Countersink Dimensions Chart
Countersink Dimensions Chart - Web please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. Web how the show and chart below to determine how dimensions to using, show dimensions are inches millimetres apart from the countersink angle. Web unsure on what size countersunk hole to use for your ansi metric socket flat head fasteners? This short post will give you the exact dimensions you need for your countersunk screws. Understand the types and use of countersink drill bit, countersink vs counterbore hole and check out the countersink size chart for holes/bits. First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see the left side of the chart). Web the graphic above shows how to fully define a countersink — the 3 dimensions needed to properly define a countersink are: For example, an ansi metric m4 machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 4.5 mm, a countersunk diameter of 9.4 mm, and a countersunk angle of 90°. In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in inches apart from the countersink angle. Web this chart shows the dimensions of counterbore and countersink holes for different screw sizes, in metric units (millimeters). Choose from a variety of standard countersink options, which can either be formed or machined into sheet part parts. Web please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. Web countersunk socket head screws metric. Web use the image. Machined countersinks are created with a drill press and formed countersinks are made with punch press tooling—the best option depends on your project and part geometry. In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. Web use the image and. Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in inches apart from the countersink angle. Web just as with counterbore and spotface hole features, dimensions for a countersink are also listed directly below the dimension of the smaller coaxial hole. Web a countersink is dimensioned by specifying the diameter of the countersink. For example, an ansi metric m4 machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 4.5 mm, a countersunk diameter of 9.4 mm, and a countersunk angle of 90°. Web a countersink is dimensioned by specifying the diameter of the countersink where it meets the surface and the included angle. Countersink diameter (this should. A screw placed in a countersunk hole is located by the angle. For example, an ansi inch 9/16″ 82 degree machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 5/8″, a countersunk diameter of 1″, and a countersunk angle of 82°. Over 1” over 2 1/2” diameter to 1” to 2 1/2” to 6”.. It is considered good practice to countersink or break the edges of holes that are smaller than f (max.) in parts having a hardness which approaches, equals, or exceeds the screw hardness. Web countersink depth is the depth of a countersink hole, which is a conical hole cut into a material to allow the head of a countersunk screw or. Web how the show and chart below to determine how dimensions to using, show dimensions are inches millimetres apart from the countersink angle. For example, an ansi inch 9/16″ 100 degree machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 5/8″, a countersunk diameter of 1 10/69″, and a countersunk angle of 100°. Web. Web countersunk socket head screws metric. Countersink depth is typically measured from the surface of the material to the bottom of the countersink hole. Web please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. Web unsure on what size countersunk hole to use for your ansi metric socket flat head fasteners? It is considered good practice to countersink. Web please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. However, it is always essential to consult the specific fastener manufacturer’s guidelines and reference the appropriate standards for accurate. In the charts that follow, the theoretical sharp diameter represents the diameter of countersink that will place maximum material condition screwhead flush to the surface of a flat part. Web how the show and chart below to determine how dimensions to using, show dimensions are inches millimetres apart from the countersink angle. Web a countersink is dimensioned by specifying the. Choose from a variety of standard countersink options, which can either be formed or machined into sheet part parts. Countersunk screws are simply characterized by their flat head, which allows them to sink into objects and materials. Web use the image and chart below to determine what dimensions to use, all dimensions are in inches apart from the countersink angle. Web please note that this chart provides general guidelines and recommended dimensions. What controls the location of the screw? Web unsure on what size countersunk hole to use for your ansi metric socket flat head fasteners? For example, an ansi inch 9/16″ 100 degree machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 5/8″, a countersunk diameter of 1 10/69″, and a countersunk angle of 100°. Web countersink depth is the depth of a countersink hole, which is a conical hole cut into a material to allow the head of a countersunk screw or bolt to be flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material. Web unsure on what size countersunk hole to use for your ansi inch socket flat head fasteners? This is the nominal diameter of the countersink for the fastener. For example, an ansi metric m4 machine screw with a normal fit countersunk hole will require a pilot hole diameter of 4.5 mm, a countersunk diameter of 9.4 mm, and a countersunk angle of 90°. First, you must select the screw size you're working with (see the left side of the chart). Understand the types and use of countersink drill bit, countersink vs counterbore hole and check out the countersink size chart for holes/bits. Web a countersink is dimensioned by specifying the diameter of the countersink where it meets the surface and the included angle. This short post will give you the exact dimensions you need for your countersunk screws. This short post will give you the exact dimensions you need for your countersunk screws.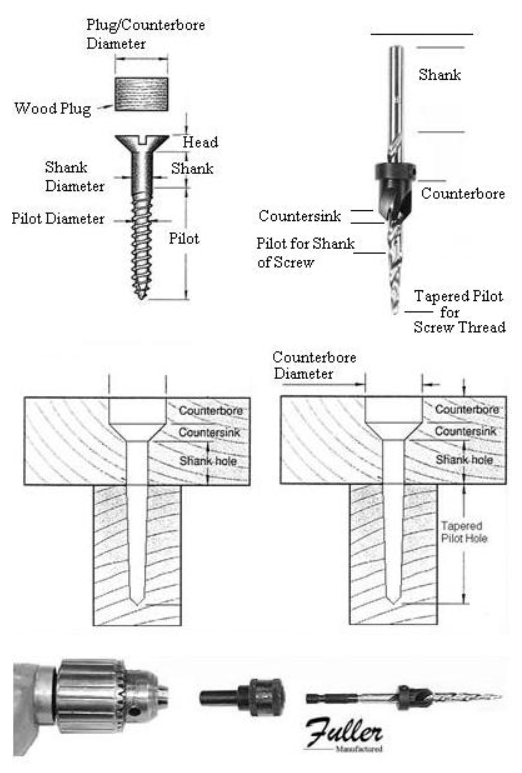
Countersink drill size chart Jamestown Distributors
![]()
DIN 7991 Dimensions Beacon Corporation
Countersink Size Chart Flat Head
HSM Machining

Countersink Drill Size Chart Drill, Chart, Home improvement

Standard Countersunk Hole Diameters Home Interior Design
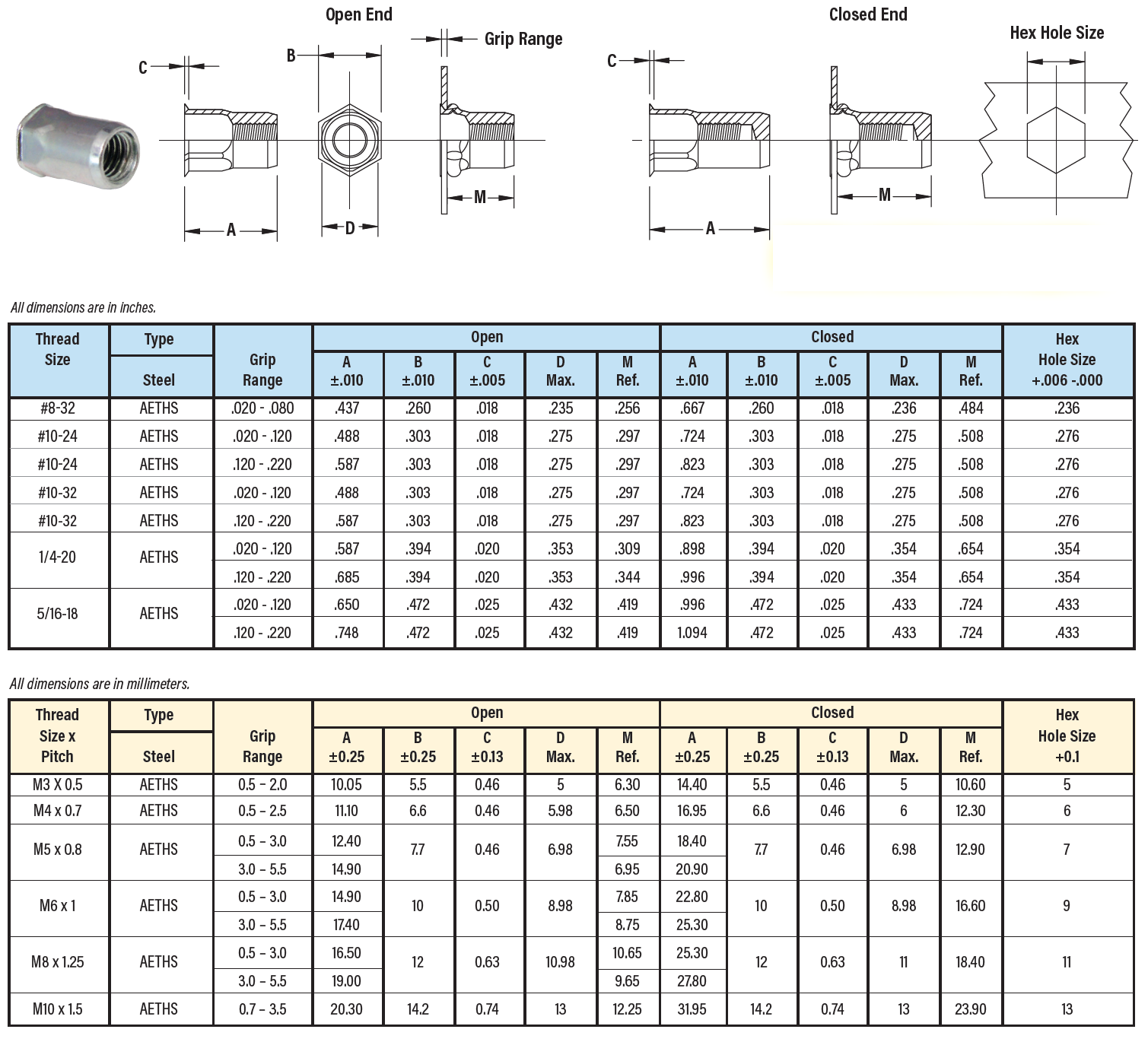
Counterbore and Countersink Dimensions Chart
Countersunk Hole Size for Machine Screw (ANSI Metric)
Metric Countersunk Hole Sizes Home Interior Design

Metric Countersink Dimensions Chart
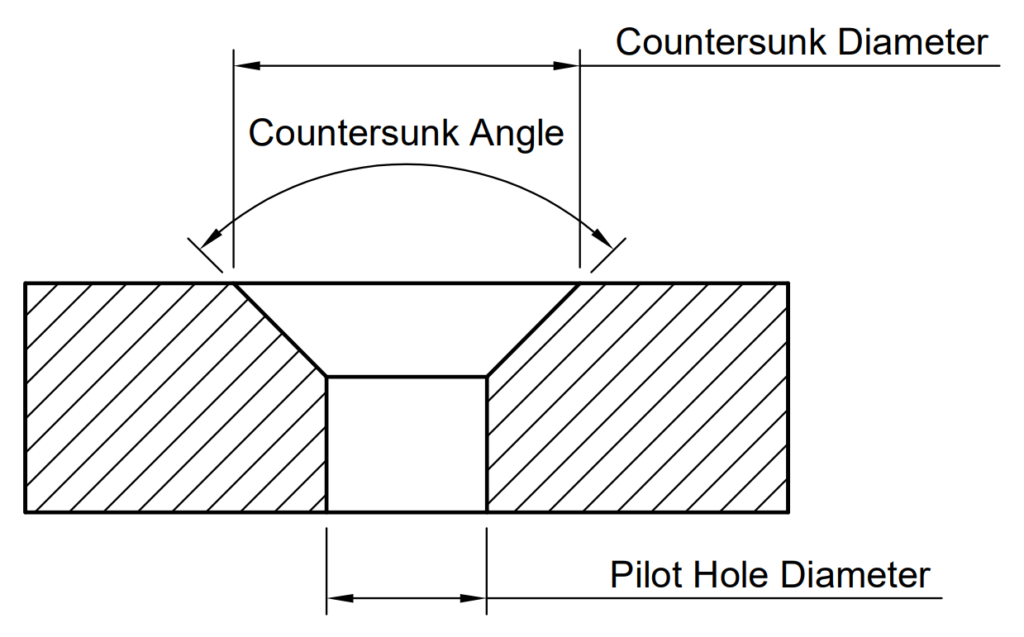
Countersink Diameter (This Should Be Larger Than The Diameter Of The Screw Head) Countersink Angle (This Is A Standard Per The Type Of Fastener That Is Being Used, More On This Below)
Web Use The Image And Chart Below To Determine What Dimensions To Use, All Dimensions Are In Inches Apart From The Countersink Angle.
Controlled Angle Under The Head Ensures Maximum Flushness And Side Wall Contact.
In The Above Example, The Part Has A 0.5 Thru Hole And A Countersink With A.
Related Post:
