Draw An Angle In Standard Position
Draw An Angle In Standard Position - Use linear and angular speed to describe motion on a circular path. Web very generally, drawing angles in standard position will follow much of the same steps. Emphasis is on reference angle, principle angle and coterminal angle. Y = 0 0 ≤ x ≤ r. The terminal ray is the terminal side of the angle. Y = tan a x r cos a ≤ x ≤ 0. 1.1k views 1 year ago angles. Convert between degrees and radians. This video shows how to draw angles in standard position. Given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position. Properly defining an angle first requires that we define a ray. The terminal ray is the terminal side of the angle. Web very generally, drawing angles in standard position will follow much of the same steps. In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. Find the length of a circular arc. Web in this video, learn how to draw an angle in standard position through one of sophia learnings many free tutorials. Properly defining an angle first requires that we define a ray. Web draw angles in standard position. In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. Y = tan a x r cos a. If the terminal side of an angle lies on the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal angle. Y = tan a x r cos a ≤ x ≤ 0. For the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure. Find the area of a sector of a circle.. If the terminal side of an angle lies on the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal angle. A ray is a directed line segment. Web the glaser tutoring company. Converting between degrees and radians. Web drawing angles in standard position. Web learn how to draw an angle in standard position both in degrees and in radians in this math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. Find the area of a sector of a circle. Examples of drawing angles in standard position. Y = 0 0 ≤ x ≤ r. Your origin of the plane will function as the vertex. In this position, the vertex of the angle (b) is on the origin of the x and y axis. Use linear and angular speed to describe motion on a circular path. Web the glaser tutoring company. Web draw angles in standard position. If the terminal side of an angle lies on the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º. Emphasis is on reference angle, principle angle and coterminal angle. Cos at + 0 2π 2 − a 2, sin at + 0 2π 2 − a 2. Web learn how to draw an angle in radians in standard position in this video math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. Y = 0 0 ≤ x ≤ r. A ray is. For the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure. Y = 0 0 ≤ x ≤ r. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. Drawing an angle in standard position measured in degrees. Web drawing angles in standard position. Find the length of a circular arc. Convert between degrees and radians. Web very generally, drawing angles in standard position will follow much of the same steps. For the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure. Cos at + 0 2π 2 − a 2, sin at + 0 2π 2 − a 2. Web drawing angles using degrees in standard position. Convert between degrees and radians. Find the length of a circular arc. We discuss how to sketch 3 different examples. Convert between degrees and radians. Web very generally, drawing angles in standard position will follow much of the same steps. Web in trigonometry an angle is usually drawn in what is called the standard position as shown below. Express the angle measure as a fraction of 360°. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. Web drawing angles in standard position. Use linear and angular speed to describe motion on a circular path. Web drawing angles using degrees in standard position. Web draw angles in standard position. Your origin of the plane will function as the vertex. In this position, the vertex of the angle (b) is on the origin of the x and y axis. Converting between degrees and radians. We discuss what the initial ray and terminal ray. A golfer swings to hit a ball over a sand trap and onto the green. All angles in this video are measured in degrees. Find the area of a sector of a circle. Web the glaser tutoring company.
Drawing an Angle in Standard Position (degrees) YouTube
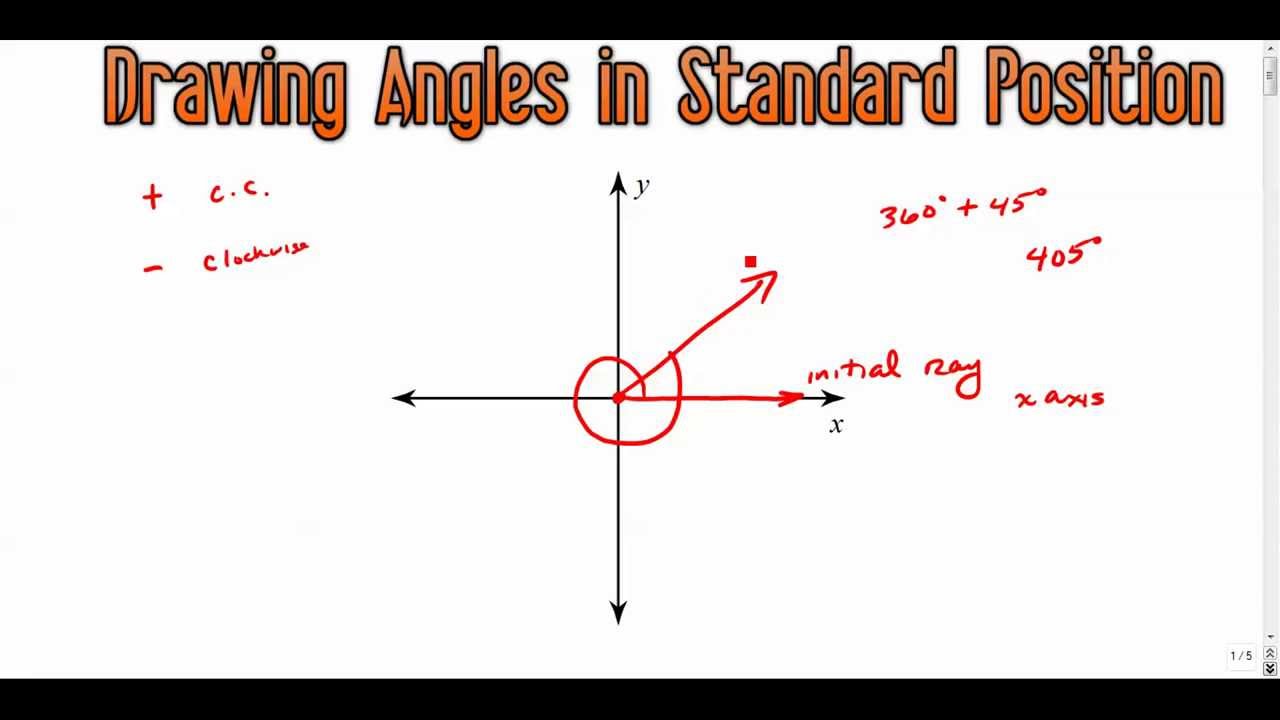
Drawing Angles in Standard Position YouTube

Draw an Angle in Standard Position (Radians & Degrees) YouTube

Angles in Standard Position Drawing & Examples Video & Lesson

Sketch Angle In Standard Position YouTube
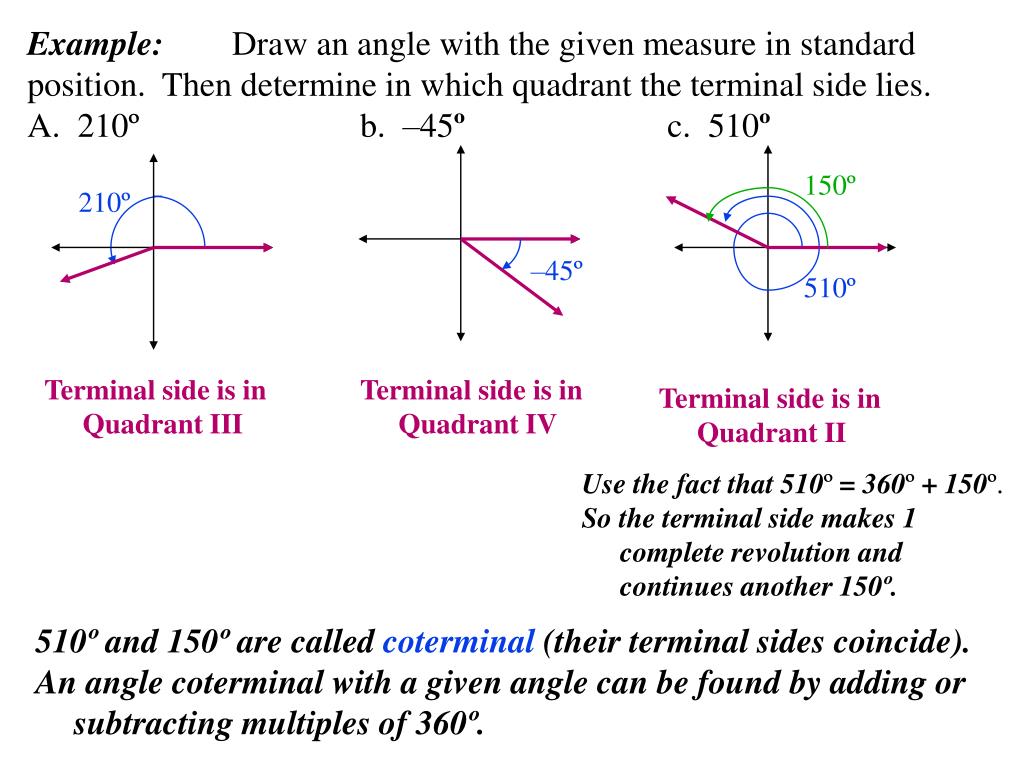
How To Draw An Angle In Standard Position With The Given Measure All
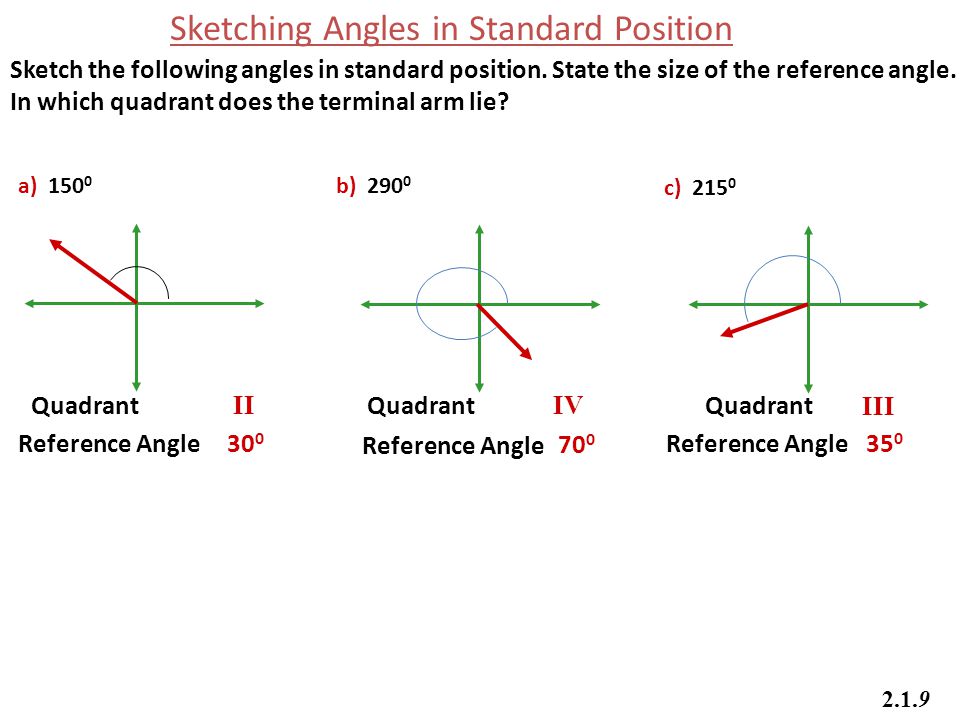
Sketch The Angle In Standard Position at Explore
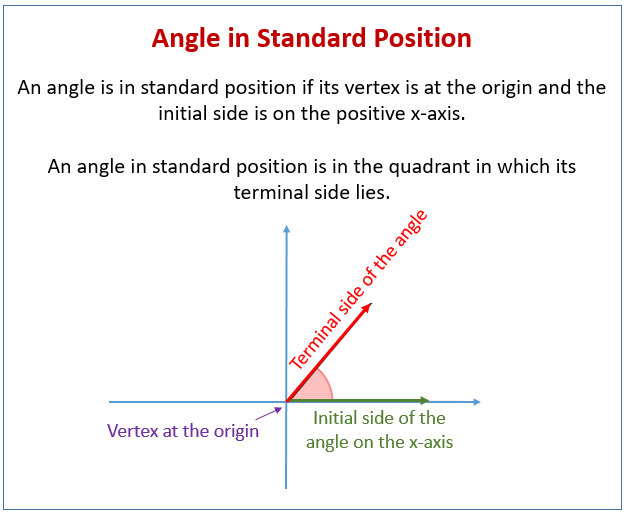
How To Draw An Angle In Standard Position With The Given Measure All

Draw an Angle in Standard Position YouTube
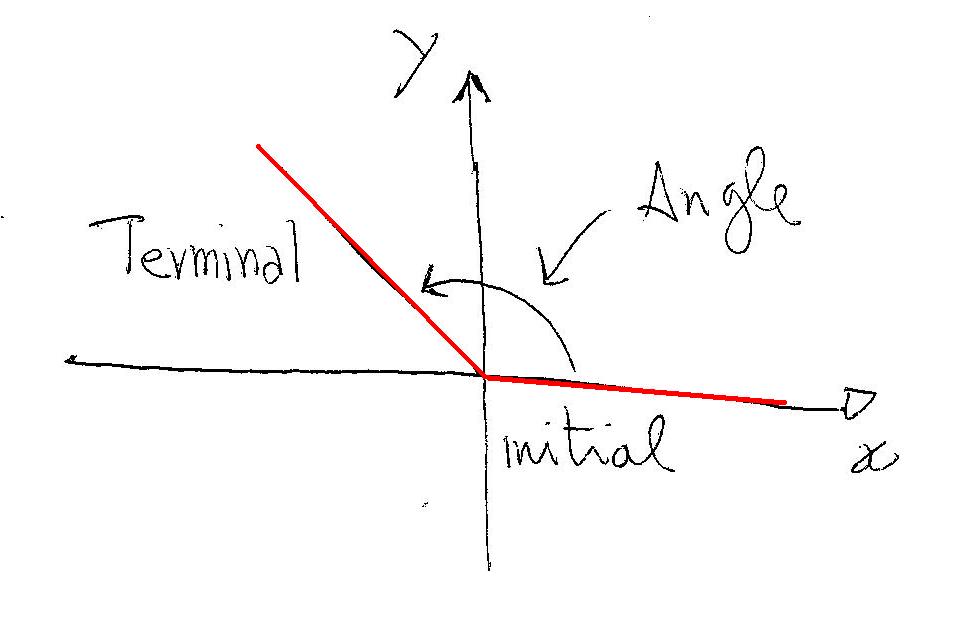
How do you draw angles of rotation in standard position? Socratic
Web Learn About The Concept Of Angle In Standard Position.
Convert Between Degrees And Radians.
Web How To Draw An Angle Of 30 Degrees In Standard Position.
T + 1 Cos At + 0 − 2Π 2 + A 2, T + 1 Sin At + 0 − 2Π 2 + A 2.
Related Post: