Flow Chart Of Gram Positive Cocci
Flow Chart Of Gram Positive Cocci - Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in enterococci. Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining ), observation of growth characteristics ( list of culture media ), determination of reactions to organic and inorganic compounds ( api gallery , microbiological techniques) and molecular techniques. Web aerobic gram positive cocci flowchart. Two of the most important human pathogens, staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes , are described in this chapter. Other tests not shown in the flow chart but included in table 2 can be used for. 1 is a flow chart developed to show the key distinguishing tests. This video is about gram. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Web back gram positive cocci. Coagulase negative staphylococci in multiple blood cultures. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in enterococci. Web guide to interpretation of positive blood cultures i arrange the potential gram stain results that one can be called w/ as follows: Oxygen requirements, morph., growth requirements (45°c and supplements), read genera descriptions. Gram positive (g+), catalase positive (+) cocci. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus. Web the six flow charts we’ll be discussing are: Web aerobic gram positive cocci flowchart. Web back gram positive cocci. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in enterococci. The tests included in the flow chart often gave strong reactions; Causative agent for endocarditis and dental abscesses. Identify similarities and differences between high g+c and low g+c bacterial groups. This video is about gram. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in enterococci. This video is about gram. Web the six flow charts we’ll be discussing are: Oxygen requirements, morph., growth requirements (45°c and supplements), read genera descriptions. Lugdunensis found in abscesses and serious wounds; Spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), and spirals or helixes (spirochetes). Two of the most important human pathogens, staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes , are described in this chapter. 1 is a flow chart developed to show the key distinguishing tests. Lugdunensis found in abscesses and serious wounds; Web aerobic gram positive cocci flowchart. Gram(+) cocci are grouped by ‘morphology’ since the lab usually tells you this: There are two main groups of staphylococci affecting humans: Give an example of a bacterium of high g+c and low g+c group commonly associated with each category. Gram staining is one way scientists can identify bacteria. Other tests not shown in the flow chart but included in. The tests included in the flow chart often gave strong reactions; Web aerobic gram positive cocci flowchart. Gram staining is one way scientists can identify bacteria. Oxygen requirements, morph., growth requirements (45°c and supplements), read genera descriptions. The bacterial cell wall of these organisms have thick peptidoglycan layers, which take up the purple/violet stain. Gram(+) cocci are grouped by ‘morphology’ since the lab usually tells you this: The bacterial cell wall of these organisms have thick peptidoglycan layers, which take up the purple/violet stain. There are two main groups of staphylococci affecting humans: The tests included in the flow chart often gave strong reactions; Gram positive (g+), catalase positive (+) cocci. The bacterial cell wall of these organisms have thick peptidoglycan layers, which take up the purple/violet stain. Web back gram positive cocci. Two of the most important human pathogens, staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes , are described in this chapter. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Gram staining is. Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining ), observation of growth characteristics ( list of culture media ), determination of reactions to organic and inorganic compounds ( api gallery , microbiological techniques) and molecular techniques. Web the six flow charts we’ll be discussing are: Gram(+) cocci are grouped by ‘morphology’ since the. Identify similarities and differences between high g+c and low g+c bacterial groups. Web guide to interpretation of positive blood cultures i arrange the potential gram stain results that one can be called w/ as follows: Web the six flow charts we’ll be discussing are: There are two main groups of staphylococci affecting humans: Web aerobic gram positive cocci flowchart. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining ), observation of growth characteristics ( list of culture media ), determination of reactions to organic and inorganic compounds ( api gallery , microbiological techniques) and molecular techniques. 1 is a flow chart developed to show the key distinguishing tests. Other tests not shown in the flow chart but included in table 2 can be used for. 16k views 4 years ago. Gram(+) cocci are grouped by ‘morphology’ since the lab usually tells you this: Causative agent for endocarditis and dental abscesses. Web back gram positive cocci. The bacterial cell wall of these organisms have thick peptidoglycan layers, which take up the purple/violet stain. Two of the most important human pathogens, staphylococcus aureus and streptococcus pyogenes , are described in this chapter. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f.
Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart
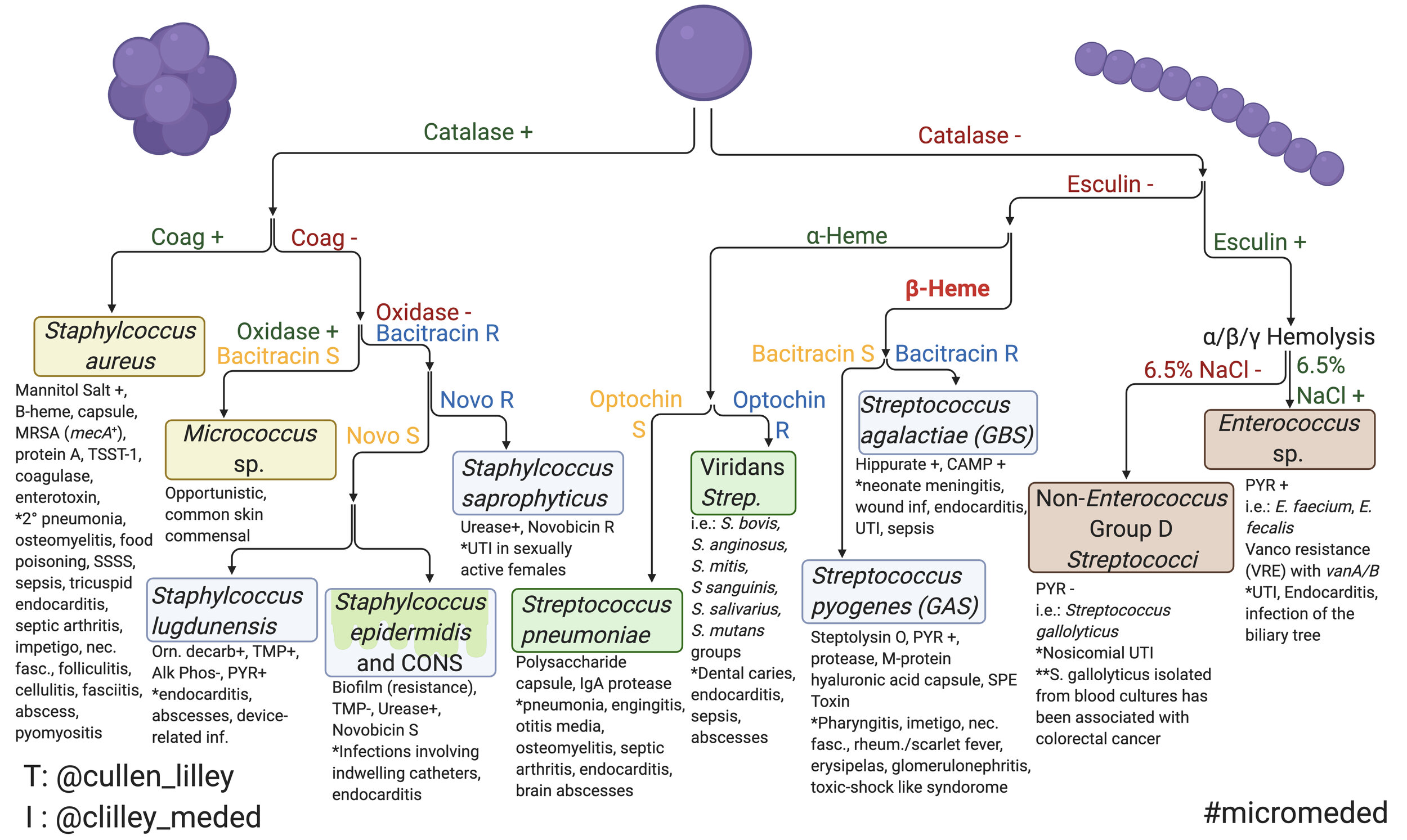
Gram Positive Cocci — PathElective
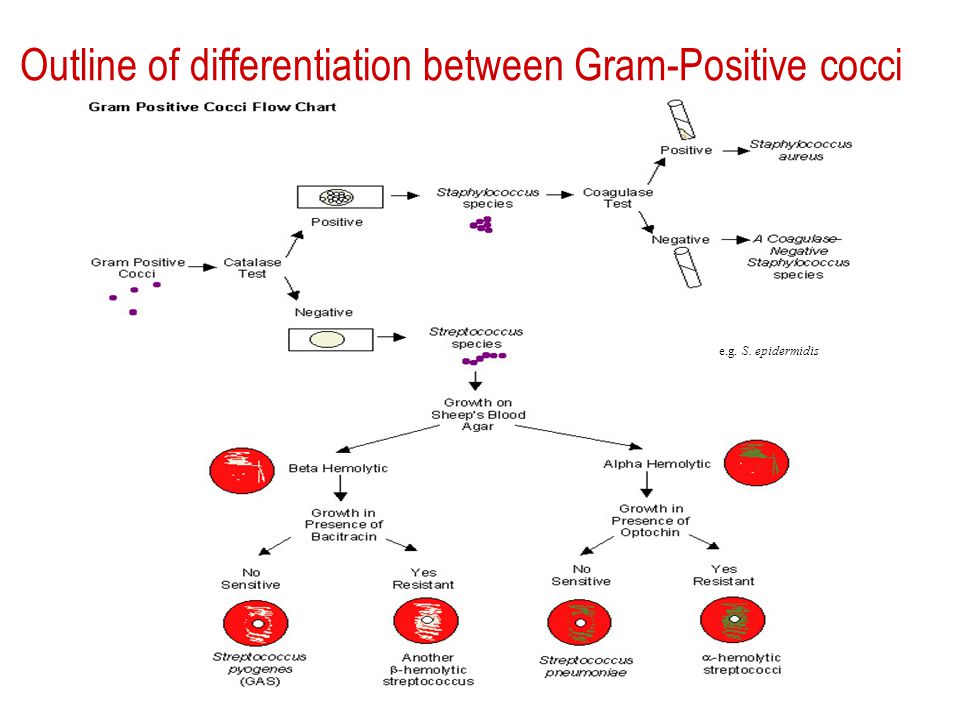
Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart

GRAM POSITIVE COCCI FLOW CHART GPC MLT Pinterest Flowchart, Flow

Microbiology Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart Gram Positive Cocci
Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart Streptococcus Prokaryote
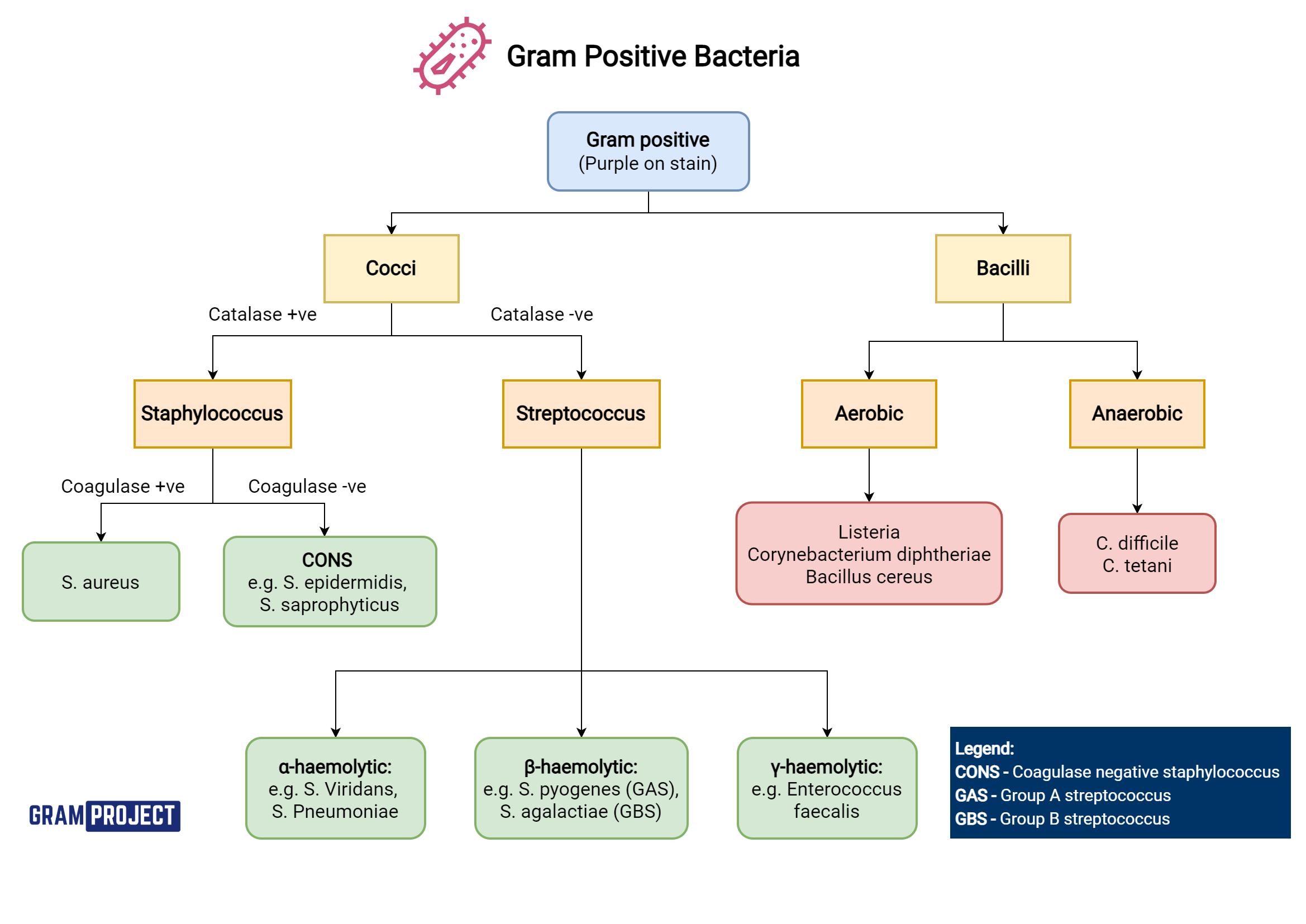
Gram Positive Organisms Chart

Gram Positive Cocci Flow Chart
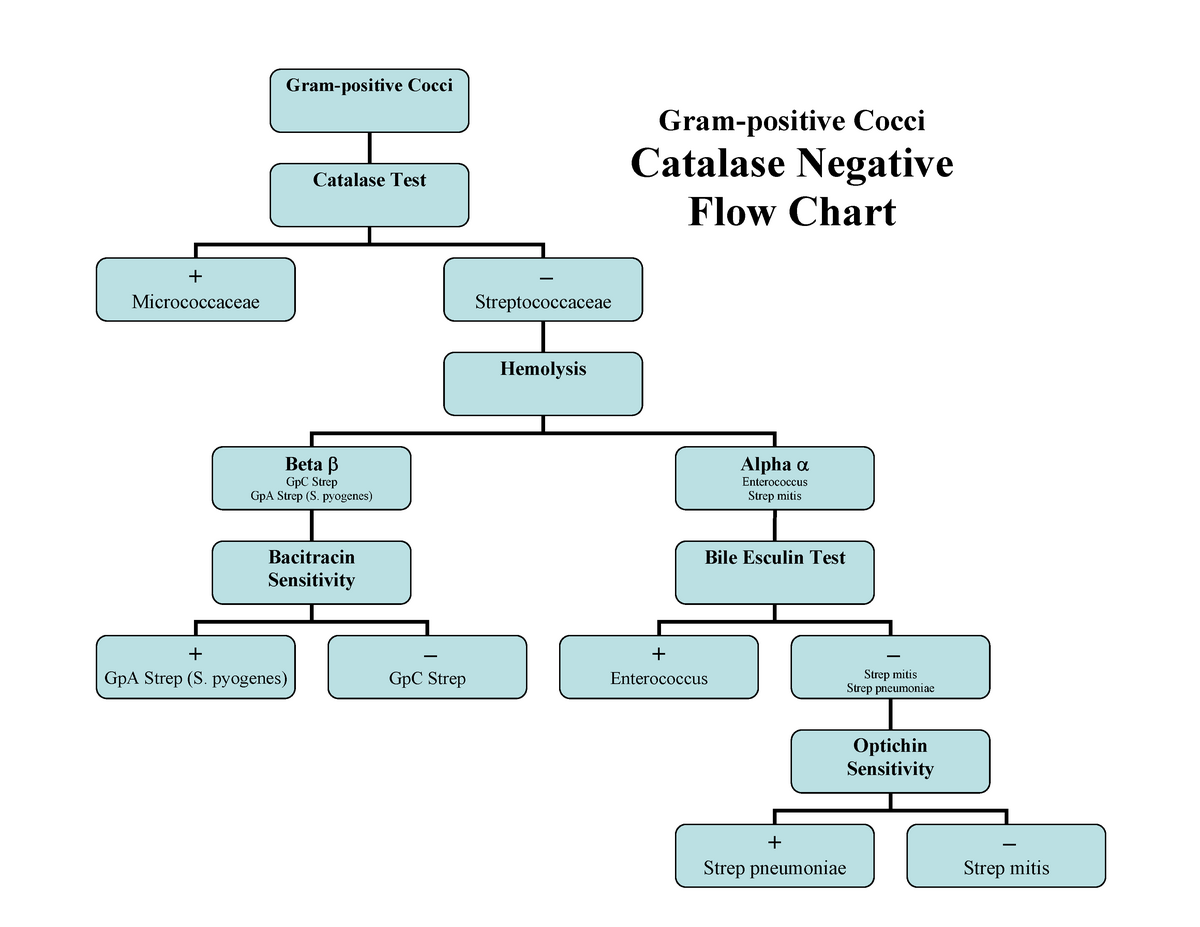
Identifying gram Flow Charts Grampositive Cocci Catalase Negative

Anatomy human Gram positive Cocci Classification
Mechanisms Of Antibiotic Resistance In Enterococci.
The Tests Included In The Flow Chart Often Gave Strong Reactions;
Lugdunensis Found In Abscesses And Serious Wounds;
Give An Example Of A Bacterium Of High G+C And Low G+C Group Commonly Associated With Each Category.
Related Post:
