Flow Chart Of Pcr
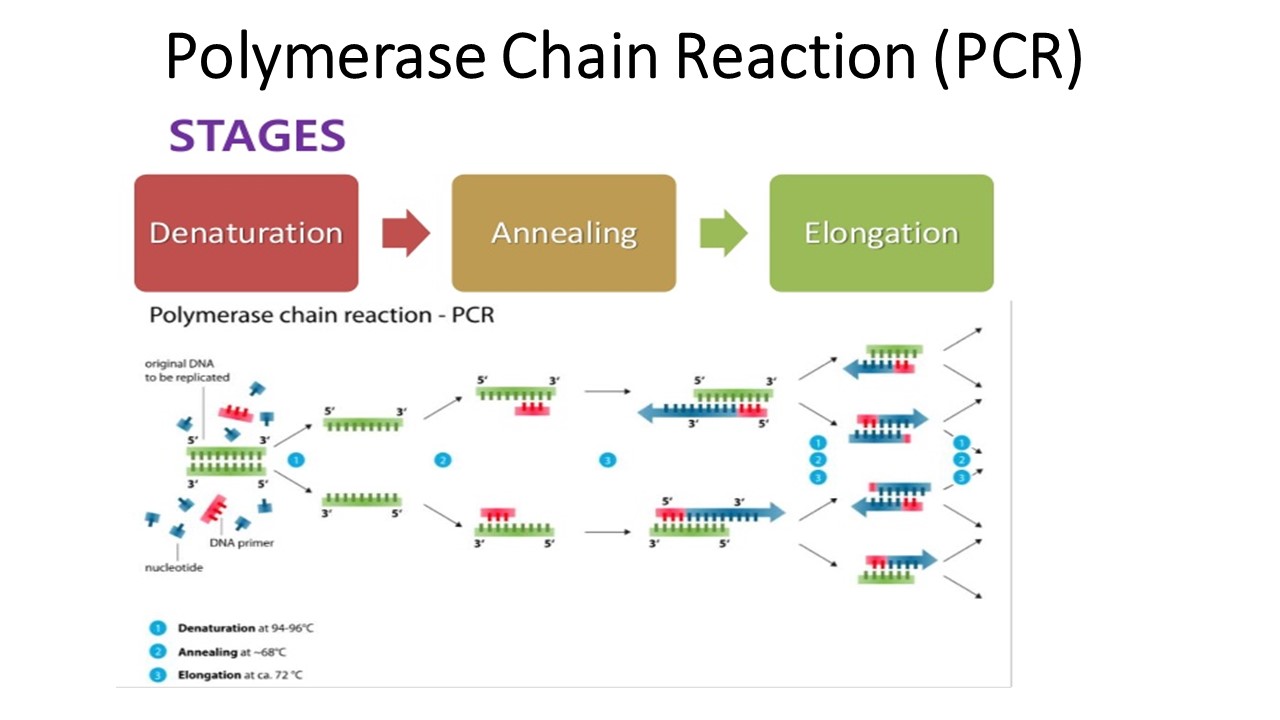
Flow Chart Of Pcr - A pcr test amplifies dna sequences. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) or ribonucleic acid (rna) sequences using dna polymerase i enzyme, an isolate from thermus aquaticus, known as taq dna. Web polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a powerful method for amplifying particular segments of dna, distinct from cloning and propagation within the host cell. Web pcr is an enzymatic process in which a specific region of dna is replicated over and over again to yield many copies of a particular sequence. The temperature is raised to 72 degree celsius for one to several minutes. In just a few hours, pcr can create a million copies of a si. This procedure is carried out entirely biochemically, that is, in vitro. Web how does the test work? In cases of pooling, repeat processing for individual samples occurs if pooling outcome is positive. Pcr was invented by kary mullis in 1983. It involves dna primers, dna bases, enzymes, a buffer solution, and thermal cycling to help replicate these sequences. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) can amplify a region of dna from any source, even from a single cell’s worth of dna or from fragments of dna obtained from a fossil. This procedure is carried out entirely biochemically, that is, in. He shared the nobel prize in chemistry with michael smith in 1993. Web 1.1 what qpcr is & how it works. Its principle is based on the use of dna polymerase which is an in vitro replication of specific dna sequences. Compared to other methodologies, pcr offers a higher level of sensitivity and specificity [2]. Pcr relies on a thermostable. Rna is isolated and cdna is generated via reverse transcription (rt); Web polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, is a technique to make many copies of a specific dna region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism). He shared the nobel prize in chemistry with michael smith in 1993. Its principle is based on the use of dna. The most widely used target nucleic acid amplification method is the polymerase chain reaction (pcr). Web polymerase chain reaction (pcr) underlies many molecular biology and molecular genetics techniques. Web polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a powerful method for amplifying particular segments of dna, distinct from cloning and propagation within the host cell. Its principle is based on the use of. Pcr is then carried out to amplify areas of interest. Web quantitative pcr is a central methodology in novel assay development. Web polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, is a technique to make many copies of a specific dna region in vitro (in a test tube rather than an organism). Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid. Pcr was invented by kary mullis in 1983. Quantitative pcr (qpcr) is one of the foremost methods for detection and quantification of nucleic acid targets. He shared the nobel prize in chemistry with michael smith in 1993. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid. In cases of pooling, repeat processing for individual samples occurs if pooling outcome is positive. Web polymerase chain reaction (pcr) underlies many molecular biology and molecular genetics techniques. Compared to other methodologies, pcr offers a higher level of sensitivity and specificity [2]. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature. Web polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a powerful method for amplifying particular segments of dna, distinct from cloning and propagation within the host cell. Web 1.1 what qpcr is & how it works. Labs must report results to the state of individual’s residence within 24 hours of test completion. Web the basic polymerase chain reaction (pcr) michael r. The most. The protocol implements multiple optimised and control steps including rna isolation, digestion. Quantitative pcr (qpcr) is one of the foremost methods for detection and quantification of nucleic acid targets. In cases of pooling, repeat processing for individual samples occurs if pooling outcome is positive. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) can amplify a region of dna from any source, even. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a laboratory nucleic acid amplification technique used to denature and renature short segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) or ribonucleic acid (rna) sequences using dna polymerase i enzyme, an isolate from thermus aquaticus, known as taq dna. Pcr relies on a thermostable dna polymerase, taq polymerase , and requires dna primers designed specifically for. Web quantitative pcr is a central methodology in novel assay development. Web five steps to optimal cdna synthesis. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) can amplify a region of dna from any source, even from a single cell’s worth of dna or from fragments of dna obtained from a fossil. This procedure is carried out entirely biochemically, that is, in vitro. Pcr relies on a thermostable dna polymerase, taq polymerase , and requires dna primers designed specifically for the dna region of interest. Quantitative pcr (qpcr) is one of the foremost methods for detection and quantification of nucleic acid targets. The polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a test tube system for dna replication which allows a “target” dna sequence to be selectively amplified several million folds in just a few hours. Its principle is based on the use of dna polymerase which is an in vitro replication of specific dna sequences. Compared to other methodologies, pcr offers a higher level of sensitivity and specificity [2]. It is the foundation for all subsequent variations of the polymerase chain reaction (pcr). He shared the nobel prize in chemistry with michael smith in 1993. Rna is isolated and cdna is generated via reverse transcription (rt); The protocol implements multiple optimised and control steps including rna isolation, digestion. The most widely used target nucleic acid amplification method is the polymerase chain reaction (pcr). Web 1.1 what qpcr is & how it works. Labs must report results to the state of individual’s residence within 24 hours of test completion.
Flowchart of an optimised protocol for qRTPCR in largescale
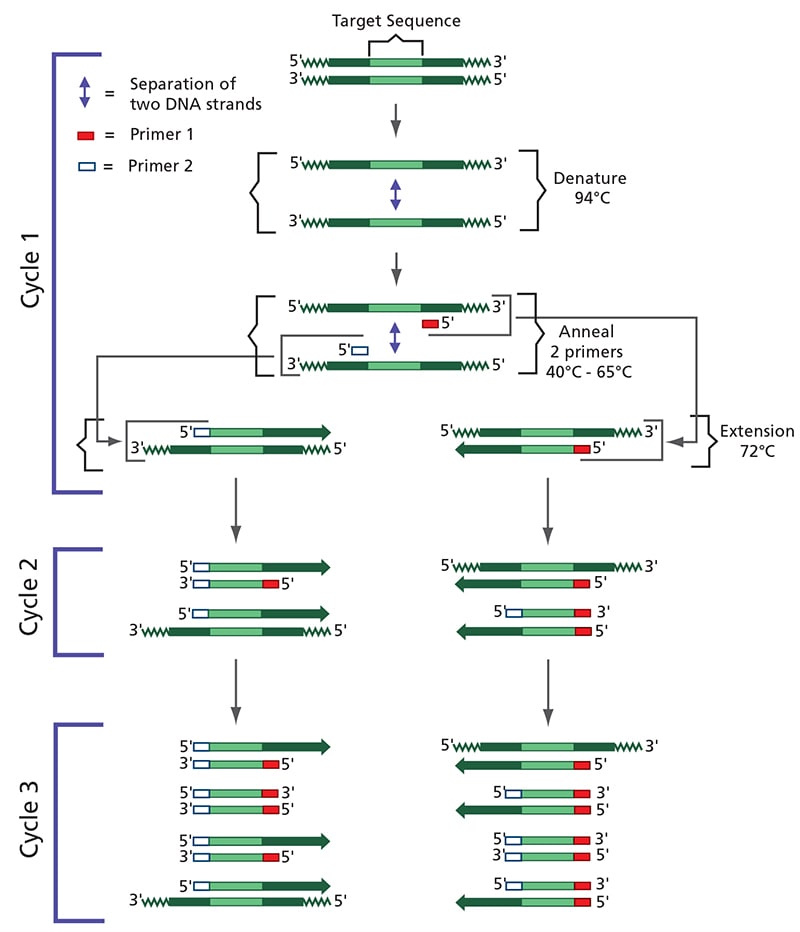
Quick Guide Polymerase Chain Reaction

PCR the Polymerase chain reaction Key points of PCR

Flow chart of PCR method for detection of GMO in foods. (adapted from
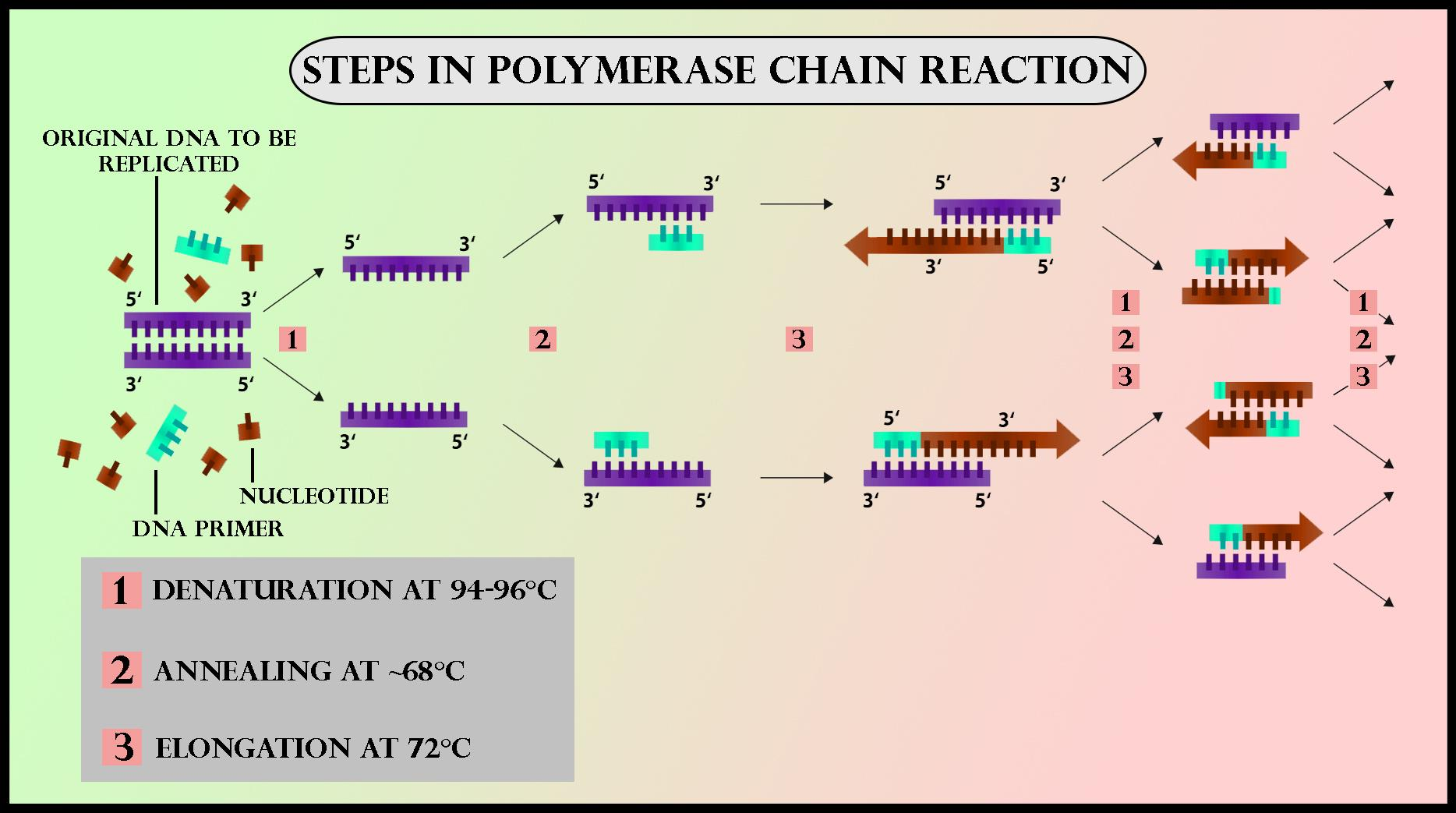
Draw a neat labelled diagram showing steps of PCR?
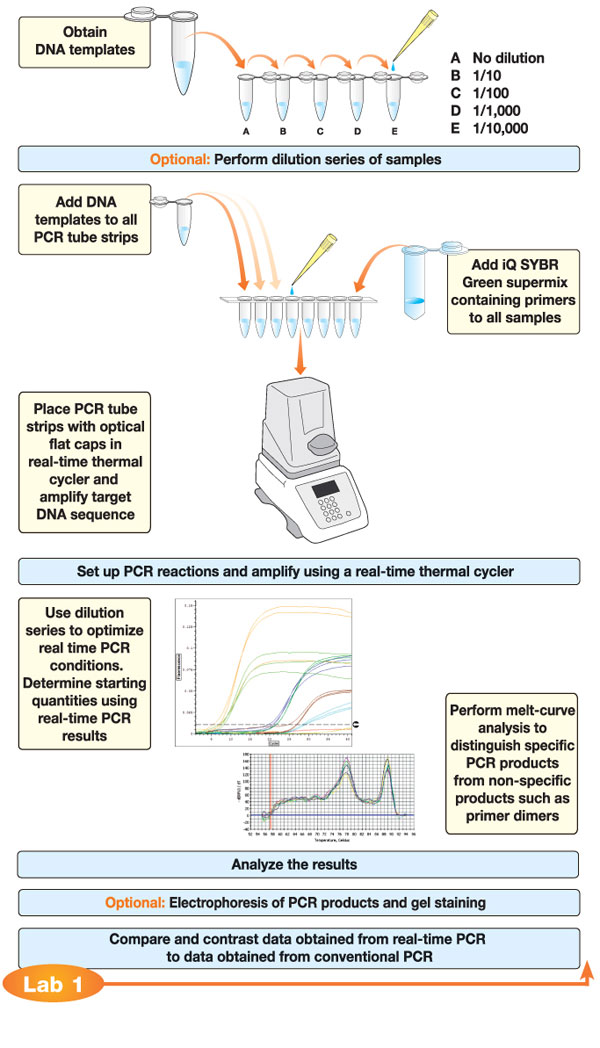
flow chart for real time PCR or quantitative PCR Biology units
pcr schematic diagram

PCR Flow Chart
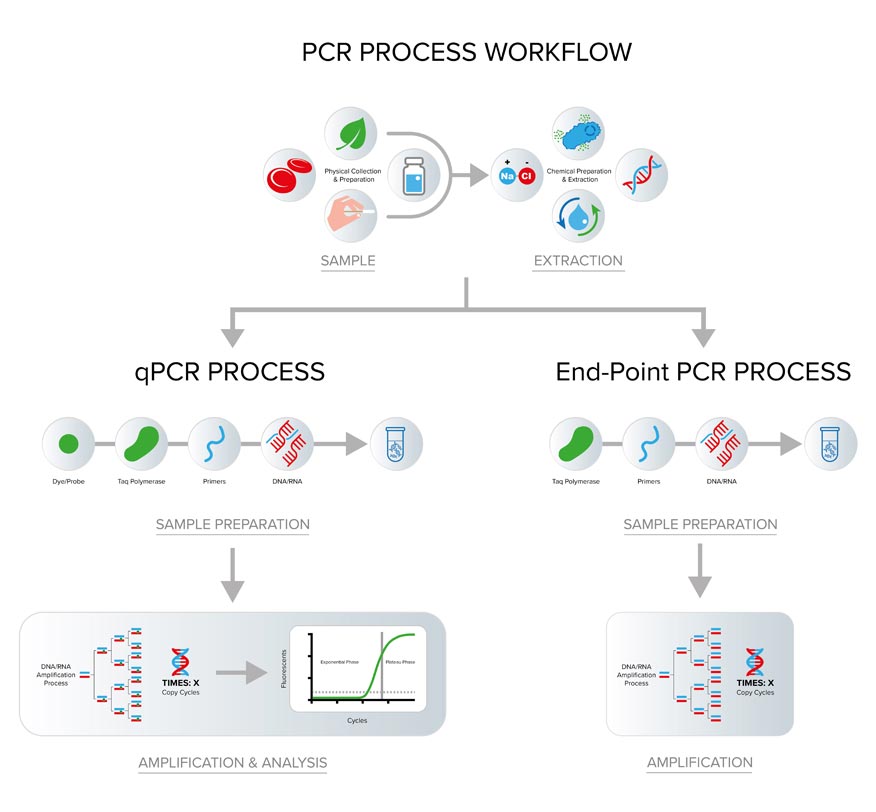
PCR Process Steps Explained ColeParmer United Kingdom
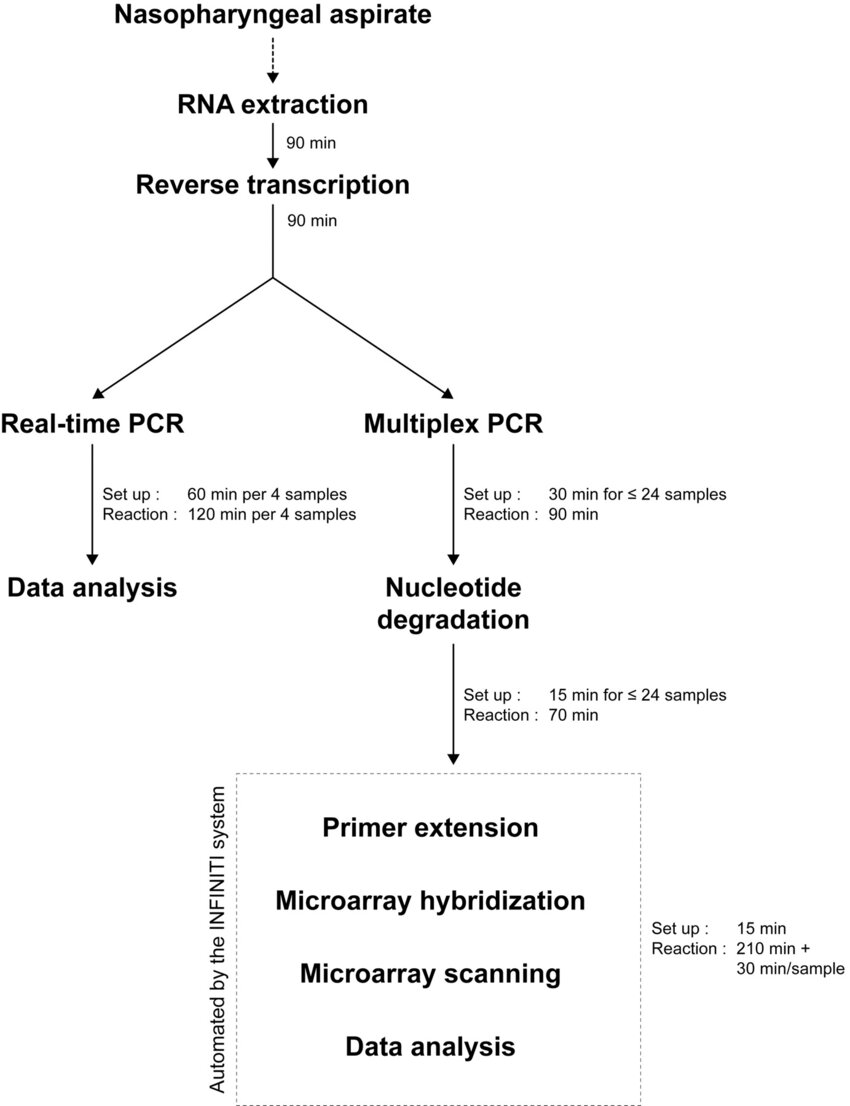
Pcr Flow Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Web The Basic Polymerase Chain Reaction (Pcr) Michael R.
A Pcr Test Amplifies Dna Sequences.
In Cases Of Pooling, Repeat Processing For Individual Samples Occurs If Pooling Outcome Is Positive.
Web Polymerase Chain Reaction (Pcr) Underlies Many Molecular Biology And Molecular Genetics Techniques.
Related Post: