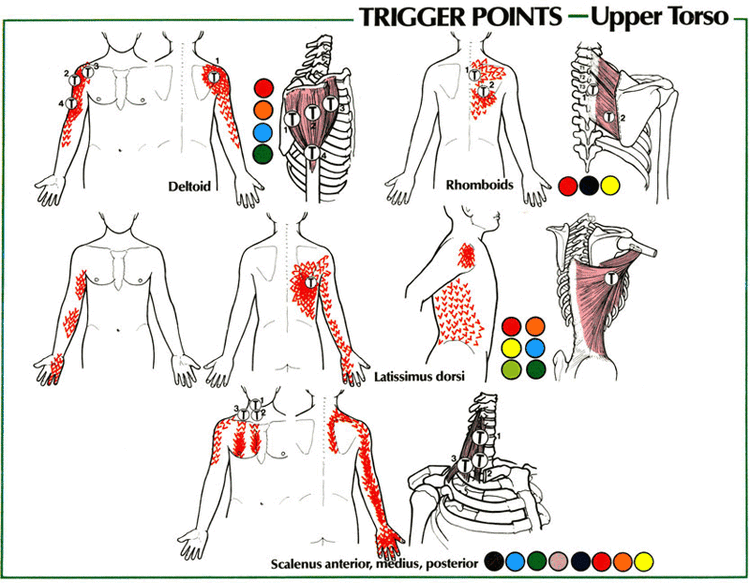
Cervical Facet Referral Patterns
Cervical Facet Referral Patterns - Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. O do not cross to the other side. Web consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Each facet joint can refer pain to a number of locations, with a great deal of overlap between the different levels. A comprehensive recognition of referred pain is important for clinicians when dealing with it. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below. Web diagnostic positive facet joint block can indicate facet joints as the source of chronic spinal pain. Identify tender areas under fluoroscopy. Web in a study of 5 such subjects, joint pain referral patterns were mapped out. The most common areas of referred pain from the lumbar facets are noted in black (low back) in descending order to the lightest regions (foot is least common). The most commonly affected cervical spine levels are c5, c6 and c7. (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. Web each joint has a distinct referral pattern illustrated below.. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. Web referral patterns for cervical facet joint pains, as described by various investigators [17, 19, 20]. O parasagittal cervical and cervicothoracic pain. Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to. Injury to the joint is not commonly detected by conventional radiographic studies. (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. Web the“pseudoradicular” referral patterns of the lumbar facet joints may mimic the pain felt from a herniated disc and may make differentiating between the two conditions difficult. Web cervical facet‐joint capsules are sources of neck pain.1 x dwyer. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. O do not cross to the other side. Web in the cervical spine the ivd and facet joints are innervated by the same spinal segment, making it difficult to determine whether both structures are implicated as the source of nociception, or, if one structure is sensitised through means of.. What clinical findings, specifically the results of examination and diagnostic injections, can help differentiate shoulder pathology from. The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding of referred pain, including its pathogenesis, characteristics, diagnosis,. The most commonly affected cervical spine levels are c5, c6 and c7. These patients may benefit from specific interventions to eliminate facet joint pain. The facet joints are small joints located between the neck vertebrae, which help to provide stability and facilitate movement. Each facet joint can refer pain to a number of locations, with a great deal of overlap between the different levels. Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. O do not/rarely. These patients may benefit from specific interventions to eliminate facet joint pain such as neurolysis, by radiofrequency or cryoablation. Injury to the joint is not commonly detected by conventional radiographic studies. Web cervical facet‐joint capsules are sources of neck pain.1 x dwyer et al.2 established pain patterns of the cervical facet joints. Match pain distribution with pain referral patterns. Striped. O parasagittal cervical and cervicothoracic pain. A thoough understanding of the mechanism of injury is essential. Web in the cervical spine the ivd and facet joints are innervated by the same spinal segment, making it difficult to determine whether both structures are implicated as the source of nociception, or, if one structure is sensitised through means of. O do not. Striped areas (hash marks) represent overlapping cervical facet joint pain maps. The purpose of this study is to summarize the current understanding of referred pain, including its pathogenesis, characteristics, diagnosis,. + response to facet interventions: The most common areas of referred pain from the lumbar facets are noted in black (low back) in descending order to the lightest regions (foot. Web understanding the relevant anatomy and referral patterns of cervical facet joints allows for more targeted diagnosis and treatment. O do not/rarely cause midline cervical pain or arm pain. Injury to the joint is not commonly detected by conventional radiographic studies. Web we use our knowledge of joint open and closing patterns, of ivd loading positions, aggravating and easing positions. + response to facet interventions: Each facet joint can refer pain to a number of locations, with a great deal of overlap between the different levels. Web in the cervical spine the ivd and facet joints are innervated by the same spinal segment, making it difficult to determine whether both structures are implicated as the source of nociception, or, if one structure is sensitised through means of. Web consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine (facet) joint pain from a multispecialty international working group. Web referral patterns for pain arising from ao and aa joints. Web cervical facet syndrome, also known as cervical facet joint pain, is a condition that occurs when the facet joints in the cervical spine become inflamed or damaged. Identify tender areas under fluoroscopy. Web understanding the relevant anatomy and referral patterns of cervical facet joints allows for more targeted diagnosis and treatment. O do not cross to the other side. Causes of facet joint syndrome. Web referred pain is a common but less understood symptom that originates from somatic tissues. Unlike the thoracic and lumbar facet joints, referral pain pattern and cobb angle rather than tenderness on the facetal area is helpful in suggesting cervical facet joint pain. (a) diagram of cervical zygapophysial joint pain distribution in volunteers. Web diagnostic positive facet joint block can indicate facet joints as the source of chronic spinal pain. (b) main referred pain distributions for the zygapophysial joints from c0/c1 to c7/t1 and the dorsal rami c3 to c7. O do not/rarely cause midline cervical pain or arm pain.
(PDF) Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine

Neck pain treatment Manor Chiropractic
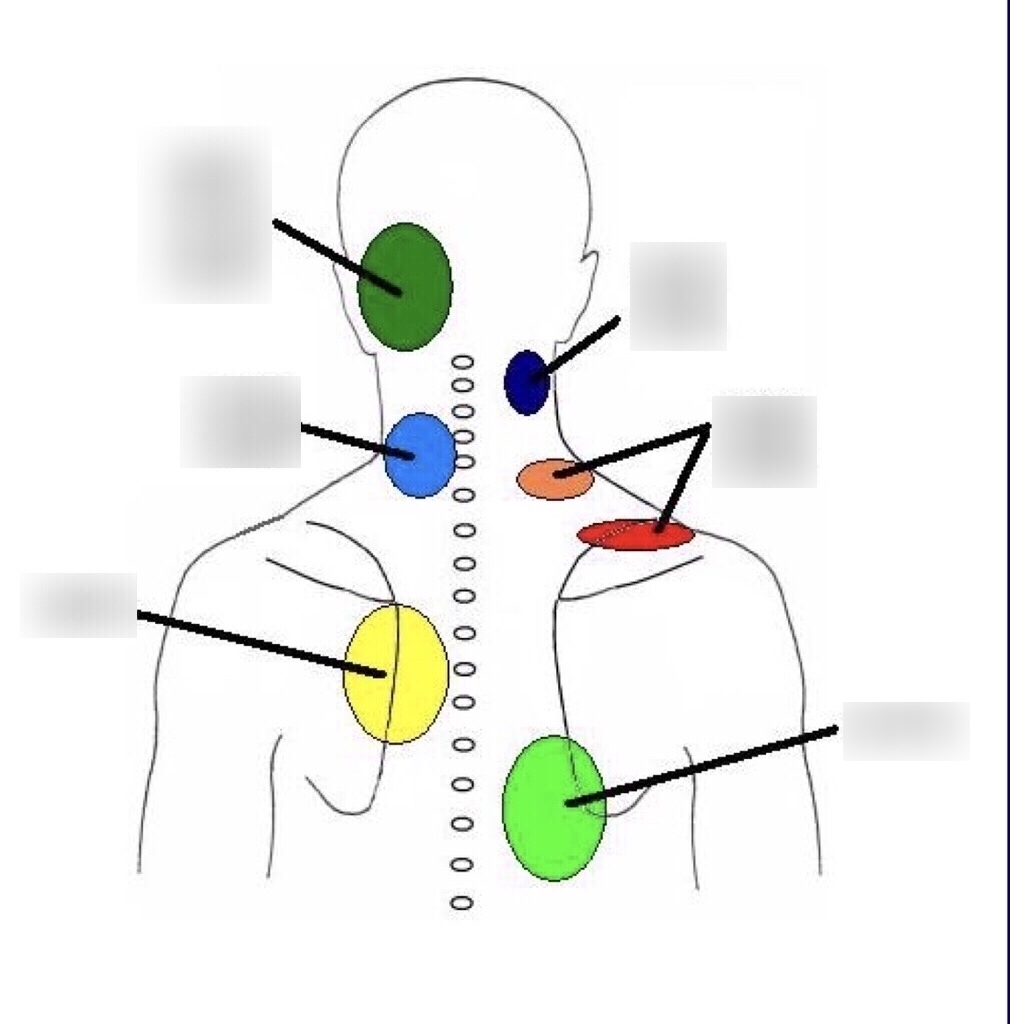
Cervical Facet Joint Referral Patterns Diagram Quizlet
![Facet referral patterns of Mooney and Robertson [31]. Download](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228329346/figure/fig21/AS:667206794883077@1536085904587/Zones-of-Head-in-Jinkins-2004_Q640.jpg)
Facet referral patterns of Mooney and Robertson [31]. Download

The patterns of referred pain from the cervical zygapophysial joints (7
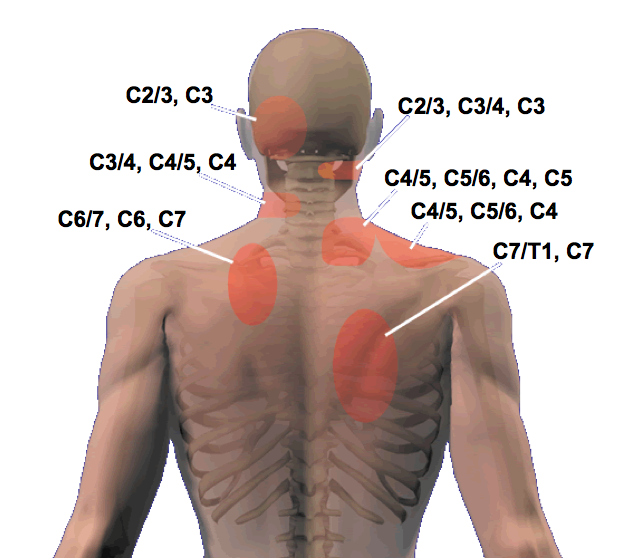
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog
Cloward sign & Cervical Referral Patterns Modern Manual Therapy Blog

Cervical Facet Referral Patterns Bead Pattern (Free)
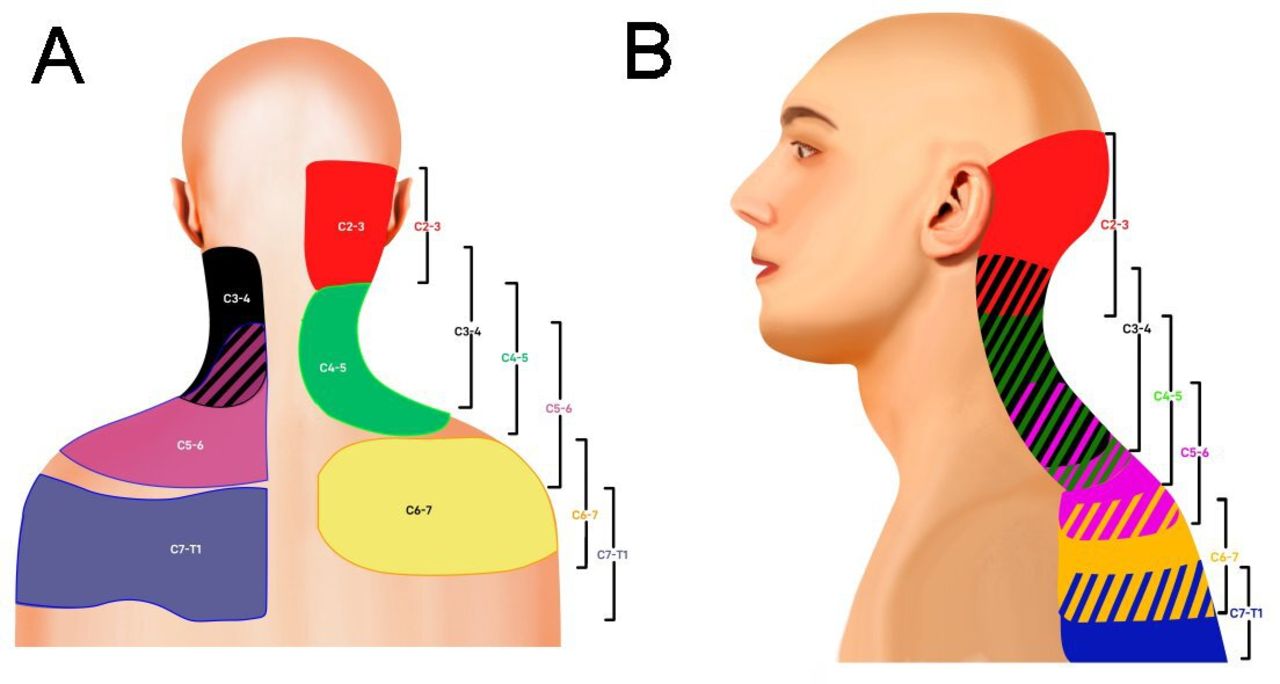
Consensus practice guidelines on interventions for cervical spine
Left Facet Joints Do Not Cause
These Patients May Benefit From Specific Interventions To Eliminate Facet Joint Pain Such As Neurolysis, By Radiofrequency Or Cryoablation.
Web In Addition, The Lower, Rather Than Upper, Cervical Facet Joints Are Also Difficult To Palpate Due To Muscles.
What Clinical Findings, Specifically The Results Of Examination And Diagnostic Injections, Can Help Differentiate Shoulder Pathology From.
Related Post: