Cholestatic Pattern Lfts
Cholestatic Pattern Lfts - 1, 2 hepatobiliary diseases with cholestasis from various causes are called cholestatic liver diseases, and cholestasis itself further aggravates liver damage in these patients. Upper limit of normal alt. Web hyperbilirubinemia may occur as disease progresses, and may lead to liver cirrhosis, liver failure, or even death. Intrahepatic cholestasis is caused by defects in bile canaliculi, hepatocellular function, or intrahepatic bile ducts. Web last update 26th jan 2021. Symptoms (if present) of dark urine or pruritus early during course. Each pattern has a specific differential, which can help narrow the differential diagnosis when combined with the clinical history and imaging findings. Often asymptomatic and diagnosed on labs. Cholestatic liver disease results from insufficient bile synthesis, secretion and/or flow through the biliary tract. Causes of an increased alp. No reliable autoantibodies have been identified and the diagnosis of psc is usually made on cholestatic liver biochemistry and typical magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography appearances of intra. Compared to hepatocellular injury, mixed pattern of dili is associated with more benign outcomes. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Causes of an increased alp. How can i recognize. Web < prev next > mixed hepatitis. 1, 2 hepatobiliary diseases with cholestasis from various causes are called cholestatic liver diseases, and cholestasis itself further aggravates liver damage in these patients. Web typically, psc causes a chronically abnormal and fluctuant liver function tests (lfts) with a cholestatic pattern (raised alp and ggt). Web determine the pattern of lft derangement. No. Web although the term liver function tests (lfts) is used commonly, it is imprecise and potentially misleading since many of the tests reflecting the health of the liver are not direct measures of its function. Upper limit of normal alt. Liver function tests (lfts) are useful blood tests to help identify liver disease, but their interpretation can be challenging. Web. The ast:alt ratio may be helpful in determining both the aetiology and the stage of liver disease (see main text). No reliable autoantibodies have been identified and the diagnosis of psc is usually made on cholestatic liver biochemistry and typical magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography appearances of intra. Compared to hepatocellular injury, cholestatic dili is more likely to result in chronicity of. Web most of the disease entities can be categorized into hepatocellular or cholestatic patterns, with characteristic traits on liver blood tests. Compared to hepatocellular injury, cholestatic dili is more likely to result in chronicity of insult. Web although the term liver function tests (lfts) is used commonly, it is imprecise and potentially misleading since many of the tests reflecting the. Web using a schematic approach that classifies enzyme alterations as predominantly hepatocellular or predominantly cholestatic, we review abnormal enzymatic activity within the 2 subgroups, the most common causes of enzyme alteration and suggested initial investigations. Often asymptomatic and diagnosed on labs. Isolated hyperbilirubinemia is defined as an elevation of bilirubin with normal alkaline phosphatase and ast/alt levels. 1, 2 hepatobiliary. Web although the term liver function tests (lfts) is used commonly, it is imprecise and potentially misleading since many of the tests reflecting the health of the liver are not direct measures of its function. Intrahepatic cholestasis is caused by defects in bile canaliculi, hepatocellular function, or intrahepatic bile ducts. Web < prev next > mixed hepatitis. Often asymptomatic and. Web last update 26th jan 2021. Web an elevation in alp and bilirubin in disproportion to alt and ast would characterize a cholestatic pattern. No reliable autoantibodies have been identified and the diagnosis of psc is usually made on cholestatic liver biochemistry and typical magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography appearances of intra. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg. Intrahepatic cholestasis is caused by defects in bile canaliculi, hepatocellular function, or intrahepatic bile ducts. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. In contrast, causes of extrahepatic cholestasis affect the extrahepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, or common bile duct. Web determine the pattern of lft derangement. Web most of the disease entities can be categorized into. Web differentiates cholestatic from hepatocellular liver injury, recommended by acg guidelines. Liver function tests (lfts) are useful blood tests to help identify liver disease, but their interpretation can be challenging. Web determine the pattern of lft derangement. 1, 2 hepatobiliary diseases with cholestasis from various causes are called cholestatic liver diseases, and cholestasis itself further aggravates liver damage in these. Cholestatic pattern of serum enzyme elevations ( r value <2), with alk p levels greater than 3 times uln (>345 u/l) at the time of peak alt or bilirubin elevation. The pattern of alt to alp rise can indicate whether the pathology is primarily cholestatic or hepatocellular: Cholestatic liver disease results from insufficient bile synthesis, secretion and/or flow through the biliary tract. Web although the term liver function tests (lfts) is used commonly, it is imprecise and potentially misleading since many of the tests reflecting the health of the liver are not direct measures of its function. Use the first lab values (alt and alp) indicating acute liver injury to calculate the r factor. A mixed injury pattern is defined as an elevation of alkaline phosphatase and ast/alt levels. How can i recognize a cholestatic pattern? Web < prev next > mixed hepatitis. Web last update 26th jan 2021. A mixed injury pattern is defined as an elevation of alkaline phosphatase and ast/alt levels. These include the hepatocellular pattern, the cholestatic pattern, and the isolated hyperbilirubinemia pattern. 1, 2 hepatobiliary diseases with cholestasis from various causes are called cholestatic liver diseases, and cholestasis itself further aggravates liver damage in these patients. Compared to hepatocellular injury, mixed pattern of dili is associated with more benign outcomes. No reliable autoantibodies have been identified and the diagnosis of psc is usually made on cholestatic liver biochemistry and typical magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography appearances of intra. Web determine the pattern of lft derangement. Web most of the disease entities can be categorized into hepatocellular or cholestatic patterns, with characteristic traits on liver blood tests.
Liver Failure Case

Pin on Infographics

PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175

PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175
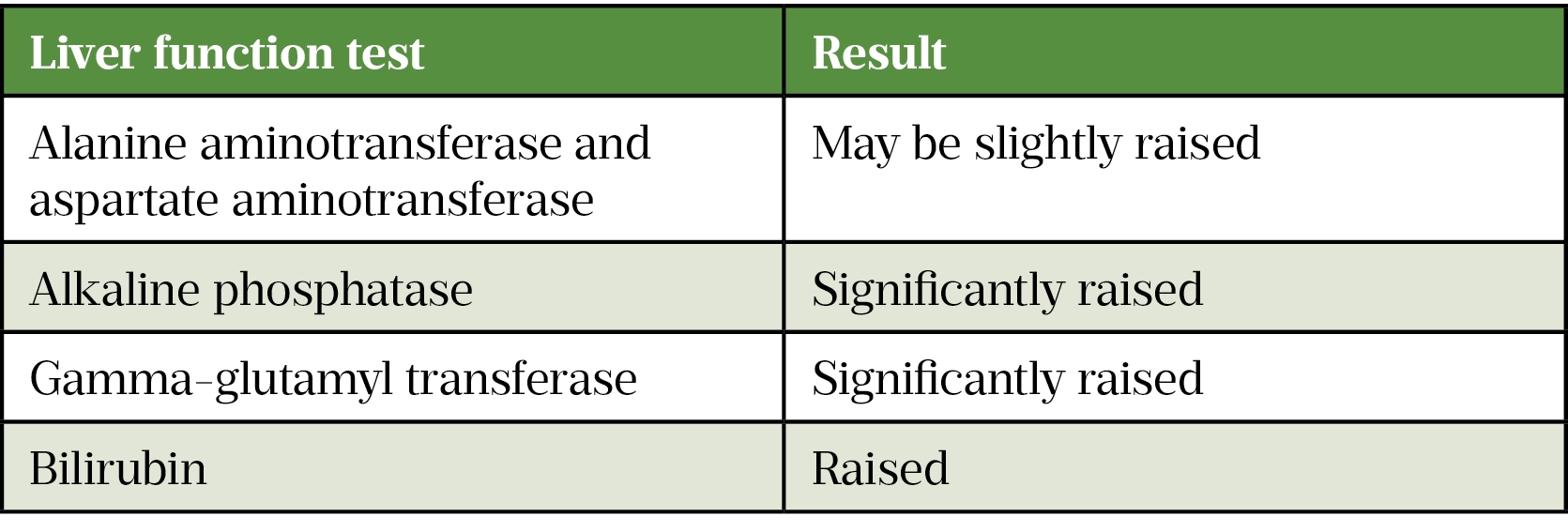
Liver function tests indication and interpretation The

Liver function tests in primary care bpacnz
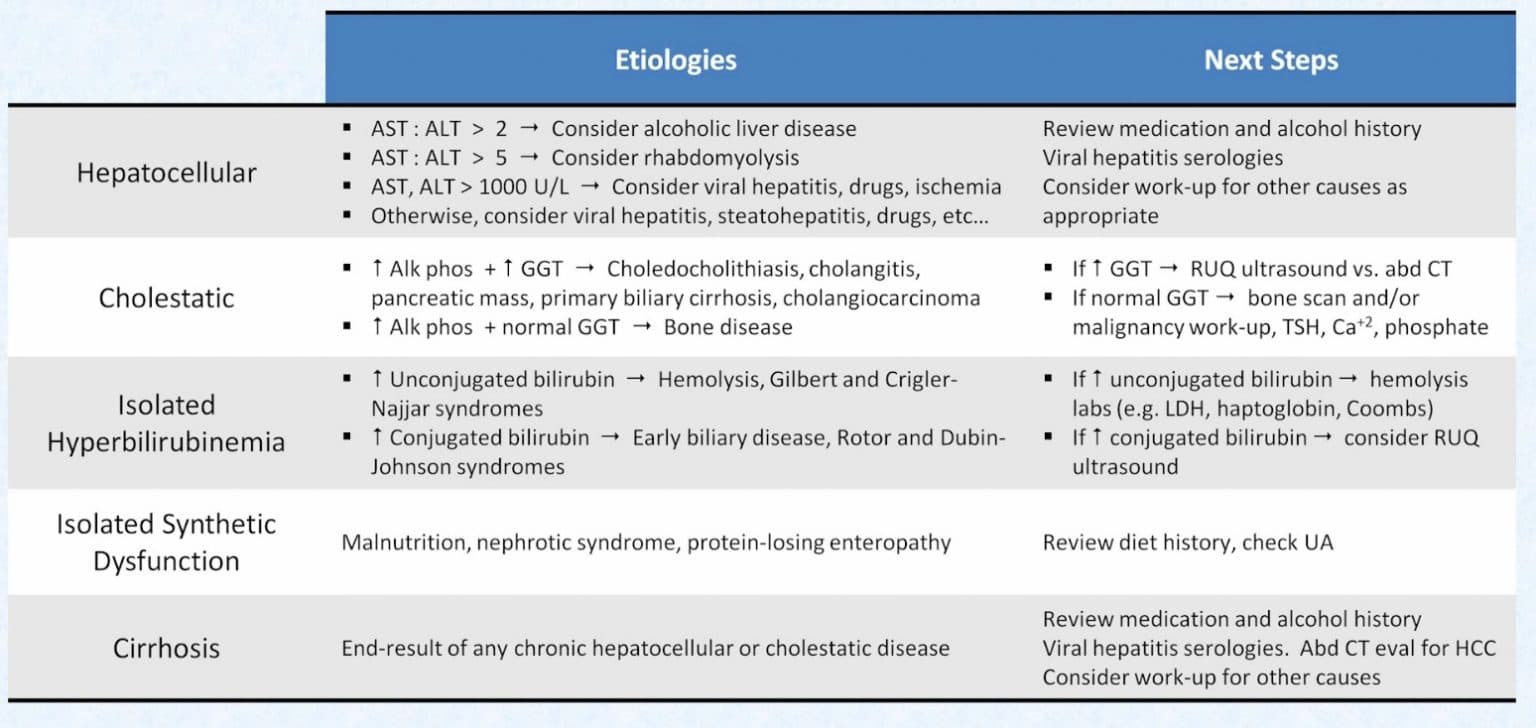
Liver Function Test (LFTs) Normal values, when to order
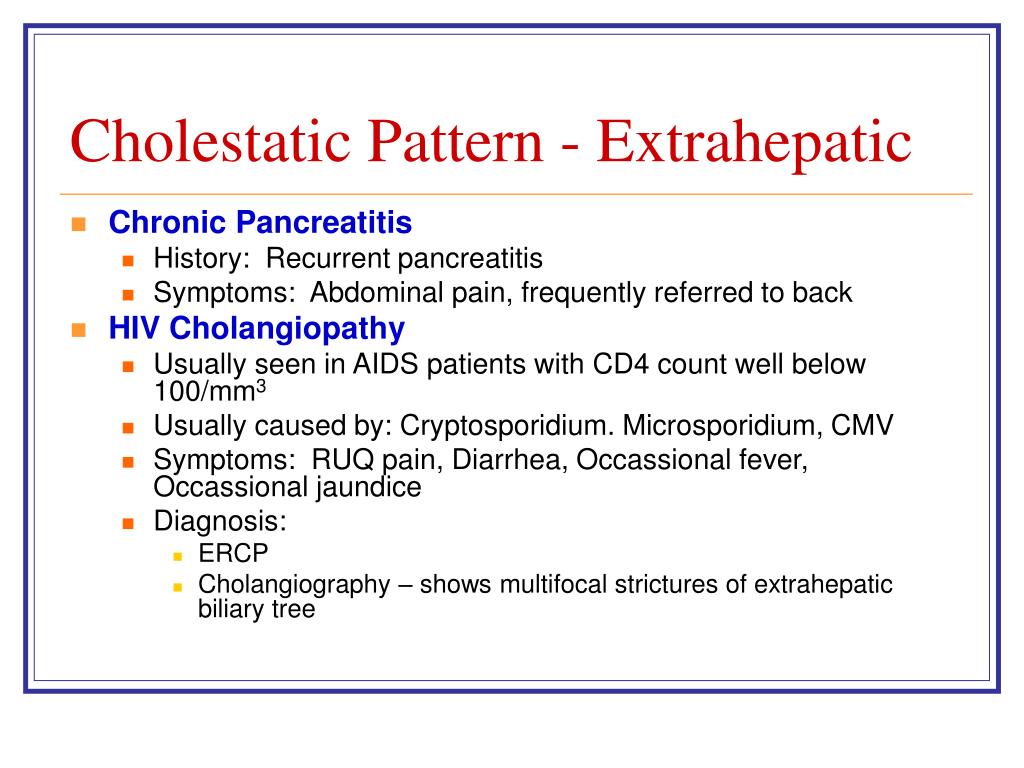
PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175

PPT Abnormal LFTs PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID139175

LFTs explained Emergency Medicine Kenya Foundation
Web Differentiates Cholestatic From Hepatocellular Liver Injury, Recommended By Acg Guidelines.
Each Pattern Has A Specific Differential, Which Can Help Narrow The Differential Diagnosis When Combined With The Clinical History And Imaging Findings.
The Course Of Drug Induced Liver Injury Is Considered Mixed If Features Of Both Hepatocellular (Acute Hepatitis) And Cholestatic Injury (Cholestatic Hepatitis) Are Present.
Upper Limit Of Normal Alt.
Related Post: