Cuticle Scale Patterns
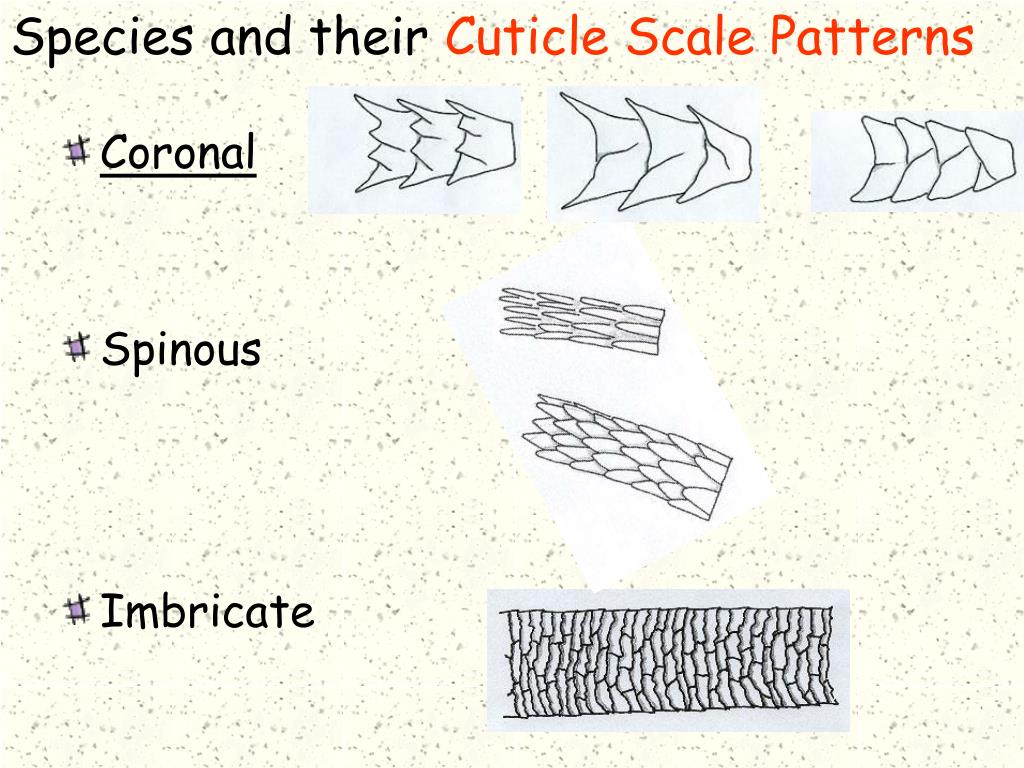
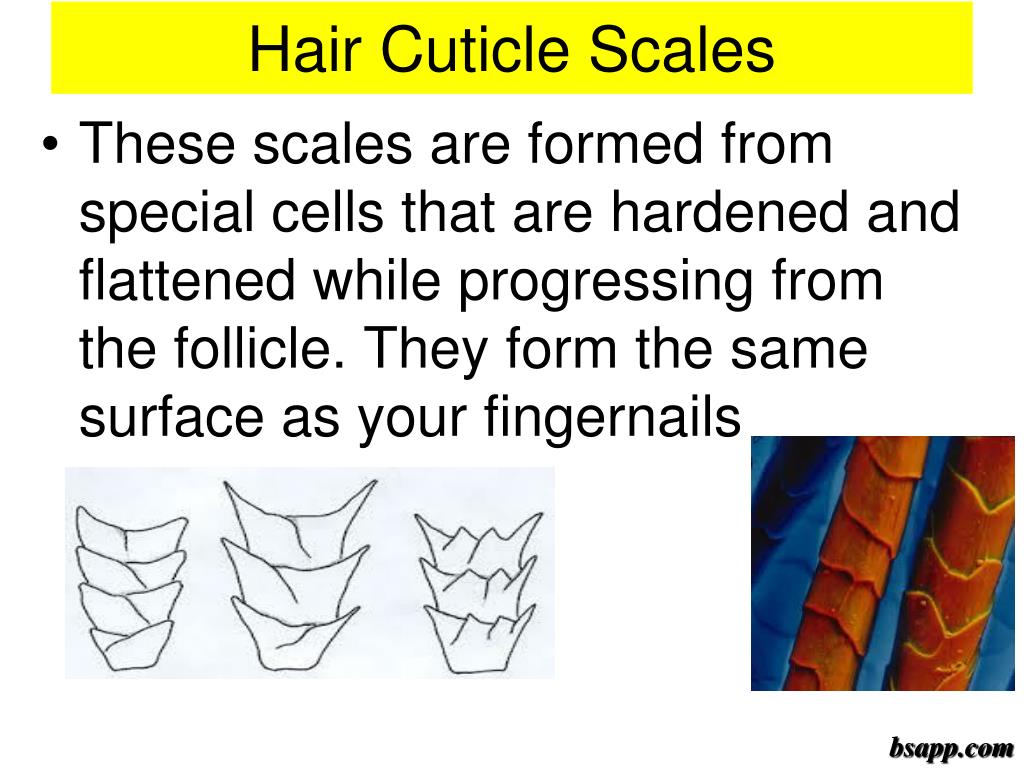
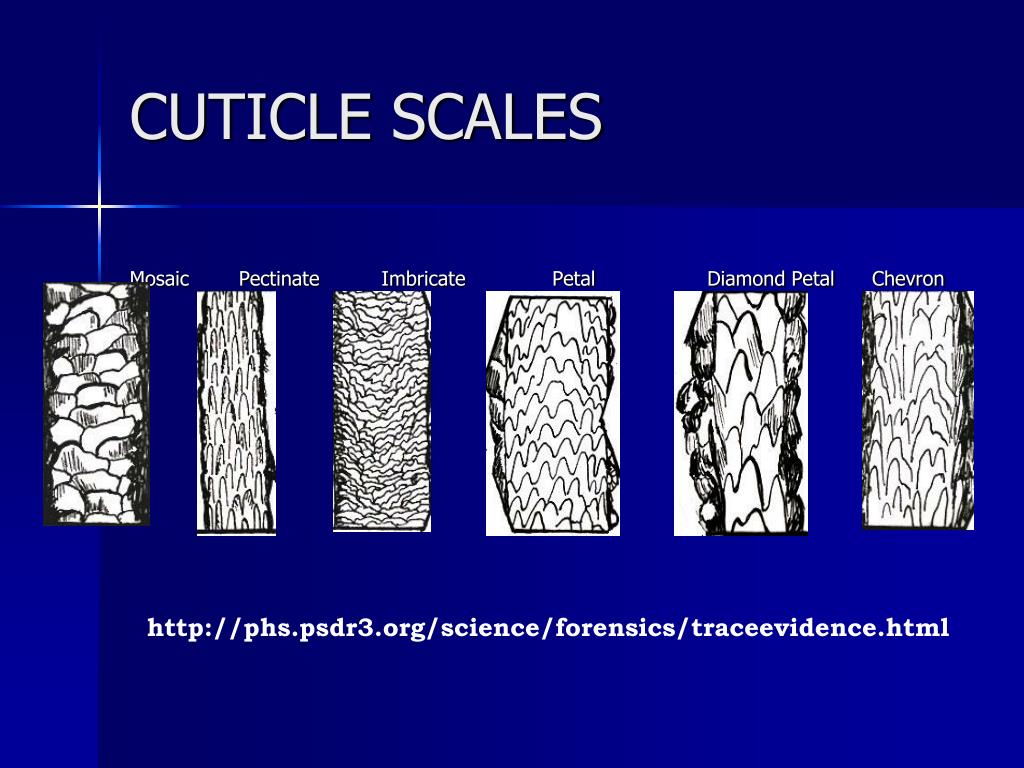
Cuticle Scale Patterns - The cortex is the main body of the shaft, and is composed of elongated, filamentous cells that grow parallel to the shaft. The hair is surrounded by the cuticle, a dead cell layer. (i) imbricate, this includes ovate, acuminate, elongate, flattened and crenate cuticles; Web three major characteristics of guard hairs were observed in our morphological analysis: In this procedure, the hair is first examined microscopically to ascertain the presence of foreign materials. Spinous scales are found in the proximal (root) region of the fur hair of some animals, including bobcat, chinchilla, fox, lynx, mink, mouse, otter, raccoon, rat, sable, sable, seal, and sea lion. Web two main patterns of cuticle scales were identified: The free edge of the cells revealed differences among domestic animals, resulting in different scaling patterns in each species. Both spinous and coronal cuticles appear in animal hair but their characteristics are significantly different. The cuticle is a translucent outer layer of the hair shaft consisting of scales covering the shaft. Spinous scales are found in the proximal (root) region of the fur hair of some animals, including bobcat, chinchilla, fox, lynx, mink, mouse, otter, raccoon, rat, sable, sable, seal, and sea lion. Web in all domestic animal species, hair was made up of three layers: Web two main patterns of cuticle scales were identified: Web mammalian hair consists of three. Making a scale casting with clear nail polish & see “microtopography” of hair. The hair is surrounded by the cuticle, a dead cell layer. The hair is composed of three concentric layers, the medulla, cortex, and cuticle of the hair, originating from the hair bulb at the base of the follicle. Web the hierarchical structure of hair in the cortex. The cuticle is a translucent outer layer of the hair shaft consisting of scales covering the shaft. The cuticle, the medulla, and the cortex. Combinations and variations of these types are possible. The free edge of the cells revealed differences among domestic animals, resulting in different scaling patterns in each species. Characteristics and comparisons of cuticle scale patterns, medulla and. Combinations and variations of these types are possible. Web mammalian hair consists of three distinct morphological units, the cuticle, the cortex and the medulla. Web the cuticle is a translucent layer of the overlapping keratin scales covering the hair shaft (deedrick & koch, 2004b), it is composed of three basic scale structures: Web based on the hair cuticle scale pattern,. The cortex is the main body of the shaft, and is composed of elongated, filamentous cells that grow parallel to the shaft. Web rapid technique for preparing hair cuticular scale casts. Characteristics and comparisons of cuticle scale patterns, medulla and pigmentation in dorsal guard hairs of domestic cat, tiger cub, tigers cub, leopard cub, and domestic dog from rajasthan are. Making a scale casting with clear nail polish & see “microtopography” of hair. Web the cuticle is the outermost of the three layers of a hair shaft, encircling the middle cortex layer and the innermost medulla. Web the hierarchical structure of hair in the cortex and cuticle. These included deedrick and koch (2004b). The cuticle, the medulla, and the cortex. Web there are three main patterns of hair cuticle and they vary depending on the organism. The proteins form intermediate filaments, which then organize into larger and larger fibres. The hair shaft is a rigid cylindrical structure which extends from the dermis or subcutaneous tissue through to the skin surface. Web though it is not possible to definitely identify a. Web based on the hair cuticle scale pattern, type and diameter of the medulla, and the pigmentation, characteristic differential features of each animal species were identified. Web 27 and at the end of each larval stage, presumably to pattern the new cuticle. Web composed mainly of keratin, it has three morphological regions: The hair is composed of three concentric layers,. Web the cuticle is the outermost of the three layers of a hair shaft, encircling the middle cortex layer and the innermost medulla. Human hair has an imbricate cuticle, which means it is flat and smooth with a flakey appearance. The cuticle is a translucent outer layer of the hair shaft consisting of scales covering the shaft. Web the cuticle. Web 27 and at the end of each larval stage, presumably to pattern the new cuticle. Both spinous and coronal cuticles appear in animal hair but their characteristics are significantly different. Hair is a characteristic attribute of mammals. And (ii) coronal, which include simple, serrate or dentate cuticles. The hair shaft is a rigid cylindrical structure which extends from the. These included deedrick and koch (2004b). Web composed mainly of keratin, it has three morphological regions: Process for obtaining a reproduciton of the shape and arrangement of the scales of a hair cuticle. Web in all domestic animal species, hair was made up of three layers: Spinous scales are found in the proximal (root) region of the fur hair of some animals, including bobcat, chinchilla, fox, lynx, mink, mouse, otter, raccoon, rat, sable, sable, seal, and sea lion. The proteins form intermediate filaments, which then organize into larger and larger fibres. Web there are three main patterns of hair cuticle and they vary depending on the organism. Web based on the hair cuticle scale pattern, type and diameter of the medulla, and the pigmentation, characteristic differential features of each animal species were identified. Hair is a characteristic attribute of mammals. Combinations and variations of these types are possible. Web the scale pattern of the cuticle in human hairs is routinely imbricate. Both spinous and coronal cuticles appear in animal hair but their characteristics are significantly different. The hair is composed of three concentric layers, the medulla, cortex, and cuticle of the hair, originating from the hair bulb at the base of the follicle. Web here we present characteristics and comparisons of cuticle scale patterns, medulla and pigmentation in dorsal guard hairs of domestic cat (felis domesticus), tiger cub (panther tigris),. The hair shaft is a rigid cylindrical structure which extends from the dermis or subcutaneous tissue through to the skin surface. The cuticle is relatively thin but highly keratinized, consisting of a single layer of overlapping keratinocytes (a.k.a.
PPT Hair PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3531073

PPT Hair Analysis Part I PowerPoint Presentation, free download

PPT Hair Evidence PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3531546

Arrangement pattern of hair cuticle scales in the medium part of a
Hair Under a Microscope Rs' Science
PPT Hairs, Fibers, and Paint PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Forensic Science PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5822230
PPT Hair Analysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3531003

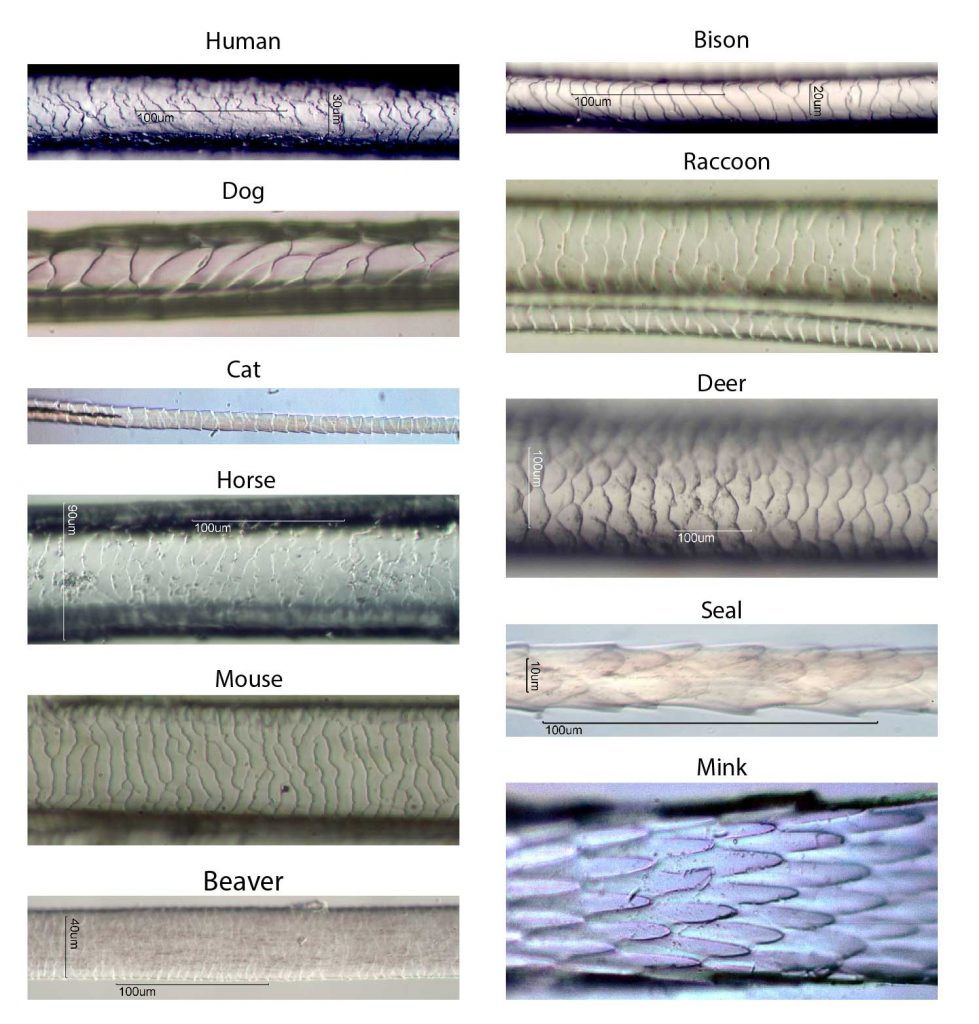
Cuticle classification system used in our hair key to identify wild and

Arrangement pattern of hair cuticle scales in the medium part of a
In This Procedure, The Hair Is First Examined Microscopically To Ascertain The Presence Of Foreign Materials.
The Cuticle Pattern, The Medullar Pattern Along All The Length Of The Shaft, And The Medullar Margins In The Thickest Part Of The Shield Region.
The Cuticle, The Medulla, And The Cortex.
The Shape Of The Hair Shaft Is Also More Variable In Animal Hairs.
Related Post: