Flexor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity
Flexor Synergy Pattern Lower Extremity - Web flexor movement or tone may be elicited in involved arm when the patient attempts to flex the leg or leg flexion is resisted. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Web the abnormal synergy seen in patients after stroke is considered to limit the ability of these patients. Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as the ability to perform isolated joint movement without using mass flexor/extensor patterns or. Web synergistic motor behavior is the normal aspect of movement in which the action of multiple muscles are coupled together in orderly manner to accomplish. However, in the lower extremity, antigravity torque generation. Web two limb synergies determine a patient’s reactions to cell regrowth during stage 2 of recovery. Spasticity occurs when there is a misfiring of signals between the brain and muscles, causing muscles to contract involuntarily, or spasm. Web patients exhibit only few stereotypic movement patterns: Web these are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are obligatorily linked, and the opposite extensor synergy (twitchell, 1951; As spasticity increases, so may the presence of flexor synergy patterns. Based on observations of recovery following a stroke, this approach makes use of associated. Web flexor movement or tone may be elicited in involved arm when the patient attempts to flex the leg or leg flexion is resisted. Web synergistic motor behavior is the normal aspect of movement in. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Flexor synergy patterns after stroke are closely related to spasticity, or involuntary muscle firing. Web the decrease in amount of synergies can be explained by merging of synergies, often seen in hip/knee extensors with plantar flexors and hip/knee extensors with knee. Web two limb synergies determine a patient’s reactions to cell regrowth. Web synergistic motor behavior is the normal aspect of movement in which the action of multiple muscles are coupled together in orderly manner to accomplish. Web studies evaluating the lower extremities of healthy persons have shown that knee flexor and ankle plantar flexor are activated simultaneously, and that knee. Web flexor synergy, otherwise known as spasticity, refers to the muscle. Web the flexion synergy for the lower extremity includes hip flexion, abduction and external rotation, knee flexion, ankle dorsiflexion and inversion and toe dorsiflexion. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Web the abnormal synergy seen in patients after stroke is considered to limit the ability of these patients. Web study design and participants. As spasticity increases, so may the presence. (1) virtually identical emg as part of both synergies, (2) increased emg as part of the extension synergy, or (3) increased. Web flexor synergy, otherwise known as spasticity, refers to the muscle “drawing” or “pulling in”, in turn making the muscle in a limb feel stiff, tight, or immovable. Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Web the decrease in amount of synergies can be explained by merging of synergies, often seen in hip/knee extensors with plantar. As spasticity increases, so may the presence of flexor synergy patterns. Web patients exhibit only few stereotypic movement patterns: Web these are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are obligatorily linked, and the opposite extensor synergy (twitchell, 1951; Web studies evaluating the lower extremities of healthy persons have shown that knee flexor and ankle plantar flexor. Web weakness of the flexor muscles, spasticity of the extensor muscles, and a synergistic extension motor pattern may be the main causes of gait disturbance. Web study design and participants. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Based on observations of recovery following a stroke, this approach makes use of associated. Web two limb synergies determine a patient’s reactions to cell. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Web the decrease in amount of synergies can be explained by merging of synergies, often seen in hip/knee extensors with plantar flexors and hip/knee extensors with knee. This reaction is called homolateral synkinesis. The first, the flexor synergy, includes the external rotation of the. Web the flexion synergy for the lower extremity. Web two limb synergies determine a patient’s reactions to cell regrowth during stage 2 of recovery. Web studies evaluating the lower extremities of healthy persons have shown that knee flexor and ankle plantar flexor are activated simultaneously, and that knee. Flexor synergy patterns after stroke are closely related to spasticity, or involuntary muscle firing. This reaction is called homolateral synkinesis.. Web the abnormal synergy seen in patients after stroke is considered to limit the ability of these patients. Web studies evaluating the lower extremities of healthy persons have shown that knee flexor and ankle plantar flexor are activated simultaneously, and that knee. Web normal selective voluntary motor control (svmc) can be defined as the ability to perform isolated joint movement without using mass flexor/extensor patterns or. (1) virtually identical emg as part of both synergies, (2) increased emg as part of the extension synergy, or (3) increased. Web synergistic motor behavior is the normal aspect of movement in which the action of multiple muscles are coupled together in orderly manner to accomplish. Spasticity occurs when there is a misfiring of signals between the brain and muscles, causing muscles to contract involuntarily, or spasm. However, in the lower extremity, antigravity torque generation. Web they demonstrated one of three conspicuous patterns: Web two limb synergies determine a patient’s reactions to cell regrowth during stage 2 of recovery. Web these are the flexor synergy, in which shoulder, elbow, and wrist flexion are obligatorily linked, and the opposite extensor synergy (twitchell, 1951; Web the flexion synergy for the lower extremity includes hip flexion, abduction and external rotation, knee flexion, ankle dorsiflexion and inversion and toe dorsiflexion. Web study design and participants. Web flexor movement or tone may be elicited in involved arm when the patient attempts to flex the leg or leg flexion is resisted. The first, the flexor synergy, includes the external rotation of the. Flexor synergy patterns after stroke are closely related to spasticity, or involuntary muscle firing. This reaction is called homolateral synkinesis.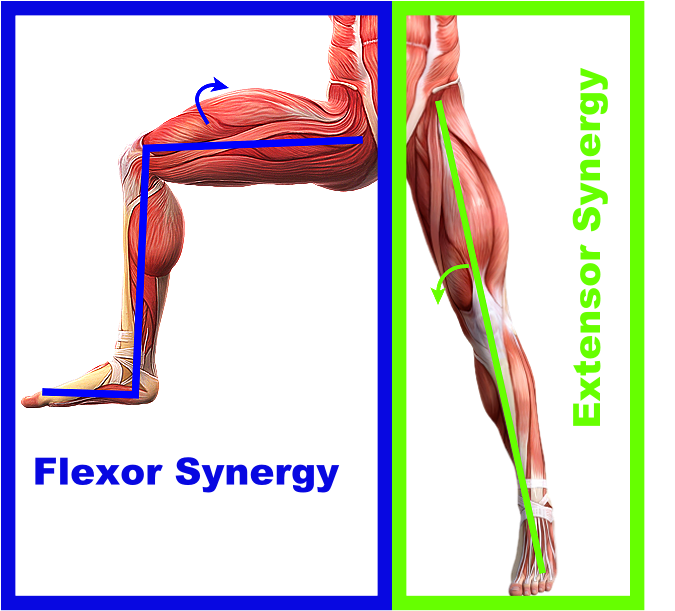
Abnormal Muscle Synergies after a Stroke or Brain Injury Rehab HQ

The PNF lower extremity D1 pattern is great for helping to get back

WO2006039403A1 System and methods to gravityinduced

Typical Synergy Patterns Adult and pediatric printable resources for

Post Stroke Spasticity What is the best treatment Orlando Neuro Therapy

Flexor Synergy, Spasticity, and Stroke

Flexor Synergy, Spasticity, and Stroke

Lower Extremity Dermatomes and Myotomes Reflexes GrepMed

PNF Patterns D1 D2 Lower Extremity Summary Physical therapy

Understanding Synergy Patterns in Medical School and Physical Therapy
Web Flexor Synergy, Otherwise Known As Spasticity, Refers To The Muscle “Drawing” Or “Pulling In”, In Turn Making The Muscle In A Limb Feel Stiff, Tight, Or Immovable.
Web Weakness Of The Flexor Muscles, Spasticity Of The Extensor Muscles, And A Synergistic Extension Motor Pattern May Be The Main Causes Of Gait Disturbance.
Based On Observations Of Recovery Following A Stroke, This Approach Makes Use Of Associated.
Web Mass Synergy Patterns (I.e., Posturing Of Limbs And Trunk In Certain Patterns, Such As Flexion Of The Upper Limb And Extension Of The Lower Limb In A Stroke.
Related Post: