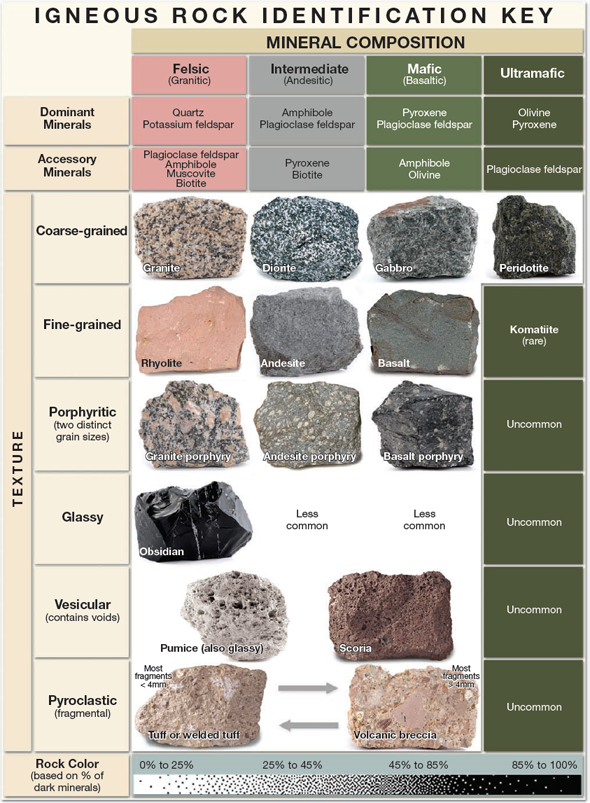
Igneous Identification Chart
Igneous Identification Chart - Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web igneous rocks can be divided into four categories based on their chemical composition: Magma is generated through the partial. Let’s put your identification skills to the test by assigning names to each of the rock samples! Web to identify an igneous rock, first determine its approximate mineral composition by judging its overall color and labeling it as felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. Web igneous rocks identification chart. Web learn more about the major types of igneous rock, which includes plutonic, intrusive, and extrusive igneous rocks. Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Please note that you can expand this image to fill the screen by clicking on the blue arrows on the right side of the diagram. These groups refer to differing amounts of silica, iron, and magnesium found in the minerals that make up the rocks. Obsidian is an example of an extrusive igneous rock that is amorphous or lacks crystalline structure. Finally, compare the properties of your rock to those of known rock types while looking for other identifying characteristics. There are a few types. Web the color of an igneous rock is related to the colors of the minerals present. Web as you know from our study of igneous rocks, if you know the rock, you know the past environment! The diagram of bowen’s reaction series ( figure 4.6) shows that differences in chemical composition correspond to differences in the types of minerals within. Andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria, and tuff. Students shared 24 documents in this course. It has a composition that is intermediate between rhyolite and andesite. To help you make your final determinations, consult this short guide on each of the 10 igneous rocks: [2] magma is molten rock that flows beneath the earth's surface. Let’s put your identification skills to the test by assigning names to each of the rock samples! Greater detail comes from estimating or measuring the percentage of different minerals found in a rock specimen. Web an igneous rock can be represented as a vertical line drawn through the top box of the diagram, and the vertical scale—with the distance between. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. The formation of igneous rocks involves several stages: Next, observe its texture based on the crystal grain sizes. Web to identify an igneous rock, first determine its approximate mineral composition by judging its overall color and labeling it as felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. Earth is composed predominantly of a large mass of igneous rock with a very thin veneer of weathered material—namely, sedimentary rock. Get examples and identification tips. Students shared 24 documents in this course. Magma. Get examples and identification tips. Web to identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Consider the arrows in the mafic field of the diagram. Web the color of an igneous rock is related to the colors of the minerals present. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. Web for igneous rock, the composition is divided into four groups: Web the color of an igneous rock is related to the colors of the minerals present. Web a colour diagram showing the mineral breakdown of common igneous rocks, including photographs of the common types of rocks in each of the compositional categories (i.e., ultramafic, mafic, intermediate, felsic). Felsic, intermediate,. Get examples and identification tips. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. Igneous rocks are formed by cooling magma. Web using the chart below, you can easily identify most of the igneous rocks you find. Earth is composed predominantly of a large mass of igneous rock with a very thin veneer of weathered material—namely, sedimentary rock. Students shared 24 documents in this course. To help you make your final determinations, consult this short guide on each of the 10 igneous rocks: Web igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. It has a composition that is. Web an igneous rock can be represented as a vertical line drawn through the top box of the diagram, and the vertical scale—with the distance between each tick mark representing 10% of the minerals within a rock by volume—is used to break down the proportion of each mineral it contains. Web examples include basalt, rhyolite, and andesite. Match the name to the rock: To help you make your final determinations, consult this short guide on each of the 10 igneous rocks: Using your senses and the scheme for sedimentary rock identification, you will be able to first classify and identify the rocks and their environments of formation. Igneous rocks are typically hard and dense, resistant to weathering, and often exhibit a crystalline structure. The formation of igneous rocks involves several stages: Classify igneous rocks into two main types: Web to identify an igneous rock, first determine its approximate mineral composition by judging its overall color and labeling it as felsic, intermediate, mafic, or ultramafic. Properties and characteristics of igneous rocks. Identification and characteristics of each igneous rock contained with. Drag the rock name to the correct rock. In plutonic rocks, all of the minerals are crystallized into visible grains. Felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic. It has a composition that is intermediate between rhyolite and andesite. Earth science activities (gol 406) 24documents.
Igneous Rock Identification Chart

General Classification of Igneous Rocks
Rock Key, Selection, and Splitting Trailism

Igneous Rock Identification Chart
Igneous Rock ID Chart

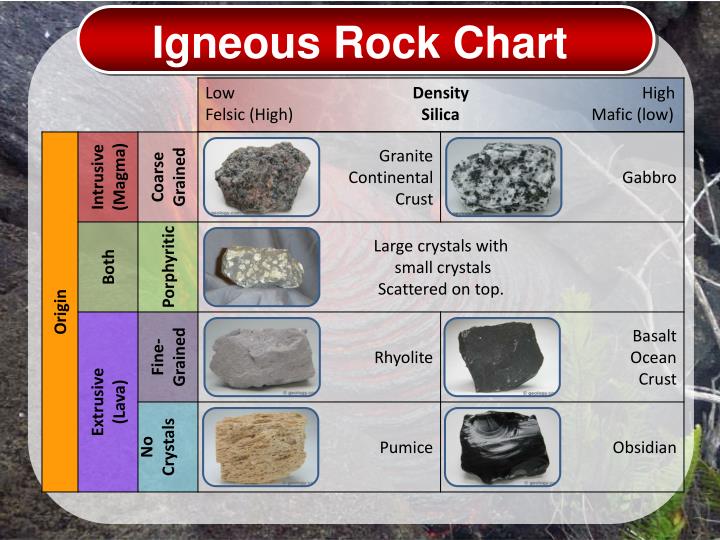
Igneous Rock Chart
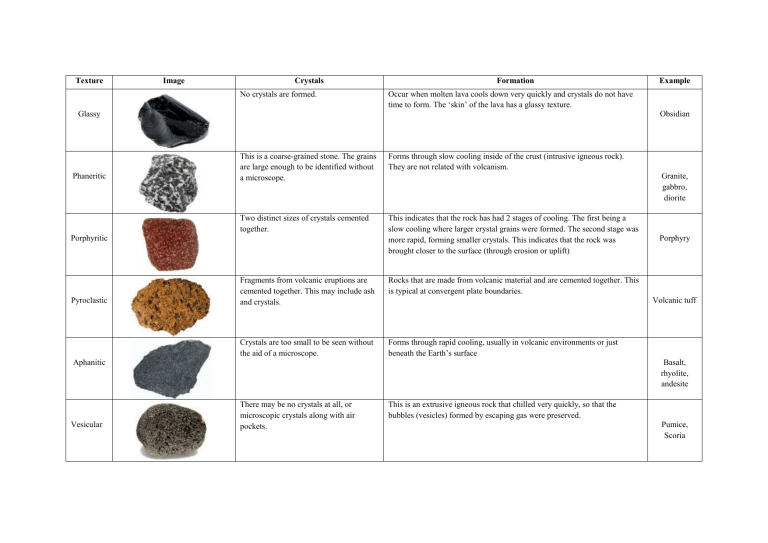
Igneous Rocks Texture Types

Igneous Rock Classification Chart Geology Igneous rock, Earth

Igneous Rock Identification Chart
[Solved] igneous rock identification chart Course Hero
Felsic, Intermediate, Mafic, And Ultramafic.
Let’s Put Your Identification Skills To The Test By Assigning Names To Each Of The Rock Samples!
Next, Observe Its Texture Based On The Crystal Grain Sizes Present In The Rock.
Web 5 Igneous Rock Identification.
Related Post: