Cell Transport Flow Chart
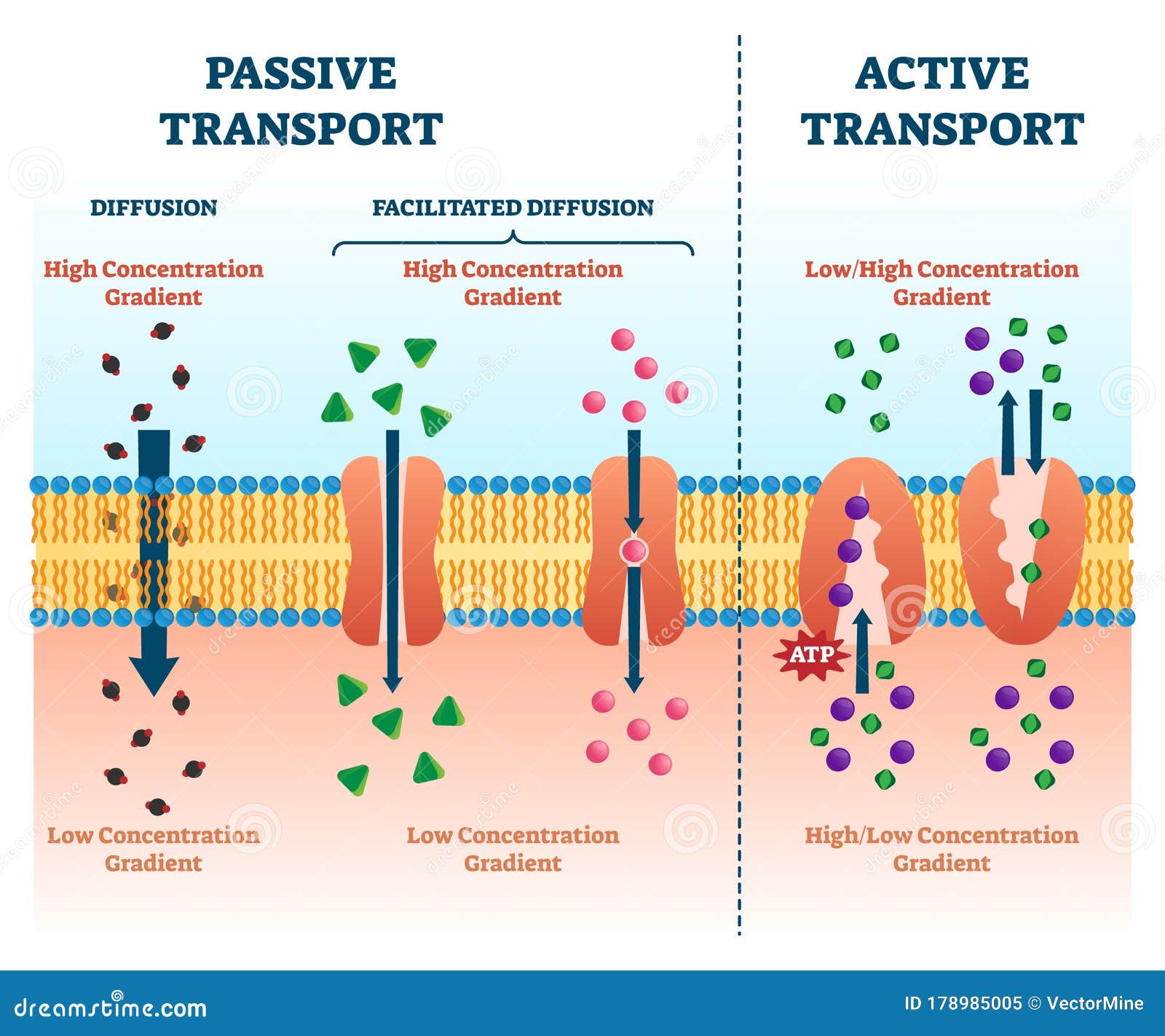
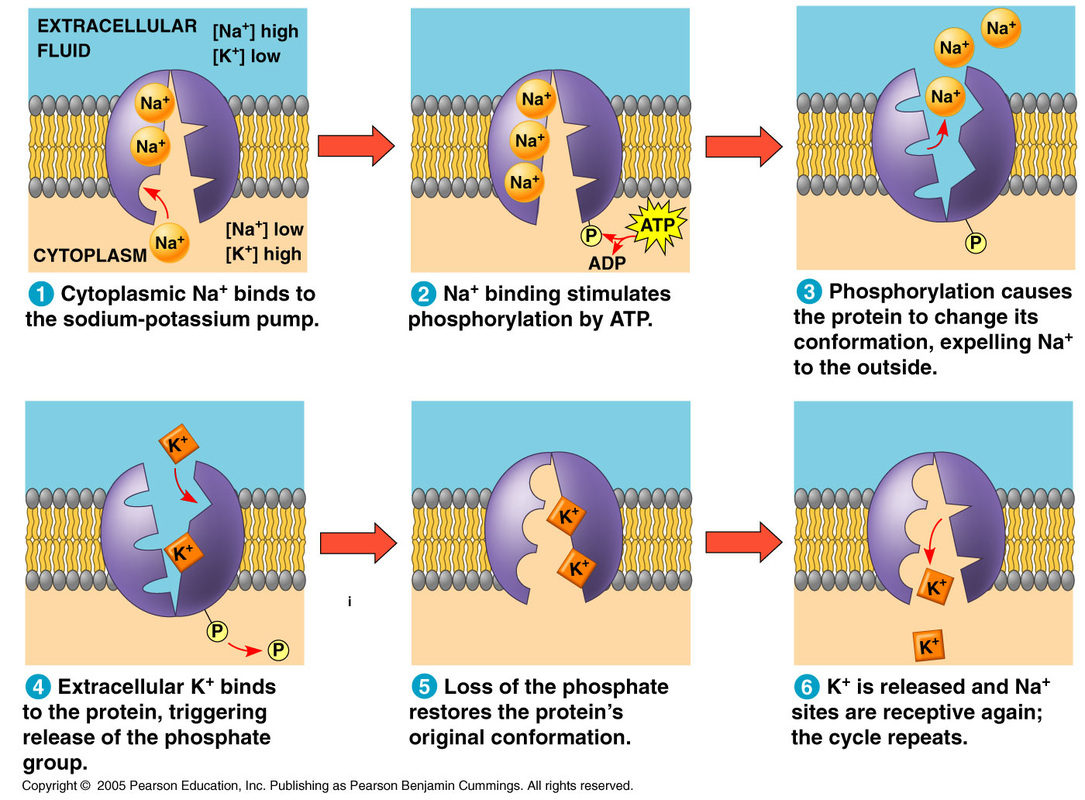
Cell Transport Flow Chart - Consider substances that can easily diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, such as the gases oxygen (o 2) and carbon dioxide (co 2 ). The diffusion of water molecules across a membrane. Here, let’s learn about them in detail. Web what is cell transport? Web steps of cellular respiration. Web this may happen passively, as certain materials move back and forth, or the cell may have special mechanisms that ensure transport. Diffusion, osmosis and active transport are some forms of transport seen across the cell membrane. Web learn about the structure and functions of the plasma membrane, the fluid mosaic model, and the types of transport across the membrane. Passive transport is explained in this section and active transport is explained in the next section, active transport and homeostasis. Much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that regulates the entry and exit of molecules. Diffusion, osmosis and active transport are some forms of transport seen across the cell membrane. Click the card to flip 👆. The teacher will review the power point presentation titled “cell transport and homeostasis” up to slide 12. It is the movement of substances across the. Cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that regulates the entry and exit of molecules. Transport of a substance across a cell membrane by diffusion. Passive transport, which requires no energy; Web in cells, some molecules can move down their concentration gradients by crossing the lipid portion of the membrane directly, while others must pass through membrane proteins in a process. Web here, we’ll look in more detail at gradients of molecules that exist across cell membranes, how they can help or hinder transport, and how active transport mechanisms allow molecules to move against their gradients. Diffusion, osmosis and active transport are some forms of transport seen across the cell membrane. Passive transport, which requires no energy; Click the card to. The teacher will review the power point presentation titled “cell transport and homeostasis” up to slide 12. The diffusion of water molecules across a membrane. It is the movement of substances across the cell membrane either into or out of the cell. Web this study guide takes a look at homeostasis and transport across membrane by passive transport and active. Have students complete this independently. The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Along the way, some atp is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. Here, we’ll look in more detail at membrane permeability and different modes of passive transport. Students may only have time to. What are the active transport methods? What are the passive cell membrane transport methods? Most cells expend most of their energy, in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp), to create and maintain an uneven distribution of ions on the opposite sides of their membranes. Web there are two basic ways that substances can cross the plasma membrane: Types of transport. And active transport, which requires energy. The teacher will review the power point presentation titled “cell transport and homeostasis” up to slide 12. Passive diffusion, facilitated transport and active transport. Sometimes things just move through the phospholipid bilayer. Molecules move in and out of cells in one of three ways: Students will the begin analysis of the wilted plants lab. Much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low. What are the passive cell membrane transport methods? Types of transport across the cell membrane. Web there are two basic ways that substances can cross the plasma membrane: Web learn about the structure and functions of the plasma membrane, the fluid mosaic model, and the types of transport across the membrane. Web what is cell transport? Passive transport is explained in this section and active transport is explained in the next section, active transport and. Passive diffusion, facilitated transport and active transport. Web this may happen passively, as certain materials move back and forth, or the cell may have special mechanisms that ensure transport. The teacher will review the power point presentation titled “cell transport and homeostasis” up to slide 12. Which diagram shows one antibody binding to the surface of a macrophage (step 1)?. And active transport, which requires energy. What are the passive cell membrane transport methods? Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others. And active transport, which requires energy. Types of transport across the cell membrane. Web this may happen passively, as certain materials move back and forth, or the cell may have special mechanisms that ensure transport. Web there are two basic ways that substances can cross the plasma membrane: A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell. Here, let’s learn about them in detail. Passive transport, which requires no energy; It is the movement of substances across the cell membrane either into or out of the cell. Graphic shows glycolysis, the krebs cycle and electron transport chain. Most cells expend most of their energy, in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp), to create and maintain an uneven distribution of ions on the opposite sides of their membranes. The structure of the plasma membrane. Web there are two basic ways that substances can cross the plasma membrane: The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells.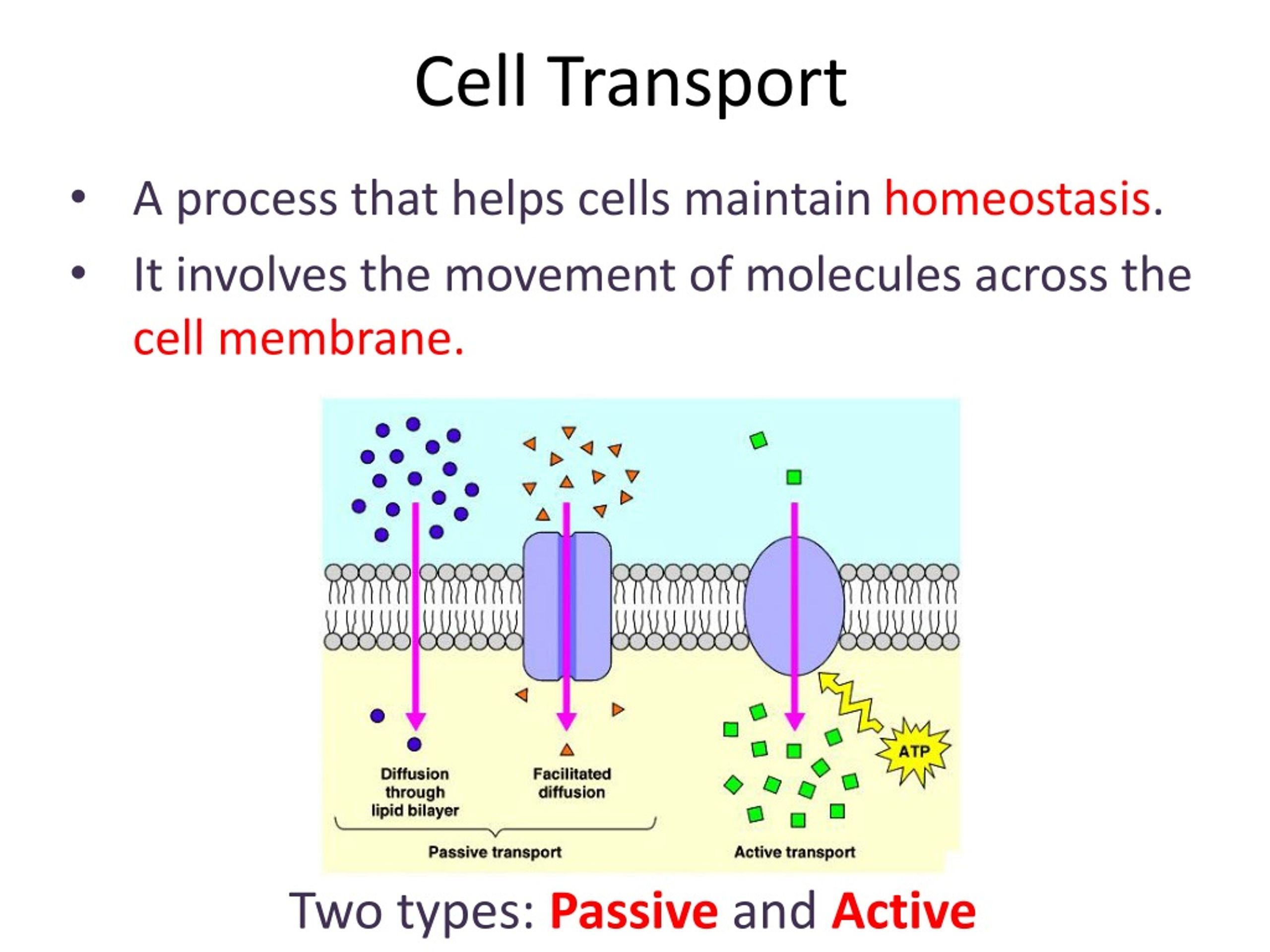
PPT Cell Transport Review PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
MUGAN'S BIOLOGY PAGE
1.4 Membrane Transport Biology 2016

Membrane Transport ION CHANNEL LIBRARY

Chapter 7 Cell Structure & Function PreAice Biology

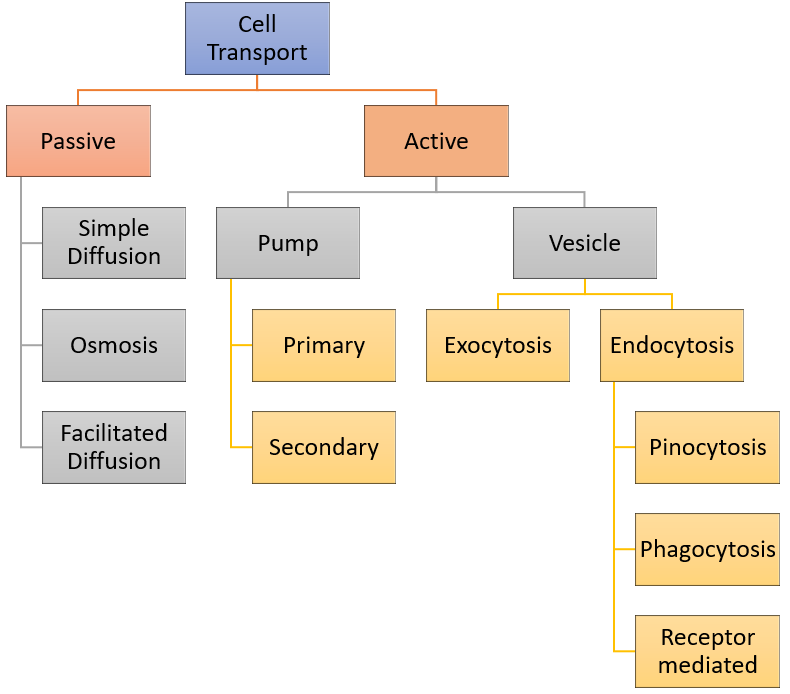
Cell Transport Flow Chart

This is a Cell Transport Flow Chart. Materials that move through the
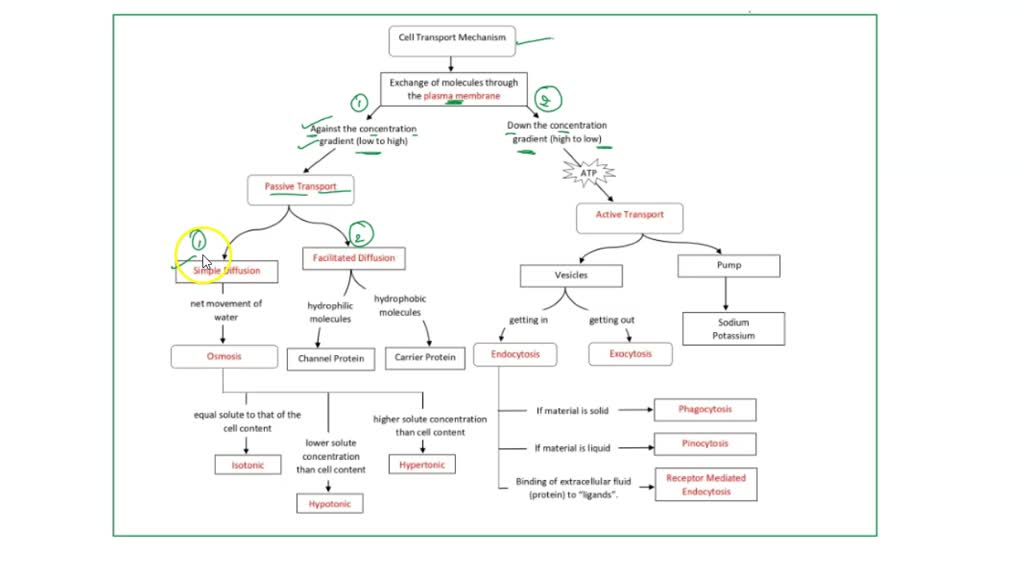
SOLVED E. Make a concept map of Cellular Transport Mechanisms for
3.7 Cell Transport Biology LibreTexts

Summary of Membrane Transport Processes PhysiologyWeb
Consider Substances That Can Easily Diffuse Through The Lipid Bilayer Of The Cell Membrane, Such As The Gases Oxygen (O 2) And Carbon Dioxide (Co 2 ).
Web The Flow Chart Shows One Theory For The Formation Of Pseudopodia.
Along The Way, Some Atp Is Produced Directly In The Reactions That Transform Glucose.
(Iii) Explain Why Water Flows Into The Part Of The Cell Where The Soluble Components Are Located (Step 3).
Related Post: