other suitable landing field, pilots need to learn the traffic rules, traffic procedures, and traffic pattern layouts in use at various airports. Web emergency crews were put on standby after the pilot reported the plane's landing gear had failed just before 10am.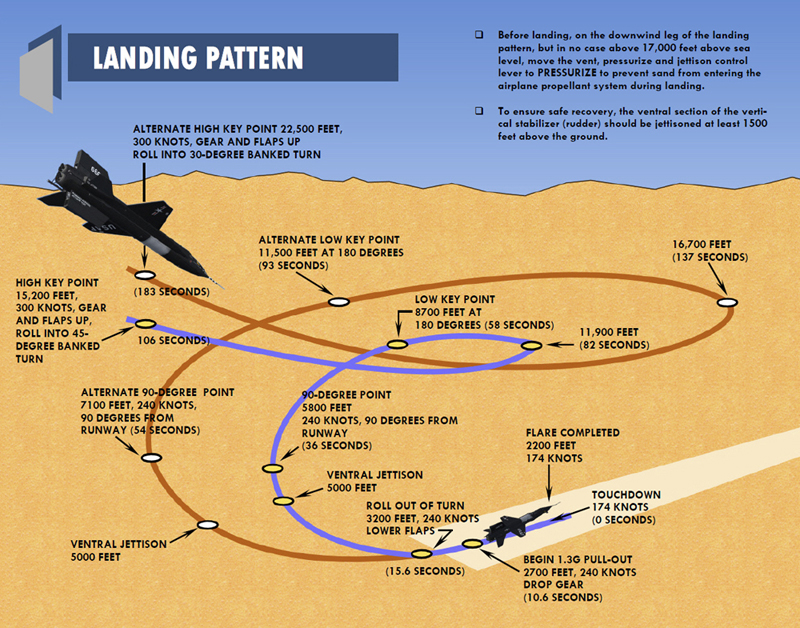
Landing

Baseline Landing Pattern Evergreen Soaring
setting waypoint to line up for pattern entry for landing r/flightsim

Chapter 7 of Airplane Flying Handbook Airport Trafic Patterns YouTube

Pattern Work, Approach Landing, Ground School, Private Pilot, Darren
/Traffic_patterns_depicted_in_FAA-H-8083-25-56a058ce3df78cafdaa1229b.jpg)
How to Fly a General Aviation Traffic Pattern
Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog
Everything You Should Know About the Airport Traffic Pattern

Landing Pattern Learning to fly the aircraft landing pattern
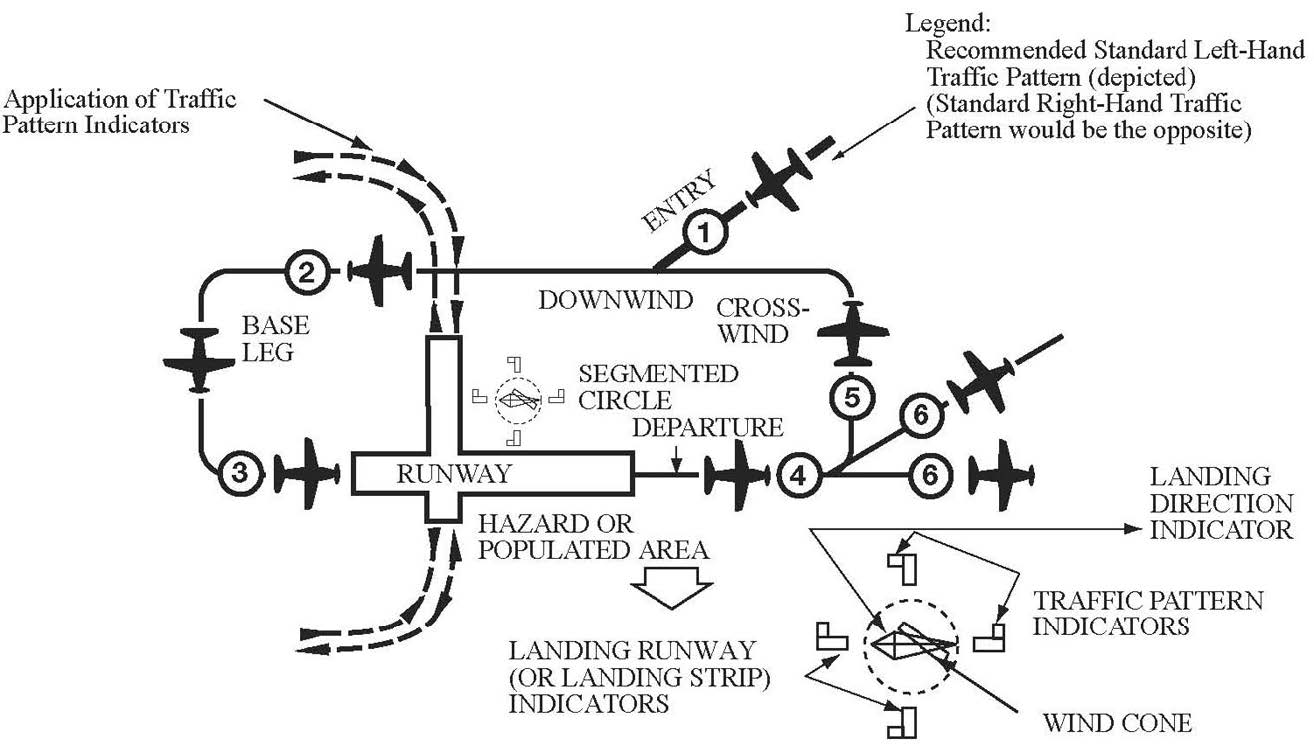
Airport Operations
In The Eliptical Pattern An Aircraft Is Both Descending And Changing Heading To Eventually Align The.
Bounces, Balloons, And Floats Are Flare Entries.
A Flight Path At Right Angles To The Landing Runway Off Its Takeoff End.
Since Both Are Best Seen From Above, Fly Directly Over The Airport.
Related Post: