Fire Hose Coefficient Chart
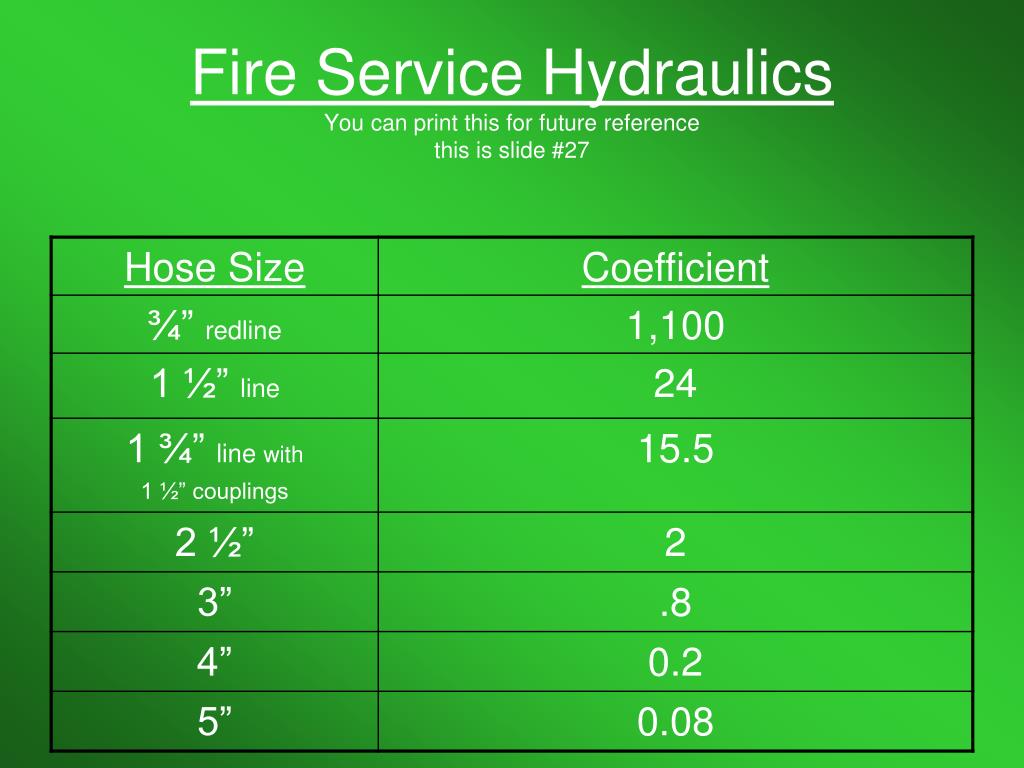
Fire Hose Coefficient Chart - There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. Web learn how to calculate the engine pressure, friction loss, and appliance friction loss for fire pumping operations. Click the link to see our friction loss data. Nozzle, what is the friction loss for 200 feet of. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. As water passes through a fire hose, friction between the water and the inside surface of the hose cause turbulence. The pressure loss is directly proportional to the length. Hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient 3⁄4. It's simply comparing the size of. Please click on the table above to view a larger version. Distance, diameter, and the gpm / volume, all affect friction loss. Please click on the table above to view a larger version. Web all fire hose has friction loss. Friction loss is determined by the gpm flowing, the size of the hose and the length of the hose. Flow rate (gpm) hose length (ft) total friction loss (psi) friction loss. All three factors must be considered. It's simply comparing the size of. The pressure loss is directly proportional to the length. Flow rate (gpm) hose length (ft) total friction loss (psi) friction loss / 50' (psi) Hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient 3⁄4. There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. Hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient 3⁄4. Fl = c(q/100)2 x (l/100). Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 7 bar setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting. Web learn how to estimate available water from a hydrant using. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 7 bar setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting. Web the conquest fire hose is a single jacket industrial fire hose that can be used in several firefighting applications. Find a cheat sheet with friction loss coefficients for different hose sizes and flows. Distance, diameter, and the gpm / volume,. Web if you calculate the gpm flow using the formula 29.72d2√p (where d is diameter in inches and p is pressure in psi), you will notice a fairly significant difference in the flow rates, which. All three factors must be considered. Web the discharge coefficient is what helps us adjust the measured pitot pressure, which is taken along the centerline. A total of 86 tests were performed by three fire service organizations on 82 fire hose samples spanning from 1 to 5 inches in diameter. Web learn how to calculate the engine pressure, friction loss, and appliance friction loss for fire pumping operations. Web all fire hose has friction loss. The pressure loss is directly proportional to the length. Q. There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. Learn more & browse all hoses. Friction loss occurs when water passes through a fire hose. Web in this episode dennis legear explains why modern hose coefficients can be tricky and why it is important to test your own fire attack system. The pressure loss is directly proportional. Friction loss is determined by the gpm flowing, the size of the hose and the length of the hose. Web all fire hose has friction loss. C = friction loss coefficient l = hose length in hundreds of feet. Friction loss is determined by the gpm flowing, the size of the hose and the length of the hose. All three. All three factors must be considered. A total of 86 tests were performed by three fire service organizations on 82 fire hose samples spanning from 1 to 5 inches in diameter. Friction loss is determined by the gpm flowing, the size of the hose and the length of the hose. Web friction loss calculations explained: The pressure loss experienced by. Web learn how to estimate available water from a hydrant using the second friction loss rule and the formula c = kq^2. All three factors must be considered. Recorded hose dimensions, pressure, flow and friction loss data were used to calculate the. Please click on the table above to view a larger version. A total of 86 tests were performed. Q = flow rate in hundreds of gpm (flow÷100) l = hose length in hundreds of feet (length÷100) if 150 gpm is flowing from. Web all fire hose has friction loss. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 7 bar setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting. Web formula for friction loss: C = friction loss coefficient l = hose length in hundreds of feet. Learn more & browse all hoses. Flow rate (gpm) hose length (ft) total friction loss (psi) friction loss / 50' (psi) Fl = c(q/100)2 x (l/100). There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. Please click on the table above to view a larger version. Hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient hose diameter and type (inches) coefficient 3⁄4. Pump discharge pressure pump discharge pressure, or pdp, is calculated so that you can properly pump your hose and nozzle combination to achieve your target flow rate. Web friction loss calculations explained: All three factors must be considered. A total of 86 tests were performed by three fire service organizations on 82 fire hose samples spanning from 1 to 5 inches in diameter. As water passes through a fire hose, friction between the water and the inside surface of the hose cause turbulence.
Friction Loss Coefficient Table For Fire Hose
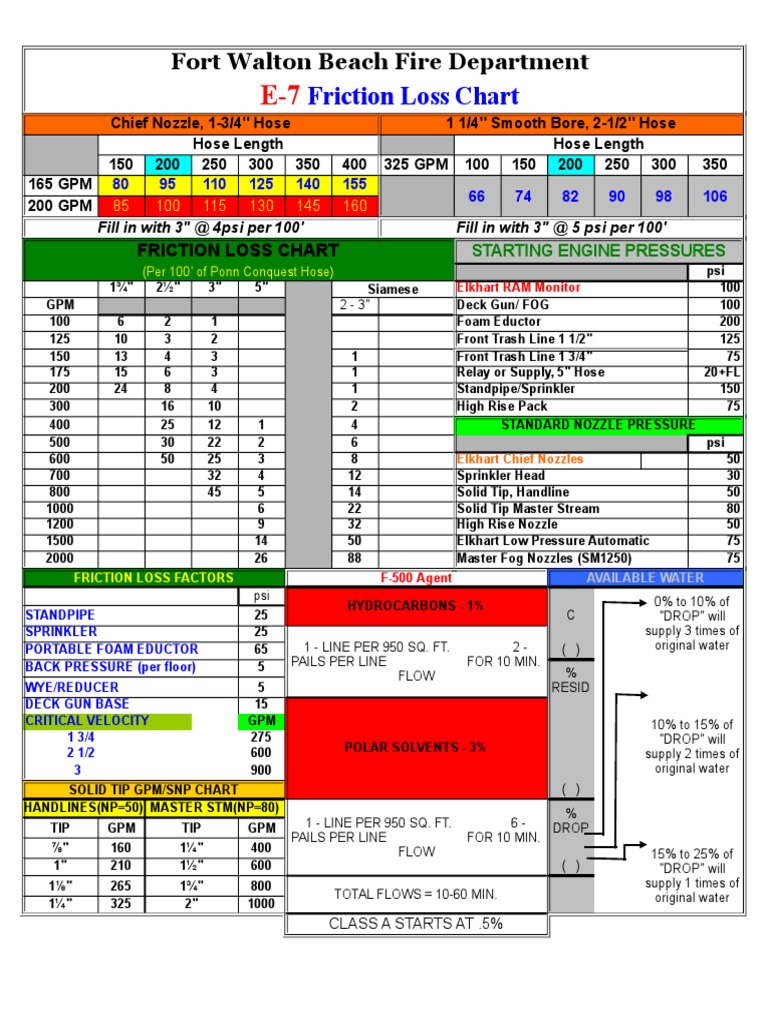
Friction Loss Chart Fort Walton Beache7 Excel Spredsheet Fire
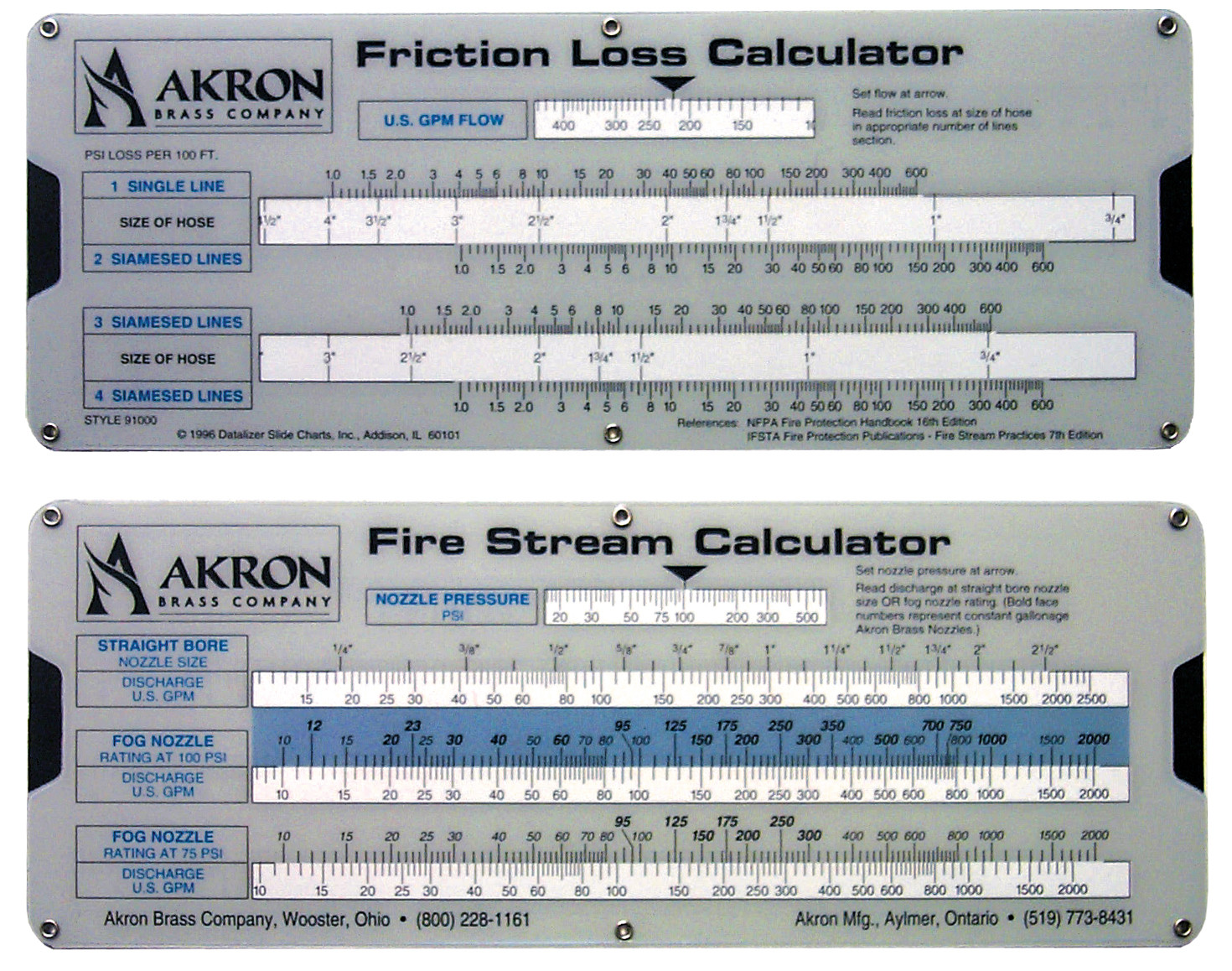
Friction Loss Coefficient Table For Fire Hose
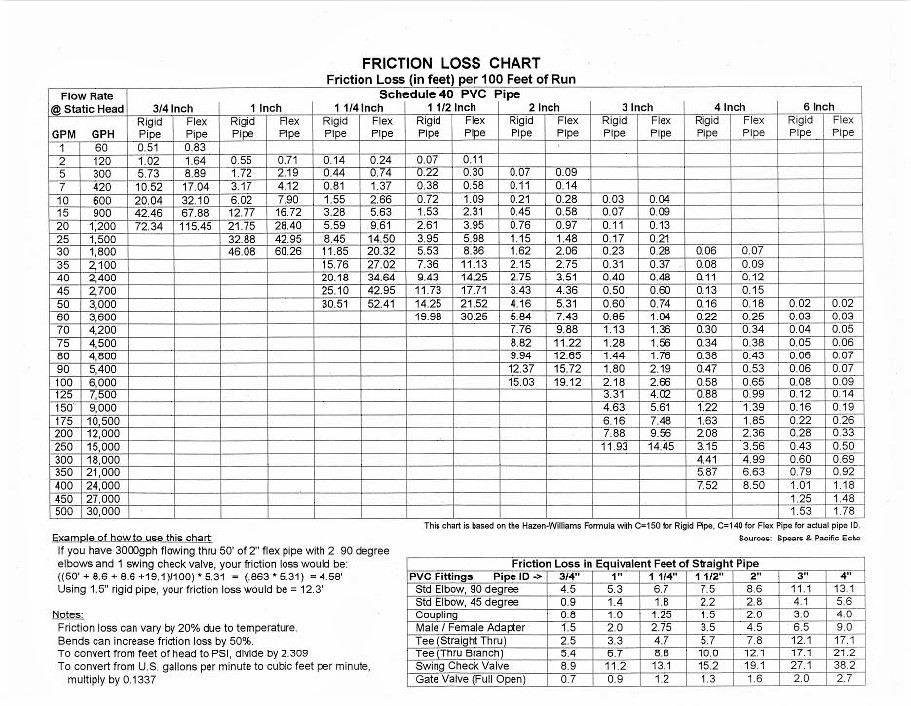
Friction Loss Tables For Fire Hose Elcho Table
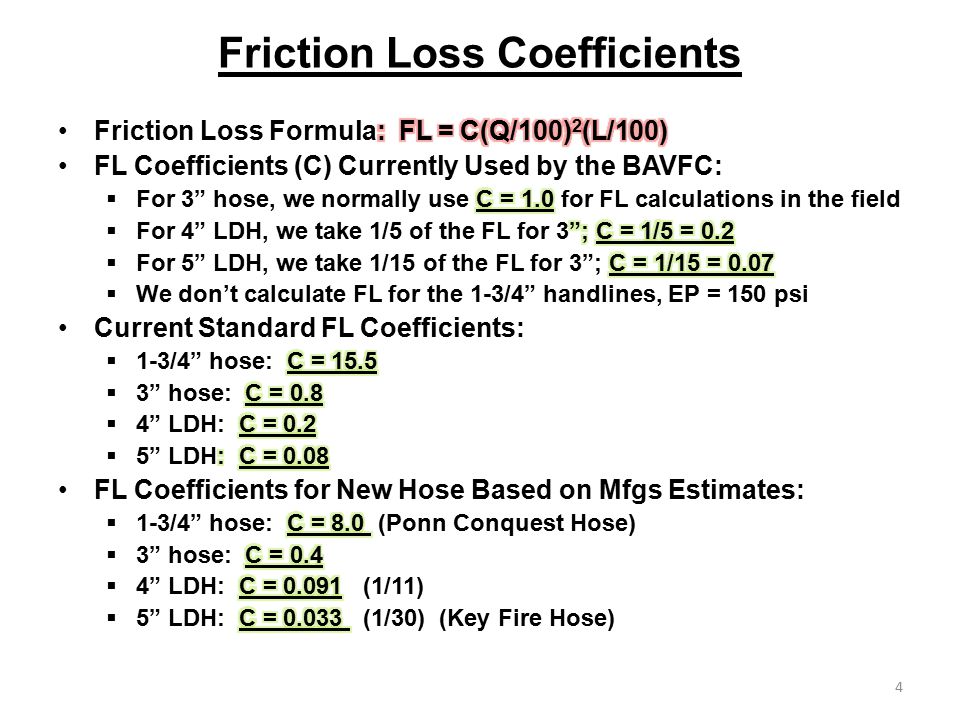
Fire Hose Friction Loss Coefficient Chart A Visual Reference of Charts

Fire Hose Friction Loss Coefficient Chart
Free Downloads FiremanSource
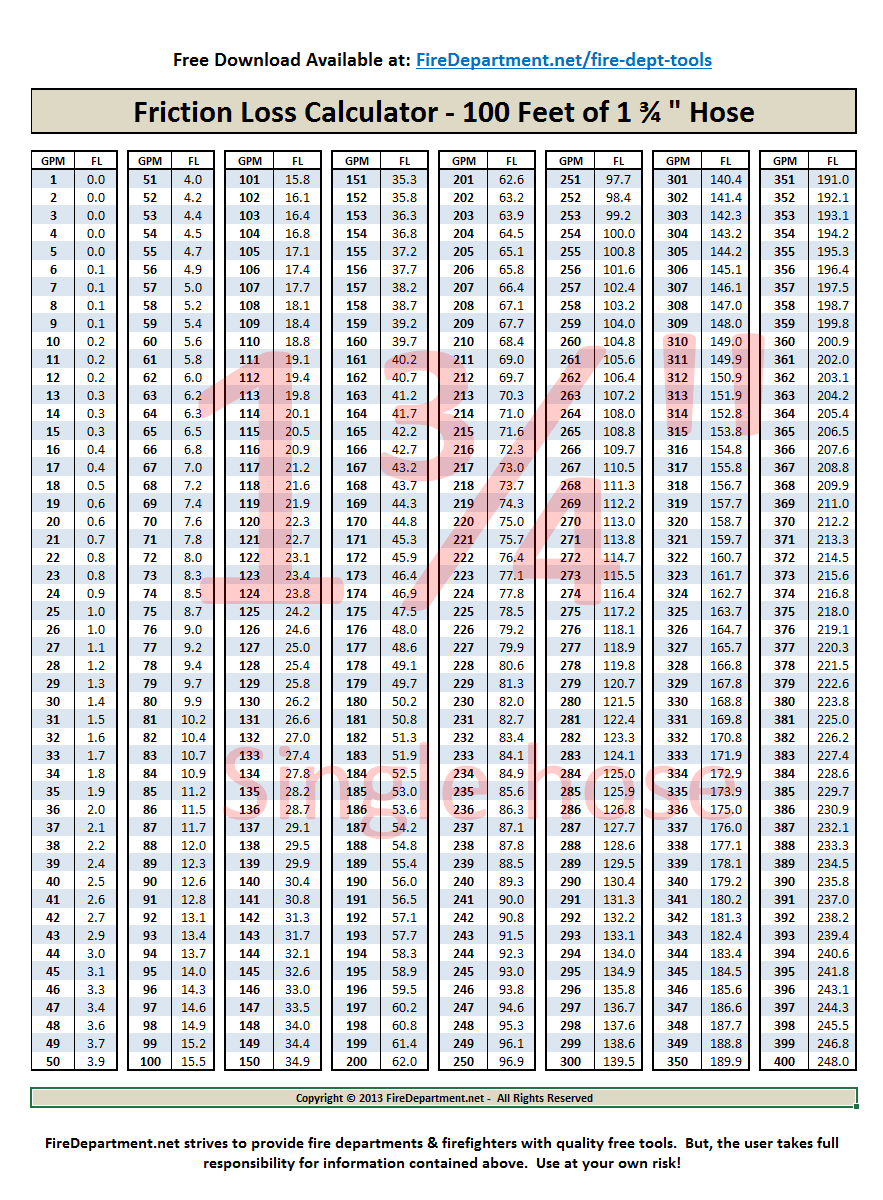
Fire Hose Friction Loss Chart

Friction Loss Coefficient Table For Fire Hose

1.75 inch Friction Loss Calculator Fire training, Firefighter
This Turbulence Reduces The Energy Produced By The Pump (Psi).
Choose Your Hose And Size Below, Enter The Flow Rate, As Well As The Hose Length To Display Friction Loss Data.
It's Simply Comparing The Size Of.
Web The Discharge Coefficient Is What Helps Us Adjust The Measured Pitot Pressure, Which Is Taken Along The Centerline Of The Stream, And Adjust For About How Much Flow Is Coming Through The Opening.
Related Post: