Fructosamine To Hba1C Chart
Fructosamine To Hba1C Chart - Web in patients with diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin (hba1c) and plasma glucose (random or fasting) are typically utilized in monitoring patient response. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: Measurement of the levels of glycated protein, such as fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin (hba1c), is the most reliable method for assessing a period of glycemic control. Overall, the hba1c test showed the best agreement with the clinical assessment when diabetes control was considered either acceptable or unacceptable, although the strength of agreement was considered fair (kappa = 0.27). Fructosamine is the product of the nonenzymatic glycation of protein (glucose bound to protein). If you are like me and get the fructosamin tests instead of the more commonly done hba1c, because for some of us, hba1c measurement is not a reliable marker of glycaemic control in diabetics with any condition associated with shortened red blood cell life span, worry not. Web the fructosamine and a1c tests for diabetes both measure blood sugar. Hba1c measurement is not a reliable marker of glycaemic control in diabetics with condition associated with shortened red. Hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61. This correlation is strengthened when the fructosamine level takes into account the serum albumin concentration [2]. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. Fructosamine is the product of the nonenzymatic glycation of protein (glucose bound to protein). Measurement of the levels of glycated protein, such as fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin (hba1c), is the most reliable method for assessing a period of glycemic control. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated. The fructosamine level was useful for the prompt evaluation of the recent therapeutic efficacy after the change in therapeutic modality. Web fructosamine and hba1c results from each dog showed a moderate correlation. Results from capillary blood glucose tests show glucose levels at a specific time and can be taken multiple times during a day. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. Overall, the hba1c test showed the best agreement with the clinical assessment when diabetes control was considered either acceptable or unacceptable, although the strength of agreement was considered fair (kappa = 0.27). Web in patients with diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin (hba1c) and plasma glucose (random. Web the fructosamine and a1c tests for diabetes both measure blood sugar. Hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61. Fructosamine is the product of the nonenzymatic glycation of protein (glucose bound to protein). Consider in patients with patient visits less than one month apart. Measurement of the levels of glycated protein, such as fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin (hba1c),. Results from capillary blood glucose tests show glucose levels at a specific time and can be taken multiple times during a day. The fructosamine level was useful for the prompt evaluation of the recent therapeutic efficacy after the change in therapeutic modality. We termed this the glycosylation gap (gg) and sought to determine its relationship to diabetic nephropathy. Comparison of. It should be seen as an umbrella term for circulating proteins that have undergone glycation. Measurement of the levels of glycated protein, such as fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin (hba1c), is the most reliable method for assessing a period of glycemic control. Web the level of fructosamine correlates well with fasting glucose and with hemoglobin a1c levels [1]. This correlation is. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. Web the fructosamine and a1c tests for diabetes both measure blood sugar. The fructosamine level was useful for the prompt evaluation of the recent therapeutic efficacy after the change in therapeutic modality. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: The fructosamine level was useful for the prompt evaluation of the recent therapeutic efficacy after the change in therapeutic modality. Overall, the hba1c test showed the best agreement with the clinical assessment when diabetes control was considered either acceptable or unacceptable, although the strength. Web in patients with diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin (hba1c) and plasma glucose (random or fasting) are typically utilized in monitoring patient response. Each 75 mol change equals a change of approximately 60 mg/dl blood sugar or 2% hba1c. The fructosamine level was useful for the prompt evaluation of the recent therapeutic efficacy after the change in therapeutic modality. Fructosamine has. Their hba1c levels showed a strong correlation with their fructosamine levels ( r =0.868, p <0.001). Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: Web we developed a measure of discordance between hba 1c and fructosamine (fa). It should be seen as an umbrella term for circulating proteins that have undergone glycation. Each 75 mol change equals a change of approximately 60 mg/dl blood sugar or 2% hba1c. Web the fructosamine and a1c tests for diabetes both measure blood sugar. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: Consider in patients with patient visits less than one month apart. Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: Web hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61 (hba1c is in dcct% terms) reference: Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. We termed this the glycosylation gap (gg) and sought to determine its relationship to diabetic nephropathy. Measurement of the levels of glycated protein, such as fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin (hba1c), is the most reliable method for assessing a period of glycemic control. Results from capillary blood glucose tests show glucose levels at a specific time and can be taken multiple times during a day. Comparison of fructosamine with glycated hemoglobin as an index of glycemic control in diabetic patients. Fructosamine has not gained as much popularity as glycated haemoglobin (hba1c) for diabetes mellitus (dm) control monitoring, and the related underlying reasons remain unclear. The clinical information value of the glycosylated hemoglobin assay. Hba1c = 0.017 x fructosamine level (µmol/l) + 1.61. Web in patients with diabetes mellitus, glycated hemoglobin (hba1c) and plasma glucose (random or fasting) are typically utilized in monitoring patient response.
HbA1c Conversion Chart Printable
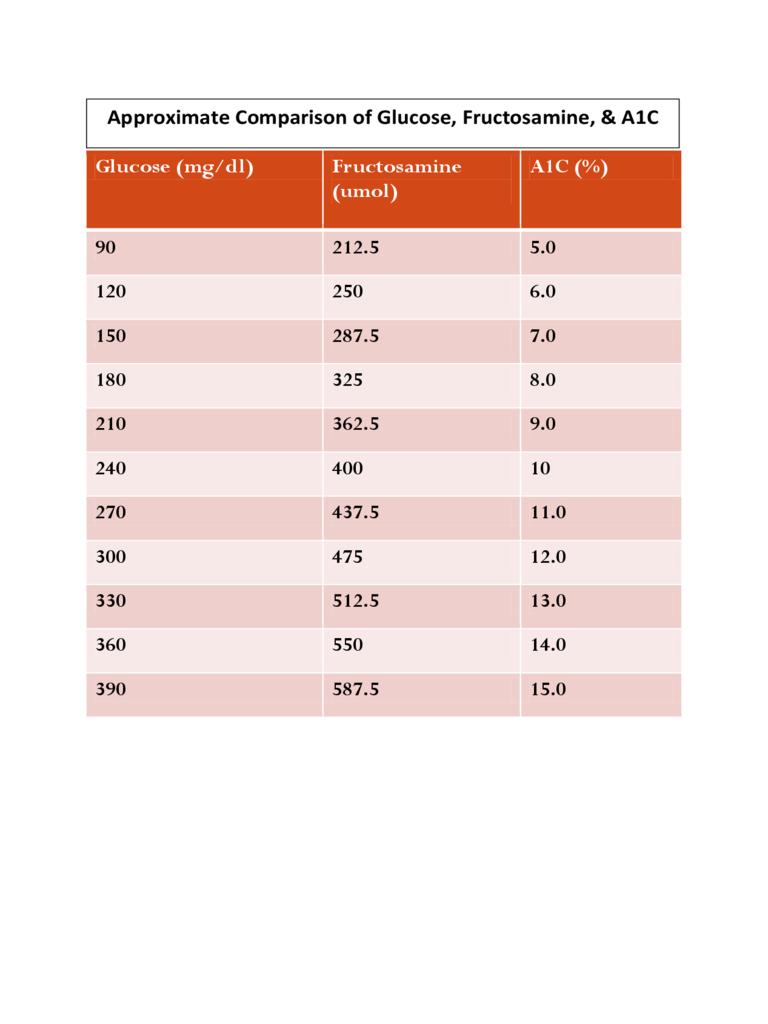
Fructosamine To Hba1c Conversion Chart Conversion Chart and Table Online
![Easy HbA1c Conversion Chart [Free PDF] The Geriatric Dietitian](https://thegeriatricdietitian.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Copy-of-Copy-of-PDF-Conversion-Chart-2-1-1536x1187.jpg)
Easy HbA1c Conversion Chart [Free PDF] The Geriatric Dietitian

HbA1c, fructosamine, and the remaining laboratory parameters for the

Table 2 from Comparative Evaluation of Fructosamine and HbA1c as a

Fructosamine To Hba1c Conversion Chart

The blood glucose, fructosamine, HbA1c, and the of the current

Fructosamine To Hba1c Conversion Chart
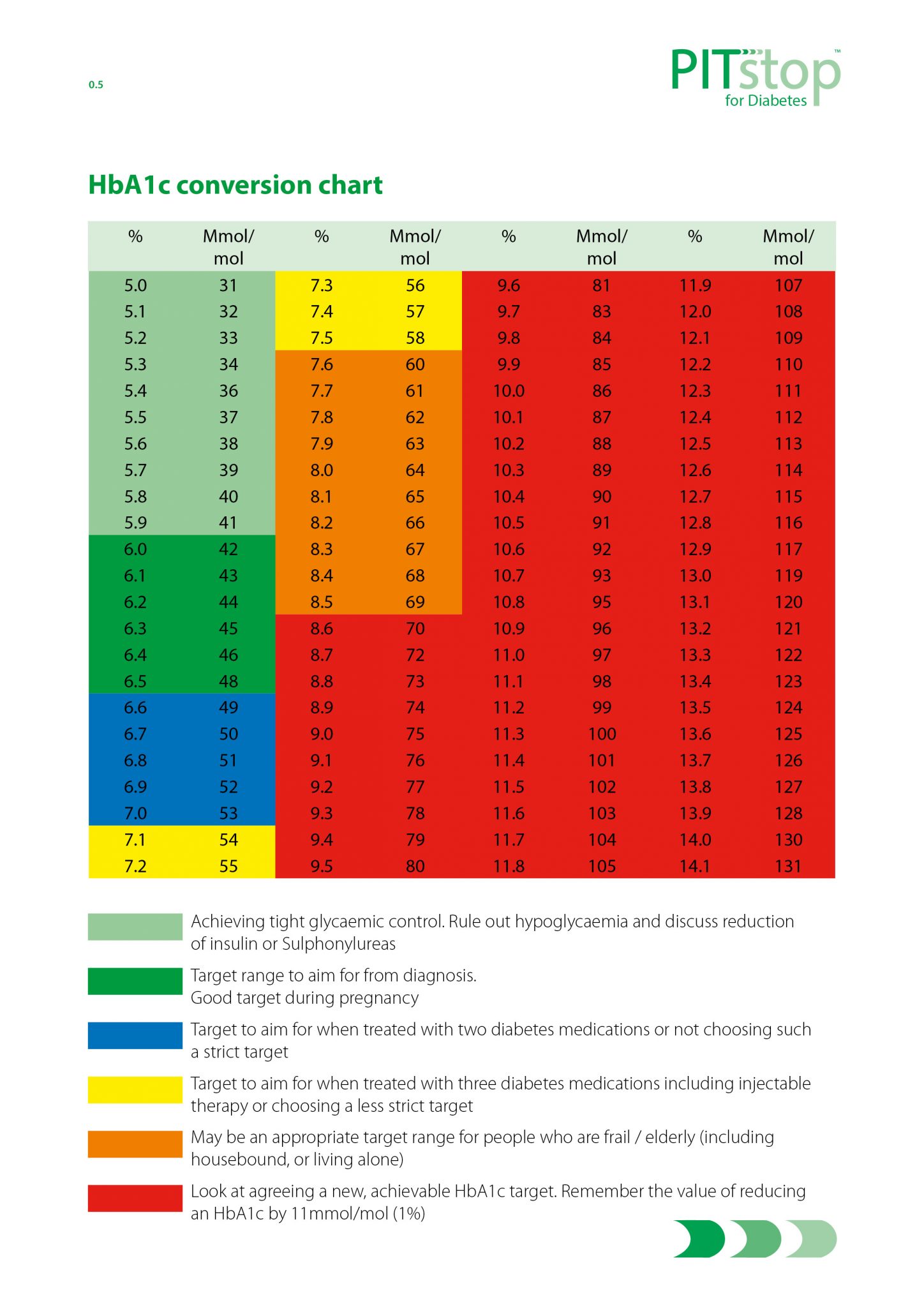
HbA1c chart Pitstop Diabetes

HbA1c Conversion Chart iPAG Scotland
Comparison Of Fructosamine With Glycated Hemoglobin As An Index Of Glycemic Control In Diabetic Patients.
Their Hba1C Levels Showed A Strong Correlation With Their Fructosamine Levels ( R =0.868, P <0.001).
Overall, The Hba1C Test Showed The Best Agreement With The Clinical Assessment When Diabetes Control Was Considered Either Acceptable Or Unacceptable, Although The Strength Of Agreement Was Considered Fair (Kappa = 0.27).
Hba1C Measurement Is Not A Reliable Marker Of Glycaemic Control In Diabetics With Condition Associated With Shortened Red.
Related Post: