Frieze Pattern
Frieze Pattern - Copy the graph and draw the figures needed to complete the pattern. A frieze is formed by the repetition of a basic motif or pictorial element in one direction. Explain why a frieze pattern can have only 180° rotations. In celtic art and design, border. At the end of this video, y. According to conway, f 2 is called a step. Frieze, in classical architecture, the middle of the three main divisions of an entablature (q.v.; All frieze patterns have translation symmetry. In elementary school, we mostly work on identifying the transformations in a geometric pattern and in figuring out how to continue a pattern. The repeating patterns may have rotational, reflectional, or glide reflectional symmetry. Web all frieze patterns have a section of the pattern which is repeated alongside itself (we call this a translation). At the end of this video, y. A translation or slide involves moving a figure in a specific direction for a specific distance. Some sections contain a person or a symmetric design. In distinguishing one frieze pattern from another we. Frieze, in classical architecture, the middle of the three main divisions of an entablature (q.v.; A frieze is called closed if it is also bounded from below by a line of 1’s (followed by a line of 0’s). Moment that the basic element is repeated just 3 times. According to conway, f 1 is also called a hop. However, they. Web a frieze is a grid of numbers bounded from above by an in nite row of 0’s, followed by a row of 1’s and satisfying the frieze rule (1). The third frieze group, f 3, contains translation and vertical reflection. Web a frieze is a decorative pattern made from repeated copies of a basic element arranged in a. Web. Achaemenid lotus and palmette scroll. The set of symmetries of a frieze pattern. Web the frieze patterns of ancient doric buildings are located between the cornice and the architrave, as shown below. A frieze is called closed if it is also bounded from below by a line of 1’s (followed by a line of 0’s). The second frieze group, f. Web a frieze is a decorative pattern made from repeated copies of a basic element arranged in a. Frieze patterns # this implements the original frieze patterns due to conway and coxeter. Translation symmetry and frieze patterns. According to conway, f 1 is also called a hop. Web mathematician john conway created names that relate to footsteps for each of. (see frieze.) frieze patterns can be classified into seven types according to their symmetries. Moment that the basic element is repeated just 3 times. This video provides on overview go how frieze patterns are constructed,. The rigid motions combine to create 7 distinct classifications of frieze patterns. In general, a frieze consists of repeated copies of a single motif. Web 7.6 frieze patterns 443 using the coordinate plane the figure shown in the coordinate plane is part of a frieze pattern with the given classification. In a frieze pattern with a glide reflection, explain why the glide reflection is always half the length of the shortest translation. Moment that the basic element is repeated just 3 times. According to. In distinguishing one frieze pattern from another we first need to find the smallest translation length in the strip. (see frieze.) frieze patterns can be classified into seven types according to their symmetries. Other sections have simple patterns of three or four vertical lines. This video provides on overview go how frieze patterns are constructed,. Make sure class is clear. A frieze is called closed if it is also bounded from below by a line of 1’s (followed by a line of 0’s). Explain why a frieze pattern can have only 180° rotations. In celtic art and design, border. Web begin learning about frieze patterns with: Web ancient greek frieze patterns. Other sections have simple patterns of three or four vertical lines. According to conway, f 1 is also called a hop. Achaemenid lotus and palmette scroll. This defines the 'cell' which is the smallest piece of the pattern to be repeated by translations. The rigid motions combine to create 7 distinct classifications of frieze patterns. In general, a frieze consists of repeated copies of a single motif. A frieze is formed by the repetition of a basic motif or pictorial element in one direction. They have been employed by essentially all human cultures to create ornamentations on buildings, textiles, metalwork, ceramics, etc. Translation symmetry and frieze patterns. Web border patterns or friezes are one type of decorative art. The second frieze group, f 2, contains translation and glide reflection symmetries. Web friezes are two‐dimensional patterns that are repetitive in one dimension. Web a frieze, or strip pattern, is a repeating pattern with translation symmetry in one direction. The frieze patterns consist of alternating sections. Copy the graph and draw the figures needed to complete the pattern. All frieze patterns have translation symmetry. To see our examples of the 7 frieze patterns, click here. A translation or slide involves moving a figure in a specific direction for a specific distance. Explain why a frieze pattern can have only 180° rotations. According to conway, f 1 is also called a hop. Such a frieze pattern is considered as a sequence of nonnegative integers following [coco1] and [coco2] using sage.combinat.path_tableaux.path_tableau.
Frieze Pattern Definition, History & Groups Lesson

Frieze Patterns at the Ashmolean Museum TOM ROCKS MATHS

Fun with Mathematics Symmetry in Art and Nature ( Part 2 of 3
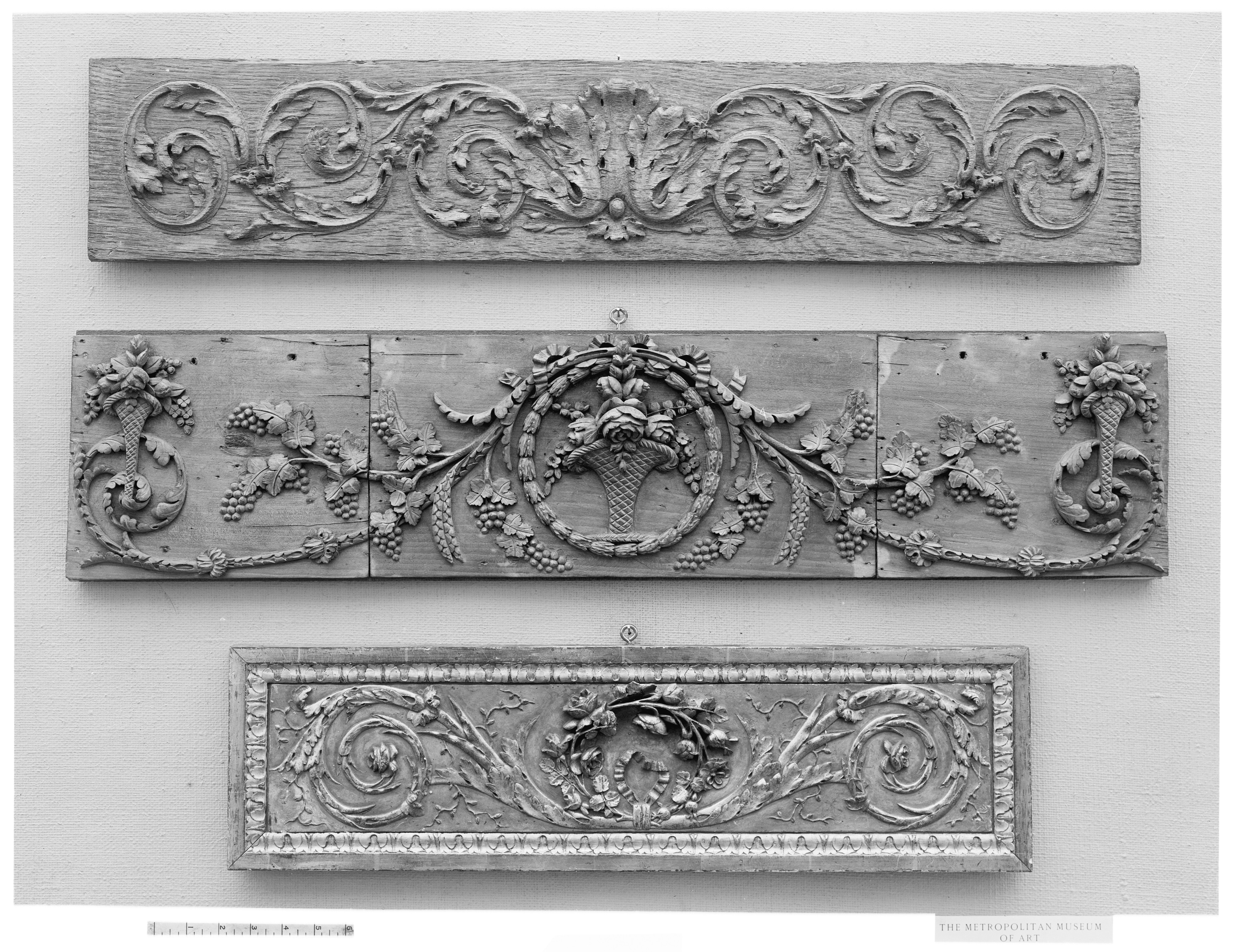

Panel or frieze French The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Floral frieze design CRAFTSMANSPACE

Curved frieze patterns CRAFTSMANSPACE
Interlaced frieze patterns CRAFTSMANSPACE

Ancient frieze patterns Craftsmanspace
Collection of Indian frieze patterns CRAFTSMANSPACE
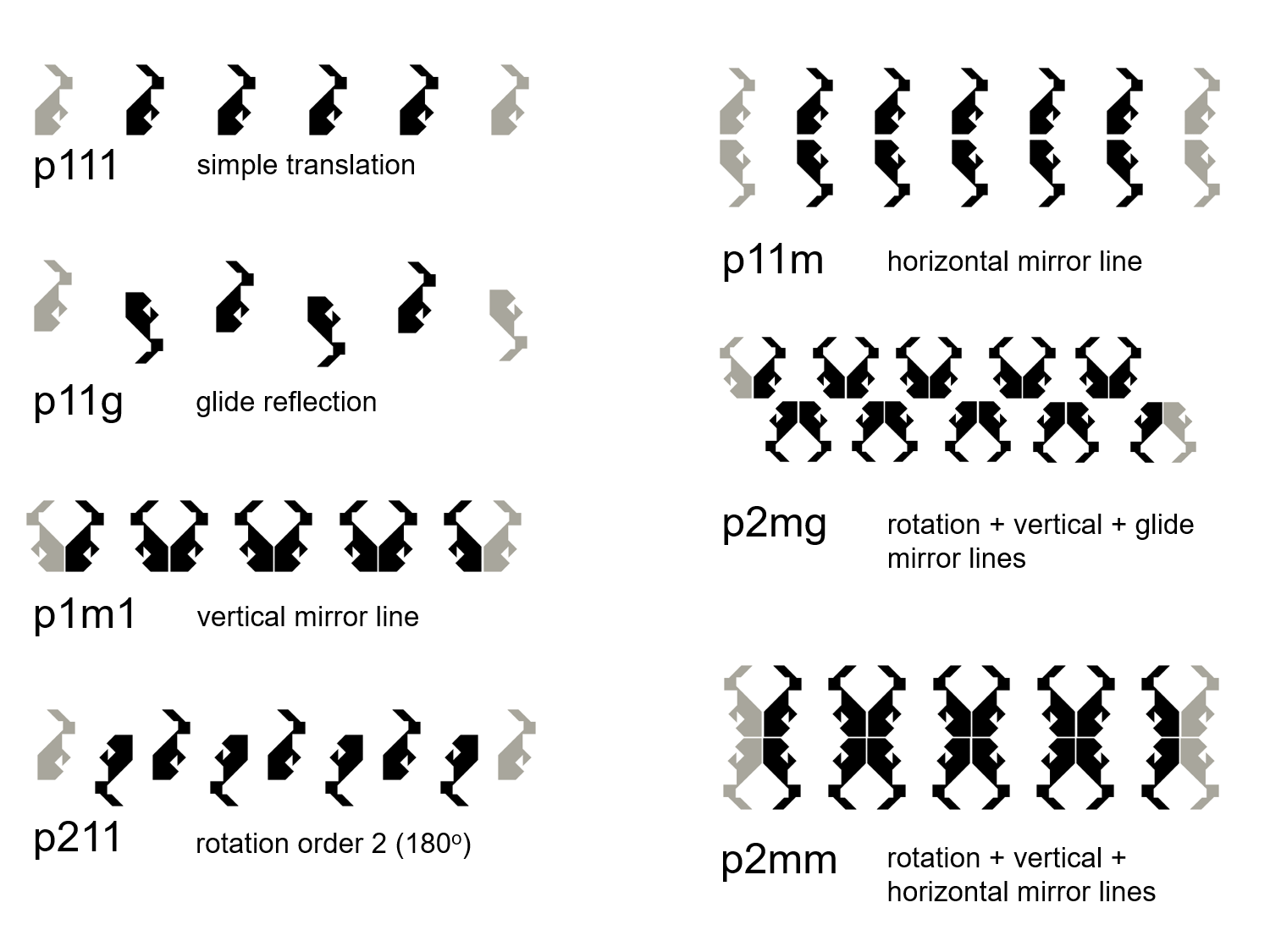
MEDIAN Don Steward mathematics teaching frieze patterns
Translation Symmetry And Frieze Patterns (60 Minutes) Session 7, Part C.
What Frieze Symmetry Group Do.
In Celtic Art And Design, Border.
Conway And Guy (1996) Define A Frieze Pattern As An Arrangement Of Numbers At The Intersection Of Two Sets Of Perpendicular Diagonals Such That (For An Additive Frieze Pattern) Or (For A Multiplicative Frieze Pattern) In Each Diamond.
Related Post: