Fingerprint Identification Chart
Fingerprint Identification Chart - Web c h a p t e r. Web use the following chart (based on ridge counts): Neither do fingerprints change, even as we get older, unless the deep or ‘basal’ layer is destroyed or intentionally changed by plastic surgery. These are mainly due to all manner of bending vibrations within the molecule. Fingerprints are unique patterns, made by friction ridges (raised) and furrows (recessed), which appear on the pads of the fingers and thumbs. Web fingerprints are unique patterns, made by friction ridges (raised) and furrows (recessed), which appear on the pads of the fingers and thumbs. (a) sampling features (singular points, orientation field, and minutiae) from appropriate statistical feature models; Prints from palms, toes and feet are also unique; Primary, major, secondary, sub secondary, final, and key classifications are the six main classifications. However, these are used less often for identification, so this guide focuses on prints from the fingers and thumbs. This is called the fingerprint region. Web in henry’s fingerprint classification system, there are 6 main divisions with 3 common extensions. Web fingerprints are unique patterns, made by friction ridges (raised) and furrows (recessed), which appear on the pads of the fingers and thumbs. Latent fingerprints—made visible by dusting with powders or the use of chemicals. Web guide to aid. Plastic fingerprints—indentations left in soft materials such as clay or wax. After a brief historical review, we provide an introduction to modern automated fingerprint identification systems (afis ) by discussing their functionalities and accuracy. However, in circumstances where the print is visible to the naked eye, finding a fingerprint is relatively easy. Web c h a p t e r.. Web process that involves analyzing and constructing hypotheses of the identity of human remains and reconciling the information collected using several lines of evidence by comparing antemortem and postmortem data ( icrc: Web the fingerprint sourcebook is the definitive guide to the science of fingerprint identification. On the palm side of each person’s hands and on the soles of each. Anatomy and physiology of adult friction ridge skin (ncj 225322); Locating a fingerprint often requires a vigilant and calculated search. On the palm side of each person’s hands and on the soles of each person’s feet are prominent skin features that single him or her out from everyone else in the world. Patent fingerprints—visible prints transferred onto smooth surfaces by. Anatomy and physiology of adult friction ridge skin (ncj 225322); Web the present chapter includes a basic introduction to fingerprints, including history, fingerprint laws, classification, types, collection and preservation methods. (a) sampling features (singular points, orientation field, and minutiae) from appropriate statistical feature models; However, these are used less often for identification, so this guide focuses on prints from the. History (ncj 225321) by jeffery g. Web fingerprint identification is a form of biometrics, a science that uses people’s physical or biological characteristics to identify them. (b) generating a master fingerprint; Web fingerprints are unique patterns, made by friction ridges (raised) and furrows (recessed), which appear on the pads of the fingers and thumbs. Web there are 3 types of. Web fingerprint identification, known as dactyloscopy, ridgeology, or hand print identification, is the process of comparing two instances of friction ridge skin impressions (see minutiae), from human fingers or toes, or even the palm of the hand or sole of the foot, to determine whether these impressions could have come from the same individual. (c) generating multiple fingerprint impressions from. Web fingerprint identification, known as dactyloscopy, ridgeology, or hand print identification, is the process of comparing two instances of friction ridge skin impressions (see minutiae), from human fingers or toes, or even the palm of the hand or sole of the foot, to determine whether these impressions could have come from the same individual. However, in circumstances where the print. History (ncj 225321) by jeffery g. Web fingerprint identification is based primarily on the minutiae, or the location and direction of the ridge endings and bifurcations (splits) along a ridge path. Web fingerprint identification is a form of biometrics, a science that uses people’s physical or biological characteristics to identify them. Web fingerprints are unique patterns, made by friction ridges. Embryology, physiology, and morphology (ncj 225323); Web in henry’s fingerprint classification system, there are 6 main divisions with 3 common extensions. (a) sampling features (singular points, orientation field, and minutiae) from appropriate statistical feature models; Web use the following chart (based on ridge counts): Patent fingerprints—visible prints transferred onto smooth surfaces by blood or other liquids. The more intricate searches take place when the print is present on a surface but not visible. Prints from palms, toes and feet are also unique; Web flow chart of the fingerprint identification system. The long story of that inescapable mark of identity has been told and retold for many years and in many ways. Web the present chapter includes a basic introduction to fingerprints, including history, fingerprint laws, classification, types, collection and preservation methods. Anatomy and physiology of adult friction ridge skin (ncj 225322); These are mainly due to all manner of bending vibrations within the molecule. On the palm side of each person’s hands and on the soles of each person’s feet are prominent skin features that single him or her out from everyone else in the world. Various development methods such as physical, chemical, optical and sophisticated instrumental analytical methods for latent fingerprints are also included. However, these are used less often for identification, so this guide focuses on prints from the fingers and thumbs. After a brief historical review, we provide an introduction to modern automated fingerprint identification systems (afis ) by discussing their functionalities and accuracy. This is called the fingerprint region. Web use the following chart (based on ridge counts): Web fingerprint identification is a form of biometrics, a science that uses people’s physical or biological characteristics to identify them. Primary, major, secondary, sub secondary, final, and key classifications are the six main classifications. Implementation of easy fingerprint image authentication with traditional euclidean and singular value.
Fingerprinting with Ink ForensiKit by Crime Scene
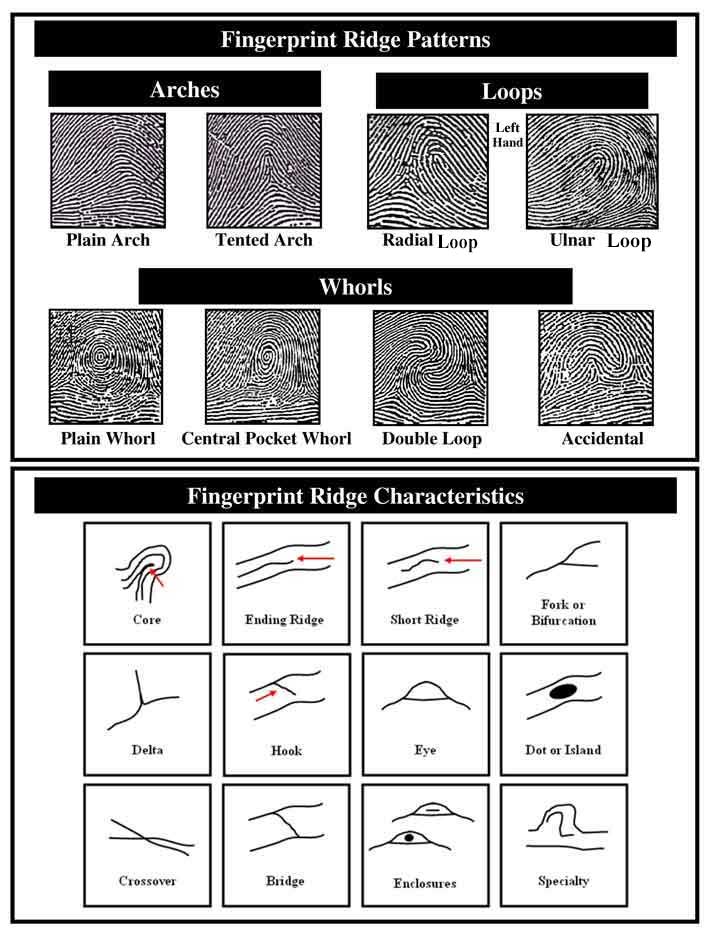
Fingerprint Ridge Patterns and Characteristics
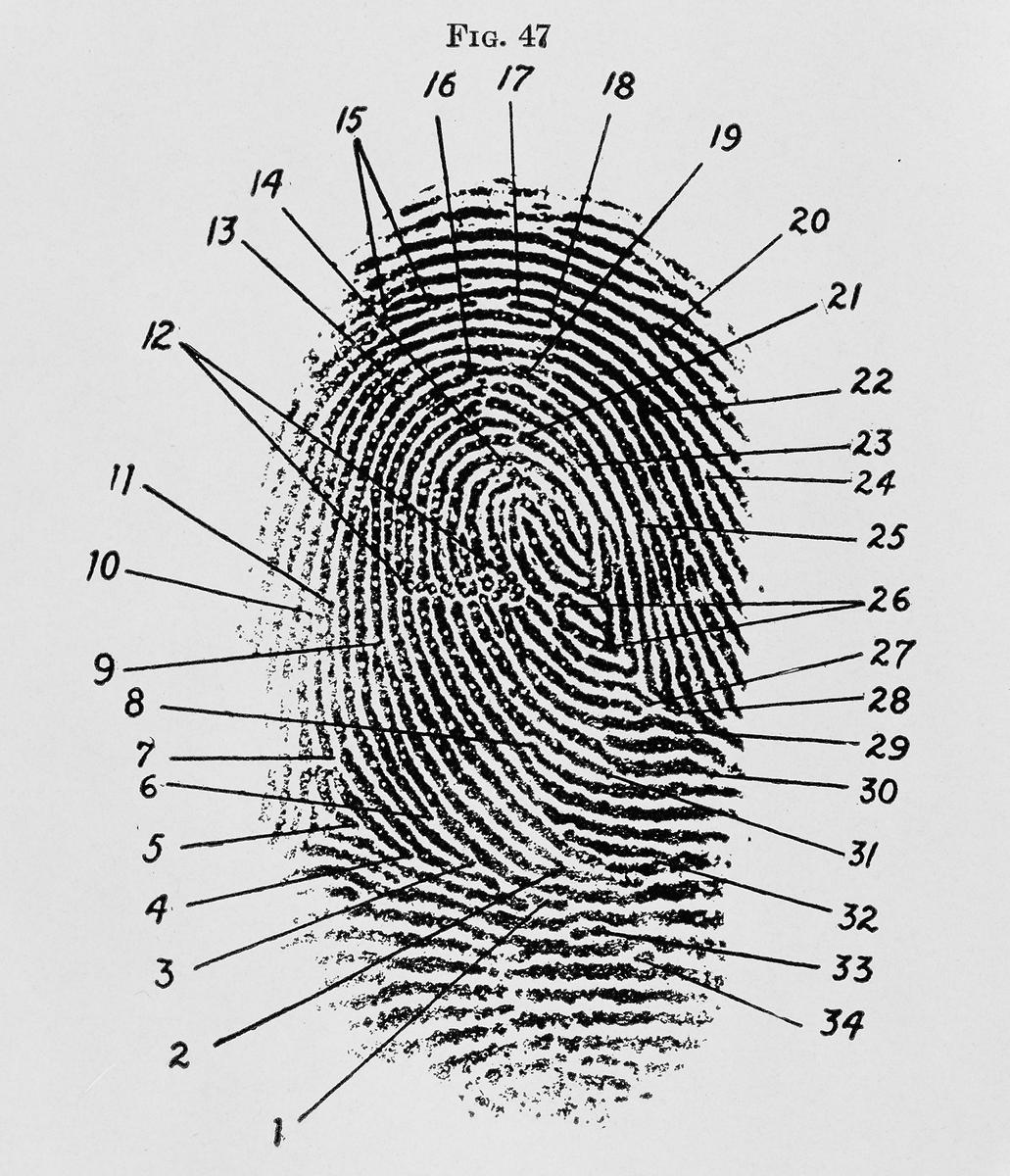

The Importance Of Fingerprint Charts In Police Investigations

Fingerprints Points, Type, and Classification — 2016WPA Crime
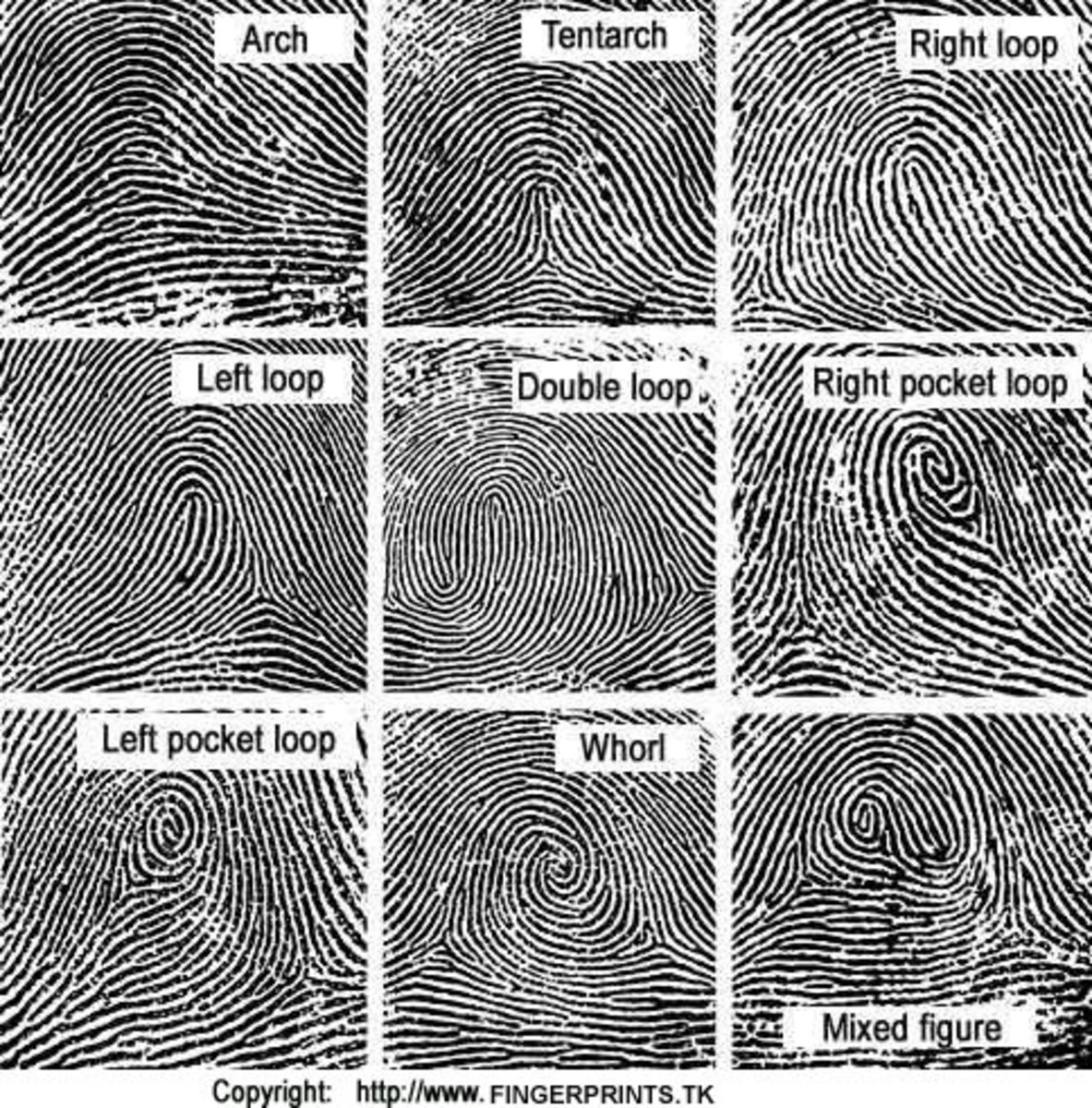

Printable Fingerprint Chart

Fingerprint Types Chart

Kirsty's Blog! Different Types Of Fingerprints.
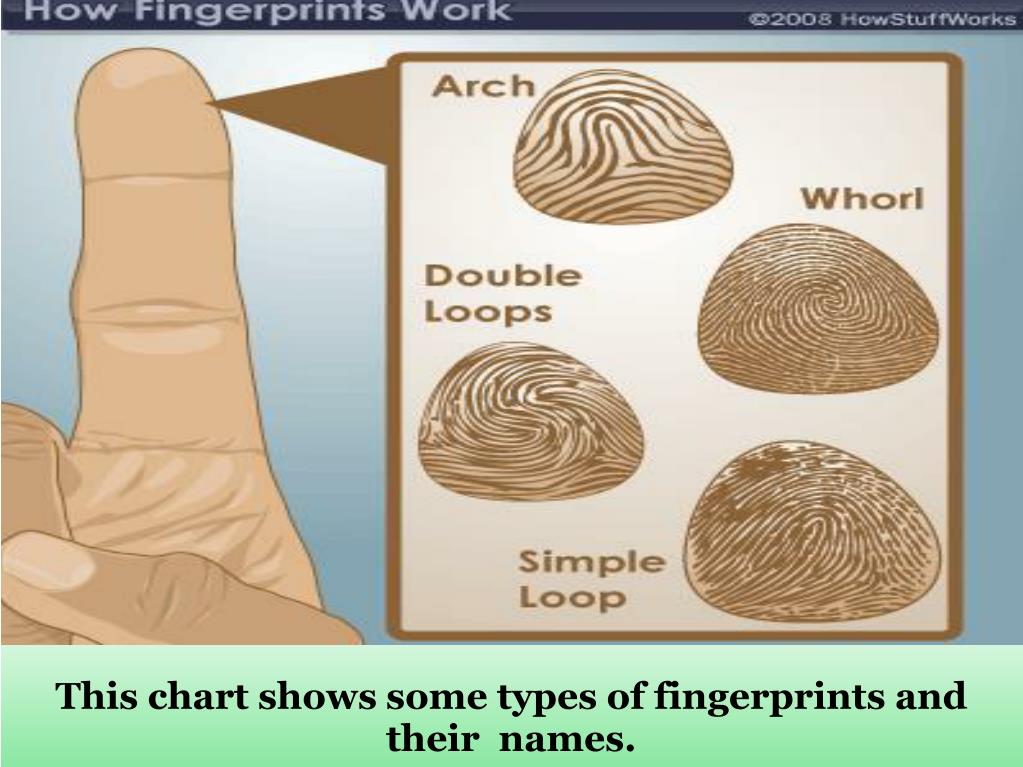
PPT Identifying Fingerprints PowerPoint Presentation, free download

Fingerprint Chart Image & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock

Forensic Fingerprinting Analysis and History Investigating Detectives
Neither Do Fingerprints Change, Even As We Get Older, Unless The Deep Or ‘Basal’ Layer Is Destroyed Or Intentionally Changed By Plastic Surgery.
Patent Fingerprints—Visible Prints Transferred Onto Smooth Surfaces By Blood Or Other Liquids.
(A) Sampling Features (Singular Points, Orientation Field, And Minutiae) From Appropriate Statistical Feature Models;
Web Fingerprints Are Unique Patterns, Made By Friction Ridges (Raised) And Furrows (Recessed), Which Appear On The Pads Of The Fingers And Thumbs.
Related Post: