Glycolysis Inputs And Outputs Chart
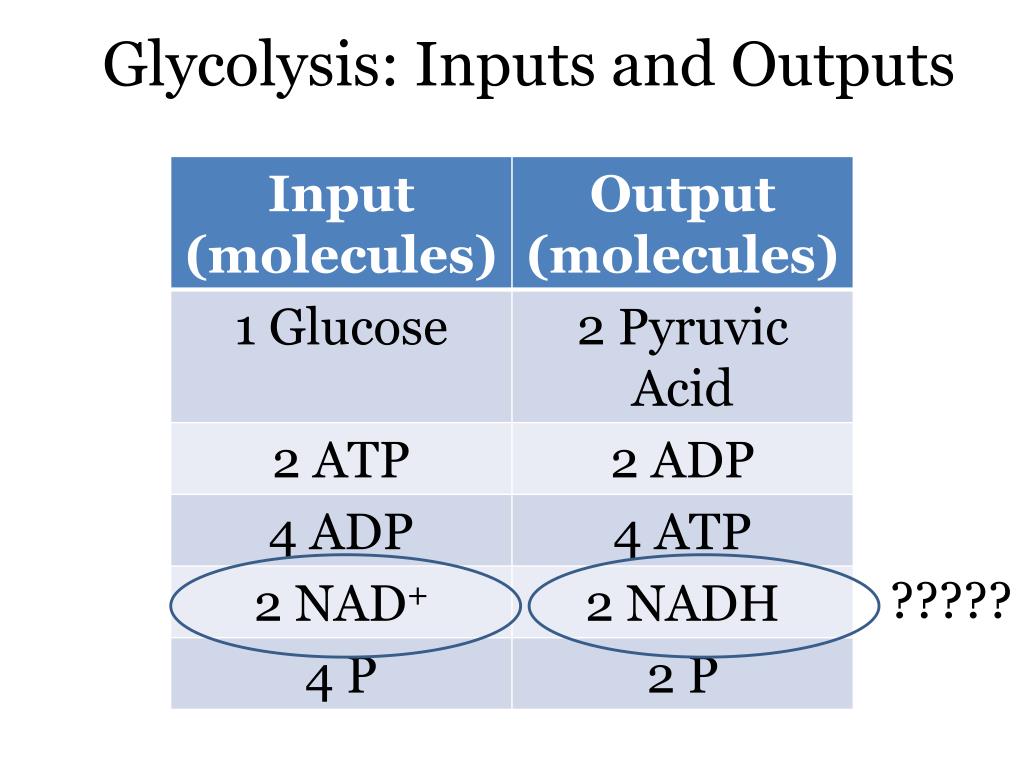
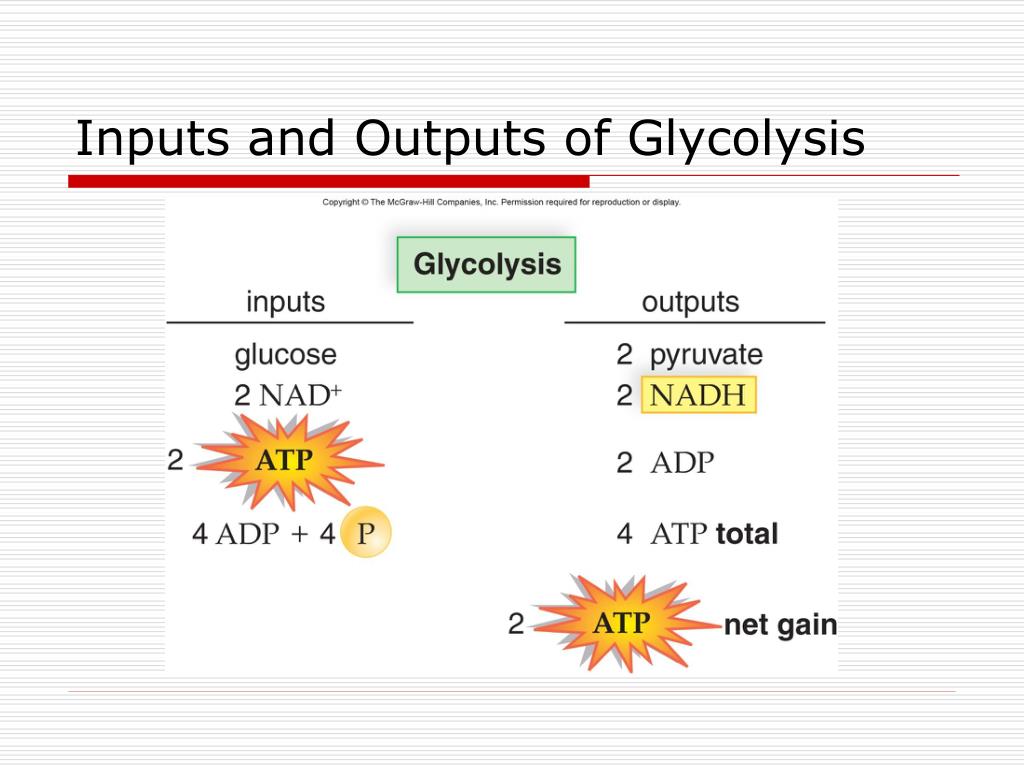
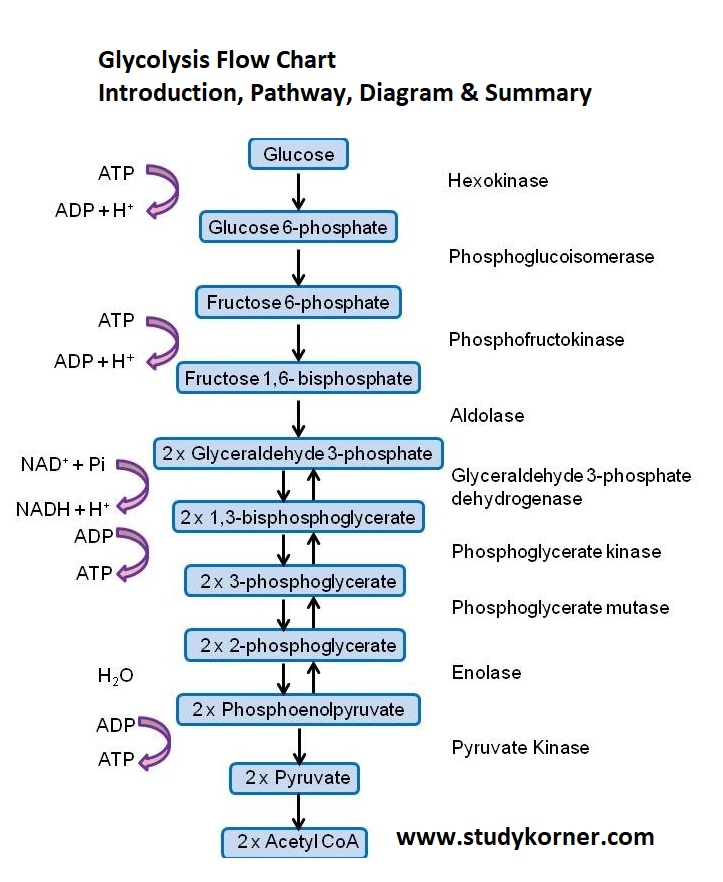
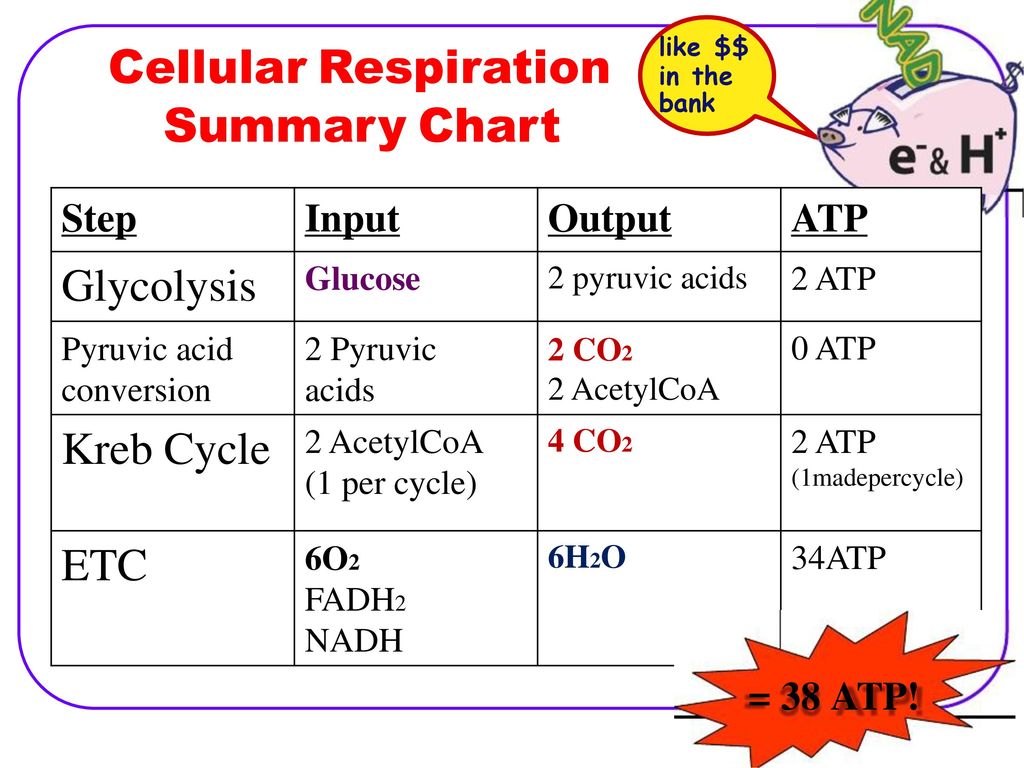
Glycolysis Inputs And Outputs Chart - Much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. • glycogen and starch are polysaccharides that feed into glycolysis by enzymes that break them down. The structures of glycolysis intermediates can be found in the following diagram: • glycolysis occurs in the cytosol. Web steps of cellular respiration. Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). Web describe the overall result in terms of molecules produced in the breakdown of glucose by glycolysis. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: The measurements of the energy at standard state (δg°'/ (kj/mol)) compared with measurements taken from a living cell (δg/ (kj/mol)). Web in the image below, you can see the outputs of glycolysis. You have read that nearly all of the energy used by living cells comes to them in the bonds of the sugar, glucose. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water. • the net reaction for glycolysis is: Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in most. It occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen to enable aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Reactions will occur in the direction that leads to a decrease in the value of the gibbs free energy. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water. Web let's explore the process of glycolysis, the first phase of cellular respiration. Web this. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: 4 atp are generated (two of which will fuel another round of glycolysis), and 2 molecules of pyruvate (c 3 h 4 o 3) and 2 nadh are ready to move to the next stage of aerobic cellular respiration. Reactions. “glycolysis is the metabolic process that converts glucose into pyruvic acid.” what is glycolysis? Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Web this table shows glycolytic enzymes and measurements of the energy at standard state (δg°'/(kj/mol)) compared with measurements taken from a living cell (δg/(kj/mol)). • the net reaction for glycolysis. • the net reaction for glycolysis is: 3.7 (3 reviews) get a hint. The structures of glycolysis intermediates can be found in the following diagram: Or lactate under anaerobic conditions along with the production of a small amount of energy. Web during glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water. Compare the output of glycolysis in terms of atp molecules and nadh molecules produced. The process takes place in the. Glycolysis starts with one molecule of glucose and ends with two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules, a total of four atp molecules, and two molecules of nadh. This is the primary step in cellular respiration. Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces two pyruvate molecules, four new atp molecules, and two molecules of nadh. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms. • the net reaction for glycolysis is: Web describe the overall result in terms of molecules produced in the breakdown of glucose by glycolysis. The structures of glycolysis intermediates can be found in the following diagram: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like input 1, input 2, input 3 and more. The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose. It occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen to enable aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway involving 10 steps where there is the conversion of glucose into lactic acid. • the net reaction for glycolysis is: Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in. Much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Web during glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; Compare the output of glycolysis in terms of atp molecules and nadh molecules produced. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. Under conditions of constant temperature and pressure,. Web compare the output of glycolysis in terms of atp molecules and nadh molecules produced. Web during glycolysis, glucose ultimately breaks down into pyruvate and energy; Glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. Glucose + 2nad + + 2pi + 2adp → 2 pyruvate + 2atp + 2nadh + 2h 2 o. Web this table shows glycolytic enzymes and measurements of the energy at standard state (δg°'/(kj/mol)) compared with measurements taken from a living cell (δg/(kj/mol)). Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: This is the primary step in cellular respiration. The cytoplasm is the place where glycolysis occurs in every living organism. Glycolysis begins with glucose and produces two pyruvate molecules, four new atp molecules, and two molecules of nadh. Web in the image below, you can see the outputs of glycolysis. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water. • glycolysis occurs in the cytosol. Web glycolysis involves 10 reactions that take place in the cytosol and generates two atp molecules without the requirement of molecular oxygen. 3.7 (3 reviews) get a hint. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. It occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen to enable aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration.
Glucose Metabolism Energy Yield Biochemistry Flashcards ditki

What are the input and output of glycolysis?
[Solved] Glycolysis Input and Output Input (Reactants) Output
PPT Sept. 20 , 2013 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2204337
PPT Chapter 8 Cellular Respiration (Outline) PowerPoint Presentation
Glycolysis Flow Chart Introduction Pathway Diagram & Summary StudyPK
Inputs And Outputs Of Glycolysis In Cellular Respiration slidesharedocs
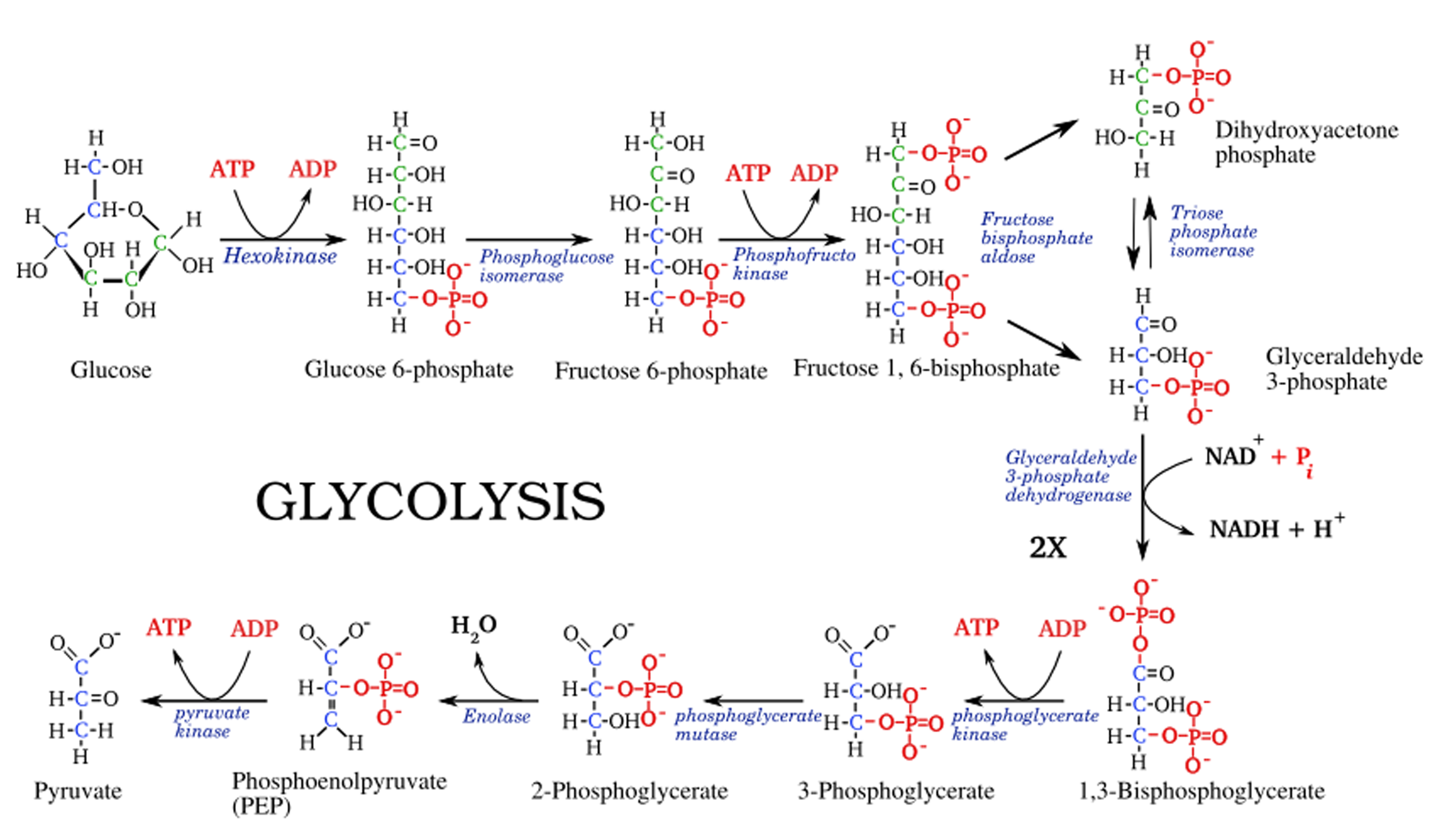
Glycolysis Online Biology Notes

Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Food Science Toolbox
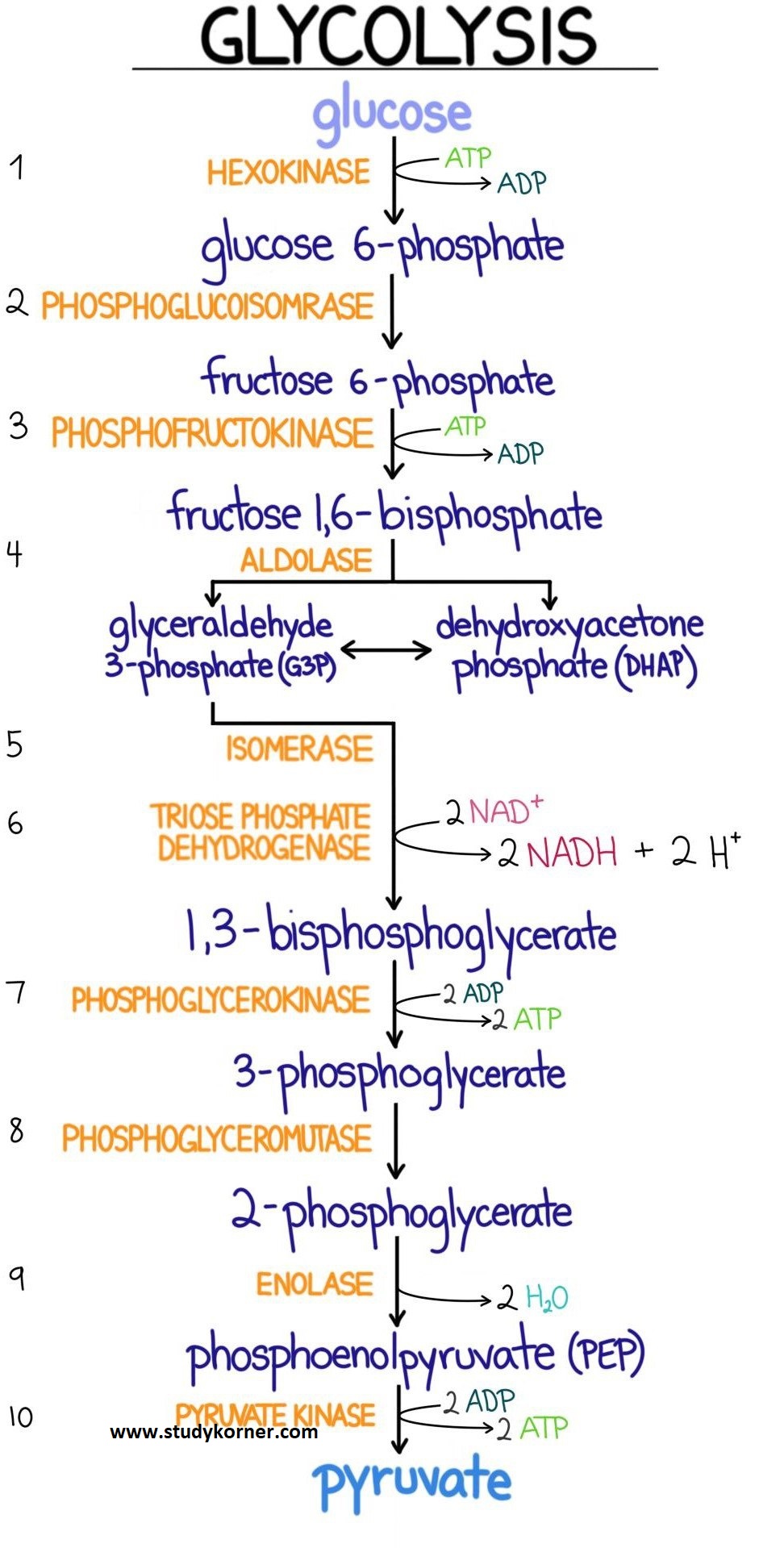
Glycolysis Flow Chart Introduction Pathway Diagram & Summary StudyPK
• The Following Compounds Inhibit Glycolysis:
Compare The Output Of Glycolysis In Terms Of Atp Molecules And Nadh Molecules Produced.
The Corresponding Anabolic Pathway By Which Glucose Is Synthesized Is Termed Gluconeogenesis.
You Have Read That Nearly All Of The Energy Used By Living Cells Comes To Them In The Bonds Of The Sugar, Glucose.
Related Post: