Enthalpy Entropy Chart
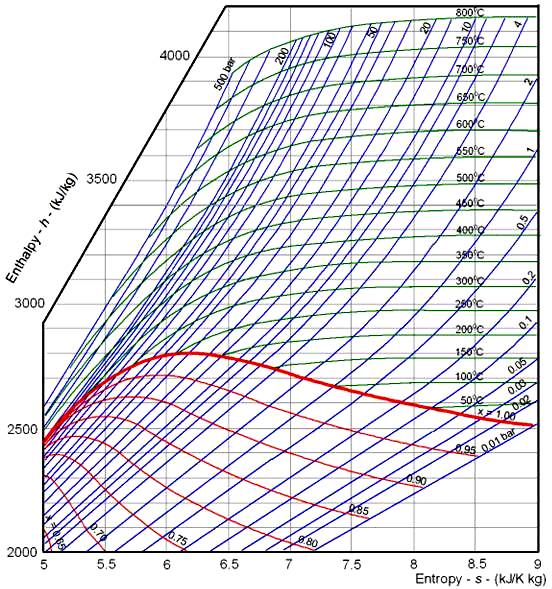
Enthalpy Entropy Chart - Web the thermodynamic arrow of time (entropy) is the measurement of disorder within a system. It is a state function. Denoted as δs δ s, the change of entropy suggests that time itself is asymmetric with respect to order of an isolated system, meaning: For the reaction \[\ce{h2}(g)+\ce{cl2}(g) \ce{2hcl}(g)\hspace{20px}δh^\circ_{298}=\mathrm{−184.6\:kj. Web the diagram below can be used to determine enthalpy versus entropy of water and steam. The standard enthalpy of formation of hcl(g) is −92.3 kj/mol. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or. Enthalpy is defined as the sum of the internal energy of a system and the product of its pressure and volume. In general, it is a relationship between enthalpy (measure of the energy of a thermodynamic system), air temperature, and moisture content. Web the standard free energy of formation of a compound can be calculated from the standard enthalpy of formation (δh ∘ f) and the standard entropy of formation (δs ∘ f) using the definition of free energy: The mollier diagram is a graph used in thermodynamics to visualize the relationships between temperature, pressure, specific volume, enthalpy, and entropy of a substance. The state of the compound is specified by the following symbols: A system will become more disordered, as time increases. Web for now, we will just look at enthalpy. It is denoted by the symbol e. For the reaction \[\ce{h2}(g)+\ce{cl2}(g) \ce{2hcl}(g)\hspace{20px}δh^\circ_{298}=\mathrm{−184.6\:kj. These lines extend at an angle from the saturated vapor line. Units used to express enthalpy are calorie, btu, or joules. Web what is the enthalpy change for the reaction of 1 mole of h 2 (g) with 1 mole of cl 2 (g) if both the reactants and products are at standard state conditions?. Enthalpy is the heat content of a system. Web the thermodynamic arrow of time (entropy) is the measurement of disorder within a system. Major players in developing the second law. Web a standard enthalpy of formation is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most. Web for now, we will just look at enthalpy. Denoted as δs δ s, the change of entropy suggests that time itself is asymmetric with respect to order of an isolated system, meaning: The state of the compound is specified by the following symbols: Web the thermodynamic arrow of time (entropy) is the measurement of disorder within a system. Web. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or. Enthalpy is defined as the sum of the internal energy of a system and the product of its pressure and volume. For the reaction \[\ce{h2}(g)+\ce{cl2}(g) \ce{2hcl}(g)\hspace{20px}δh^\circ_{298}=\mathrm{−184.6\:kj. Web what is the enthalpy change for the reaction of 1 mole of h 2 (g). A system will become more disordered, as time increases. Enthalpy is the heat content of a system. The enthalpy change of a reaction is roughly equivalent to the amount of energy lost or gained during the reaction. Web what is the enthalpy change for the reaction of 1 mole of h 2 (g) with 1 mole of cl 2 (g). In general, it is a relationship between enthalpy (measure of the energy of a thermodynamic system), air temperature, and moisture content. Web the figures and tables below shows how water enthalpy and entropy changes with temperature (°c and °f) at water saturation pressure (which for practicle use, gives the same result as atmospheric pressure at temperatures < 100 °c (212°f)).. Major players in developing the second law. Denoted as δs δ s, the change of entropy suggests that time itself is asymmetric with respect to order of an isolated system, meaning: In general, it is a relationship between enthalpy (measure of the energy of a thermodynamic system), air temperature, and moisture content. It is a state function. Web the diagram. Web the thermodynamic arrow of time (entropy) is the measurement of disorder within a system. It is a state function. Web the standard free energy of formation of a compound can be calculated from the standard enthalpy of formation (δh ∘ f) and the standard entropy of formation (δs ∘ f) using the definition of free energy: Units used to. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or. Enthalpy is defined as the sum of the internal energy of a system and the product of its pressure and volume. The state of the compound is specified by the following symbols: Enthalpy is the heat content of a system. It is. Web what is the enthalpy change for the reaction of 1 mole of h 2 (g) with 1 mole of cl 2 (g) if both the reactants and products are at standard state conditions? Web the figures and tables below shows how water enthalpy and entropy changes with temperature (°c and °f) at water saturation pressure (which for practicle use, gives the same result as atmospheric pressure at temperatures < 100 °c (212°f)). Enthalpy is defined as the sum of the internal energy of a system and the product of its pressure and volume. Web the diagram below can be used to determine enthalpy versus entropy of water and steam. Most engineers understand the role units play in definition and verification of the engineering concepts, principles, equations and. Enthalpy is the heat content of a system. A system will become more disordered, as time increases. Web definition and explanation of the terms standard state and standard enthalpy of formation, with listing of values for standard enthalpy and gibbs free energy of formation, as well as standard entropy and molar heat capacity, of 370 inorganic compounds. It is denoted by the symbol e. Major players in developing the second law. For the reaction \[\ce{h2}(g)+\ce{cl2}(g) \ce{2hcl}(g)\hspace{20px}δh^\circ_{298}=\mathrm{−184.6\:kj. Web the standard free energy of formation of a compound can be calculated from the standard enthalpy of formation (δh ∘ f) and the standard entropy of formation (δs ∘ f) using the definition of free energy: Web the thermodynamic arrow of time (entropy) is the measurement of disorder within a system. The mollier diagram is a graph used in thermodynamics to visualize the relationships between temperature, pressure, specific volume, enthalpy, and entropy of a substance. The standard enthalpy of formation of hcl(g) is −92.3 kj/mol. In general, it is a relationship between enthalpy (measure of the energy of a thermodynamic system), air temperature, and moisture content.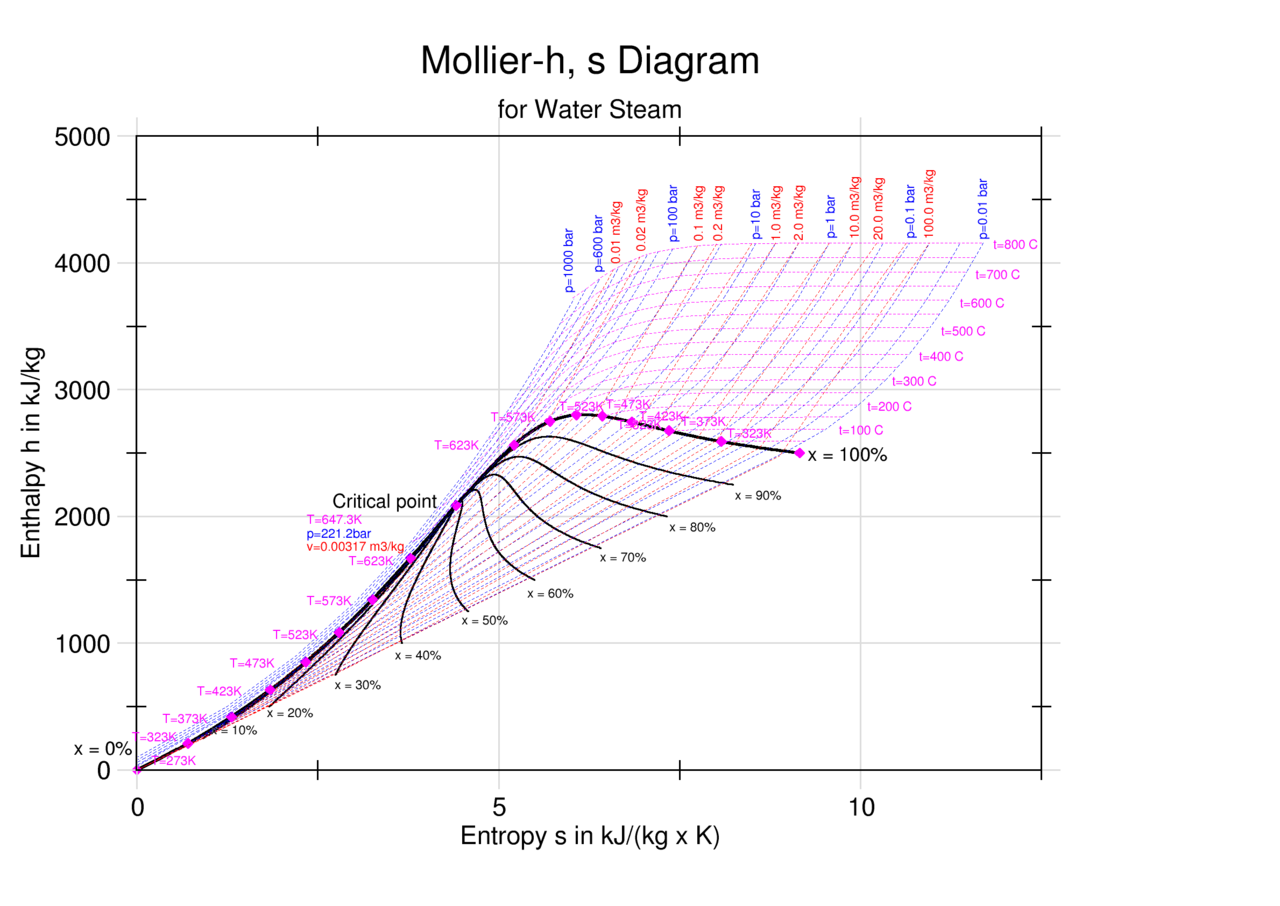
Enthalpy Entropy (hs) or Mollier Diagram
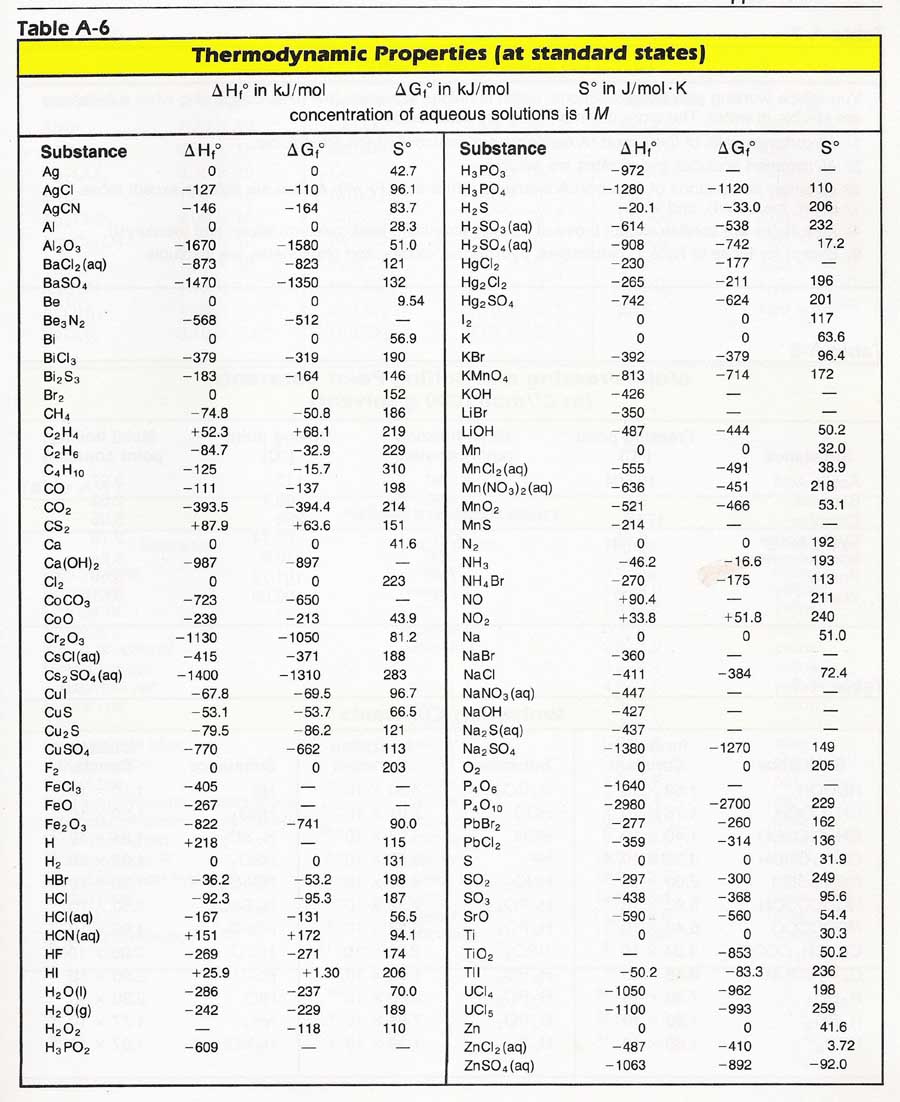
Entropy Table
Enthalpy And Entropy Pdf flavilen
Enthalpy And Entropy Chart
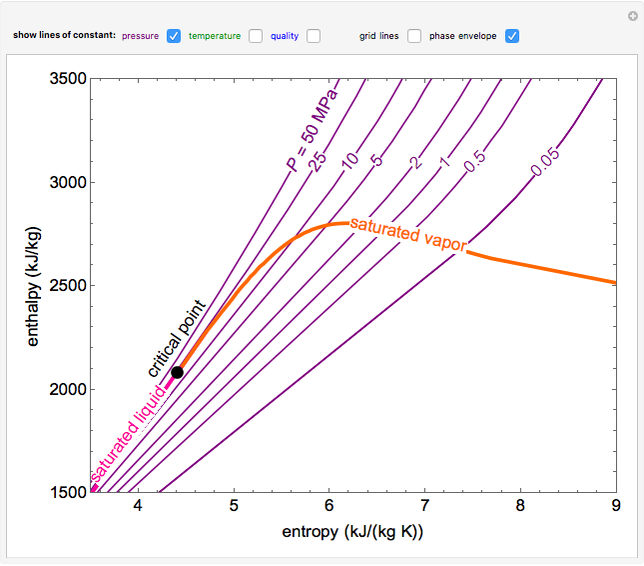
enthalpyentropydiagramforwater LearnChemE

Entropy And Enthalpy Chart
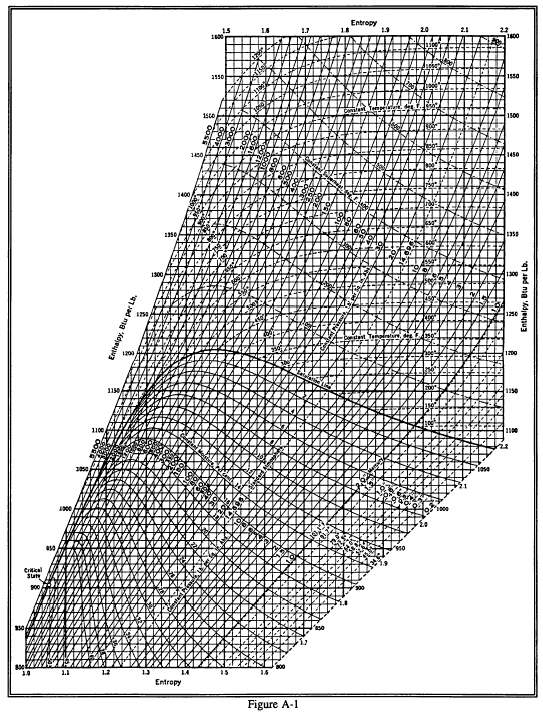
Enthalpy Entropy (hs) or Mollier Diagram Engineers Edge www
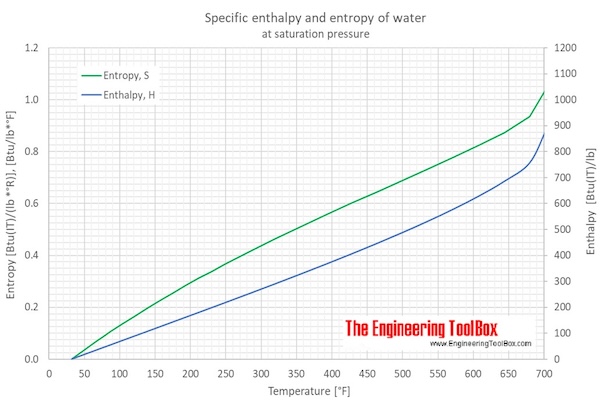
Water Enthalpy and Entropy vs. Temperature

Enthalpy And Entropy Chart
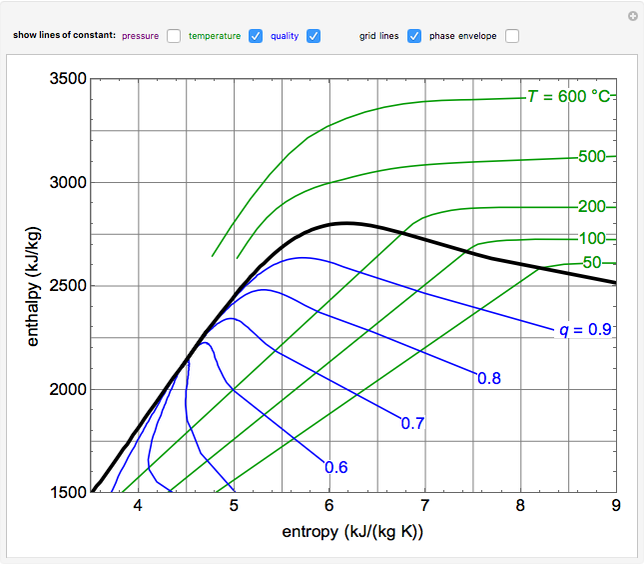
EnthalpyEntropy Diagram for Water Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Denoted As Δs Δ S, The Change Of Entropy Suggests That Time Itself Is Asymmetric With Respect To Order Of An Isolated System, Meaning:
These Lines Extend At An Angle From The Saturated Vapor Line.
Web A Standard Enthalpy Of Formation Is An Enthalpy Change For A Reaction In Which Exactly 1 Mole Of A Pure Substance Is Formed From Free Elements In Their Most Stable States Under Standard State Conditions.
A Reaction Is Favored If The Enthalpy Of The.
Related Post: