Juvenile T Wave Pattern
Juvenile T Wave Pattern - T wave inversion in v1 to v3 in an adult is consistent with a persistent juvenile pattern. Case series and literature review,. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. Web the t waves in the right precordial leads (v1 through v3) are asymmetrically inverted in childhood and become upright (except for v1 and occasionally v2) by adulthood. Uptodate, electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on adult primary care and internal medicine, allergy and immunology, cardiovascular medicine. Should be upright in leads v5 and v6 in a normal ecg; Persistent juvenile t wave pattern. It is named because it resembles the normal child's ecg [62, 63]. Persistent juvenile t wave patterns were classified into three types. Type a = biphasic t waves with. Type i had negative t waves in lead v 1 only, type ii in lead v 1 and v 2 and type iii in v 1 to lead v 3 or v 4. Web juvenile t wave pattern refers to the t wave inversions commonly seen in the anterior leads. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and. For example, the whales would systematically modulate certain aspects of their codas based on the. Web juvenile t wave pattern refers to the t wave inversions commonly seen in the anterior leads. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. Web aurora seen in atlanta. Type i had negative t waves in lead v 1 only, type ii in lead v 1 and v 2 and type iii in v 1 to lead v 3 or v 4. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. Rsr’ pattern (partial rbbb. For example, the whales would systematically modulate certain aspects of their codas based on the. Web the persistent juvenile t wave pattern consists of asymmetric t wave inversion seen in v1 through to v3 or v4. Rsr’ pattern (partial rbbb morphology) in v1. (emily smith/cnn) a stunning aurora, caused by a severe geomagnetic storm, is painting the sky shades of. The three dynamical phases are: Web the t waves in the right precordial leads (v1 through v3) are asymmetrically inverted in childhood and become upright (except for v1 and occasionally v2) by adulthood. Web the persistent juvenile t wave pattern consists of asymmetric t wave inversion seen in v1 through to v3 or v4. It is named because it resembles. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. Web juvenile t wave pattern refers to the t wave inversions commonly seen in the anterior leads. Hyperkalaemia, lvh (volume overload), cerebral vascular accident. Web aurora seen in atlanta area around 10:30 p.m. It is named because. Type a = biphasic t waves with. Web the researchers identified something of a “sperm whale phonetic alphabet,” where various elements that researchers call “rhythm,” “tempo,” “rubato,” and “ornamentation” interplay to form a vast array of distinguishable codas. The changes may be seen in all or most of the leads (diffuse changes), or they may be present contiguous leads, such. Persistent juvenile t wave patterns found in mass examination and in clinical cases were studied for the purpose of clarifying their significance. The changes may be seen in all or most of the leads (diffuse changes), or they may be present contiguous leads, such as the inferior, lateral, or anterior leads. This pattern, when found in adults, has been described. Persistent juvenile t wave patterns were classified into three types. This pattern, when found in adults, has been described as a “persistent juvenile” pattern, where the juvenile pattern has “persisted” since childhood (4). Hyperkalaemia, lvh (volume overload), cerebral vascular accident. These inversions show a slow descent, with a relatively brisk upstroke, and there is no associated st segment deviation (fig.. Web the t waves in the right precordial leads (v1 through v3) are asymmetrically inverted in childhood and become upright (except for v1 and occasionally v2) by adulthood. The three dynamical phases are: T wave inversion in v1 to v3 in an adult is consistent with a persistent juvenile pattern. Type i had negative t waves in lead v 1. The changes may be seen in all or most of the leads (diffuse changes), or they may be present contiguous leads, such as the inferior, lateral, or anterior leads. Persistent juvenile t wave patterns found in mass examination and in clinical cases were studied for the purpose of clarifying their significance. (emily smith/cnn) a stunning aurora, caused by a severe geomagnetic storm, is painting the sky shades of pink, purple and green as it spreads into. Anterior twi, however, is also the hallmark of. This pattern, when found in adults, has been described as a “persistent juvenile” pattern, where the juvenile pattern has “persisted” since childhood (4). Hyperkalaemia, lvh (volume overload), cerebral vascular accident. In the first week of life, the t waves are all upright. Web the t waves in the right precordial leads (v1 through v3) are asymmetrically inverted in childhood and become upright (except for v1 and occasionally v2) by adulthood. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. T wave inversion in v1 to v3 in an adult is consistent with a persistent juvenile pattern. For example, the whales would systematically modulate certain aspects of their codas based on the. Web juvenile t wave pattern refers to the t wave inversions commonly seen in the anterior leads. Persistent juvenile t wave pattern. Uptodate, electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on adult primary care and internal medicine, allergy and immunology, cardiovascular medicine. It is characterized by twi in the right precordium, and has been understood to represent an arrested stage of the normal electrocardiographic evolution. Persistent juvenile t wave patterns were classified into three types.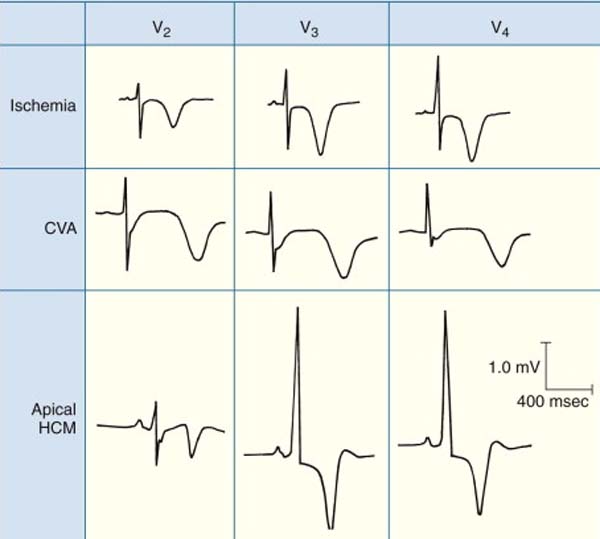
ECG T wave changes and interpretation Medicine Hack
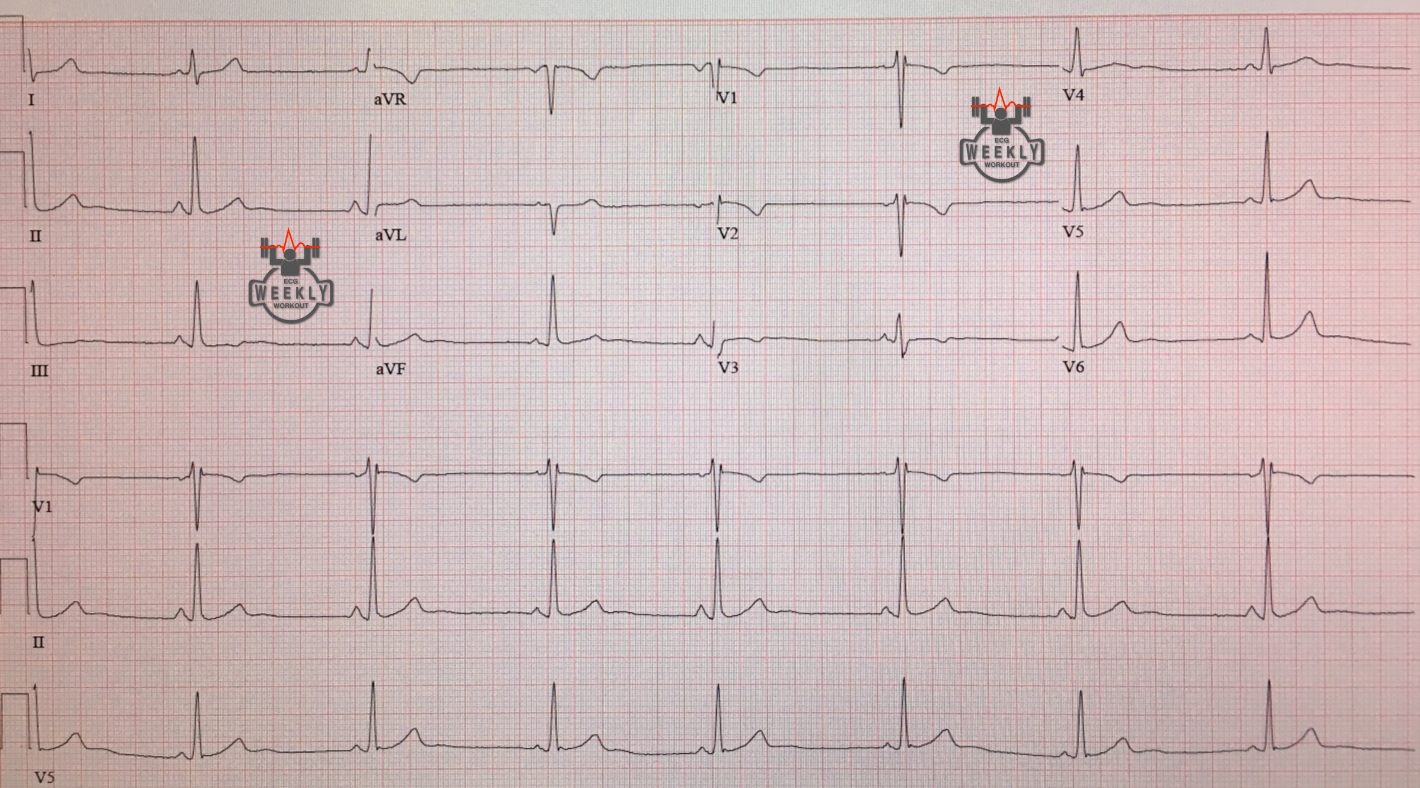
Persistent juvenile Twave pattern ECG Weekly

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Persistent Juvenile Twave Pattern
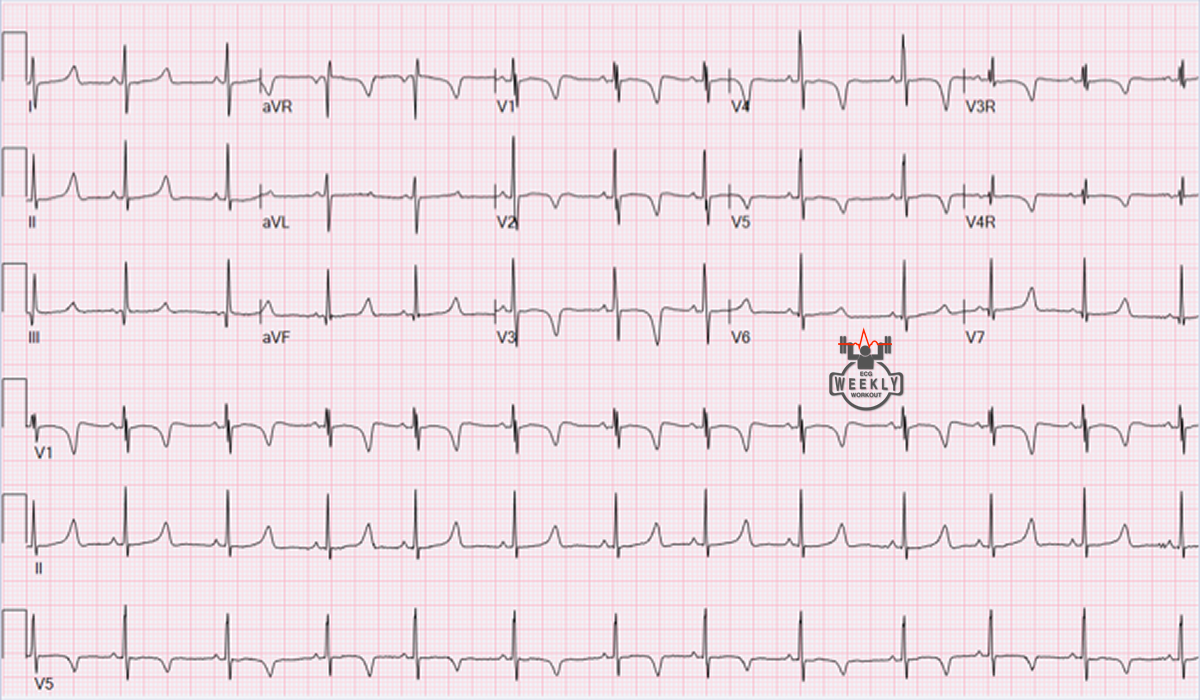
Juvenile Twave pattern ECG Weekly

“Persistent Juvenile” TWave Pattern May Not Be Persistent Case Series
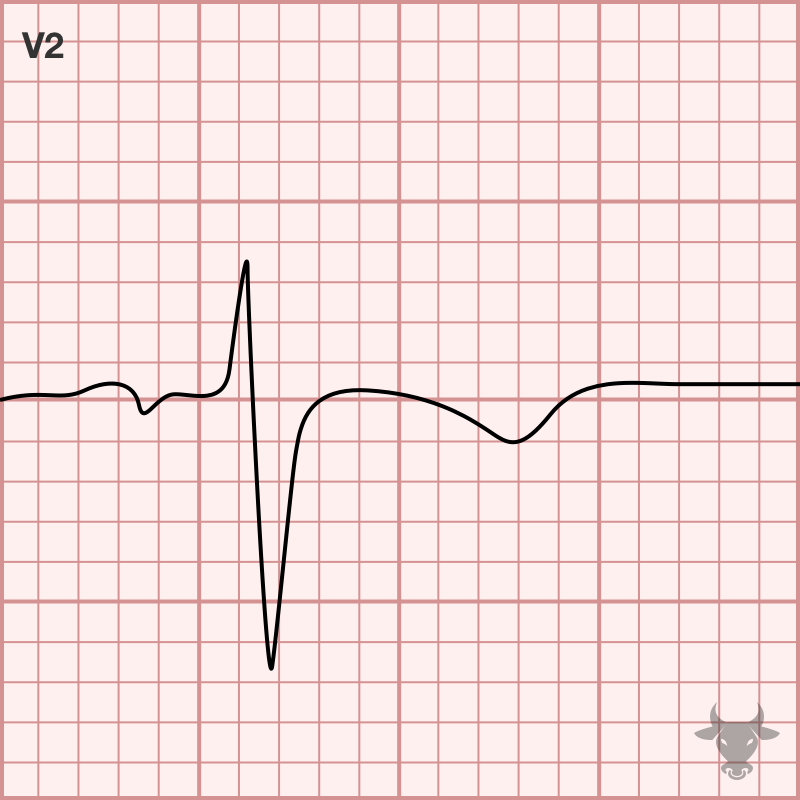
Persistent Juvenile T Wave Pattern ECG Stampede

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Persistent Juvenile Twave Pattern
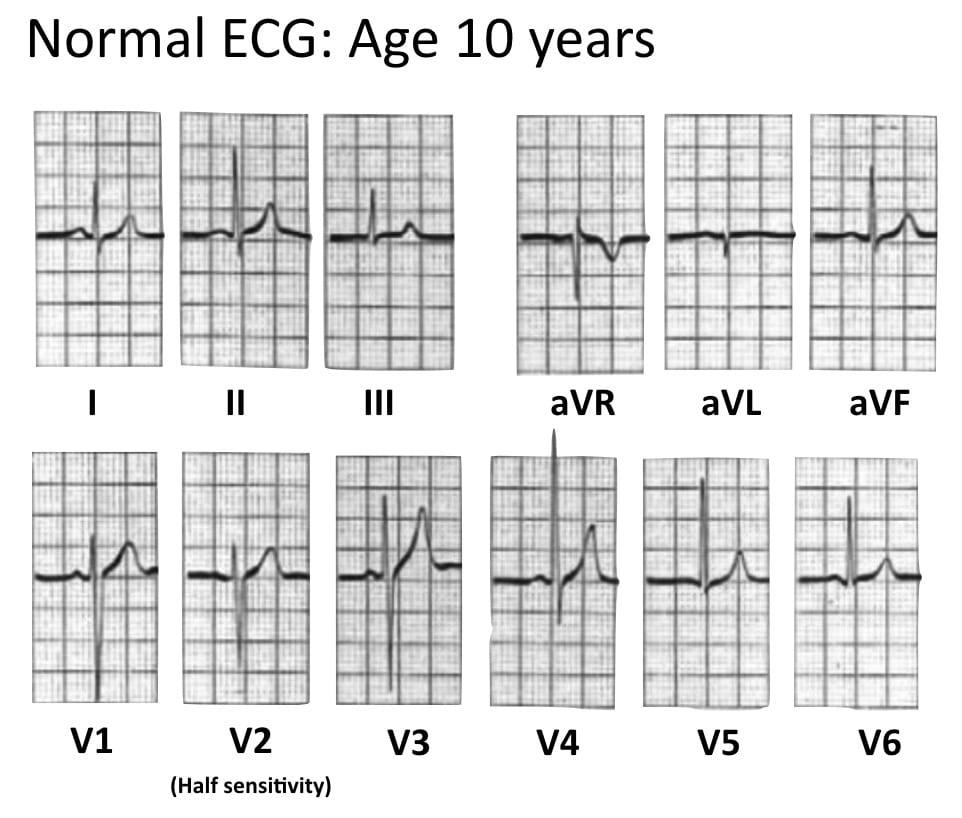
Paediatric ECG Interpretation • LITFL • ECG Library Basics

Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Persistent Juvenile Twave Pattern

The Twave physiology, variants and ECG features EKG & ECHO
It Is Named Because It Resembles The Normal Child's Ecg [62, 63].
The Types Of Abnormalities Are Varied And Include Subtle Straightening Of The St.
Web Aurora Seen In Atlanta Area Around 10:30 P.m.
It Is Characterized By Twi In The Right Precordium, And Has Been Understood To Represent An Arrested Stage Of The Normal Electrocardiographic Evolution.
Related Post: