Cell Respiration Flow Chart
Cell Respiration Flow Chart - The goal of cellular respiration is to. Provide a concise summary of the process. Web the reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: Web cellular respiration (also known as 'oxidative metabolism') is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. A word bank is provided to help them trace the flow of atp and nadh in the process as well as identifying where each step occurs. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. Web cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. Web cellular respiration extracts the energy from the bonds in glucose and converts it into a form that all living things can use. Web cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation: The process of respiration is divided into three major steps ― glycolysis,krebs cycle, and electron chain transport. Web external respiration, also known as breathing, involves both bringing air into the lungs (inhalation) and releasing air to the atmosphere (exhalation). Web cellular respiration. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. State what happens during glycolysis. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Figure below gives an overview of these three stages, which are further discussed in the concepts that follow. Web answer key to the flow chart showing the main events and products in cellular respiration. Web the overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: The tca cycle and oxidative phosphorylation require oxygen, while glycolysis can. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. What are the products in anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation) in yeast? To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of. During normal human respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to produce the energy needed for. Describe. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. Web cellular respiration is a chemical process in which the bonds of food molecules and oxygen molecules are broken and new compounds are formed that can transport energy. Web in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose move gradually through the electron transport chain towards oxygen, passing to lower and lower energy states and releasing energy at each step. What are the products in anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation) in yeast? Web respiration is the process in which organisms exchange gases between their body cells and the environment. And the electron. And the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Web the reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: Web cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions, but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation: To create atp and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives. Web what is the purpose of cellular respiration? Web cellular respiration (also known as 'oxidative metabolism') is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. During normal human respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to produce the energy needed for.. From plants and animals to prokaryotic bacteria, archaeans, eukaryotic protists, fungi, and animals, all living organisms undergo respiration. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion. Web cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (atp), and then release waste products. During normal. Glucose, 2 nad +, 2 adp + 2 pi. Because it has such high potential energy, atp is unstable and is not stored. Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: Web in cellular respiration, electrons from glucose move gradually through the electron transport chain towards oxygen, passing. The citric acid (tca) or the krebs cycle; Both plants and animals carry out the process of respiration, but only plants proceed to another process called ‘photosynthesis‘. Web students complete a graphic organizer that shows the process of cellular respiration. Web what is the purpose of cellular respiration? 2 ethyl alcohol (2c) + 2 co2 + 2 atp + heat. What are the products in anaerobic cellular respiration (fermentation) in yeast? Provide a concise summary of the process. Web the four main steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, pyruvate decarboxylation (link reaction), the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle), and the electron transport chain with oxidative phosphorylation. What happens during the electron transport stage of cellular respiration? Cellular respiration also releases the energy needed to maintain body temperature despite ongoing energy transfer to the surrounding environment. Web cellular respiration extracts the energy from the bonds in glucose and converts it into a form that all living things can use. The process of breathing takes place with the lungs of the organism. Web 9.1 an overview of cellular respiration. State what happens during glycolysis. Web review your understanding of cellular respiration in this free article aligned to ngss standards. Describe the structure of a mitochondrion.Cellular Respiration Flowchart Cellular Respiration Adenosine
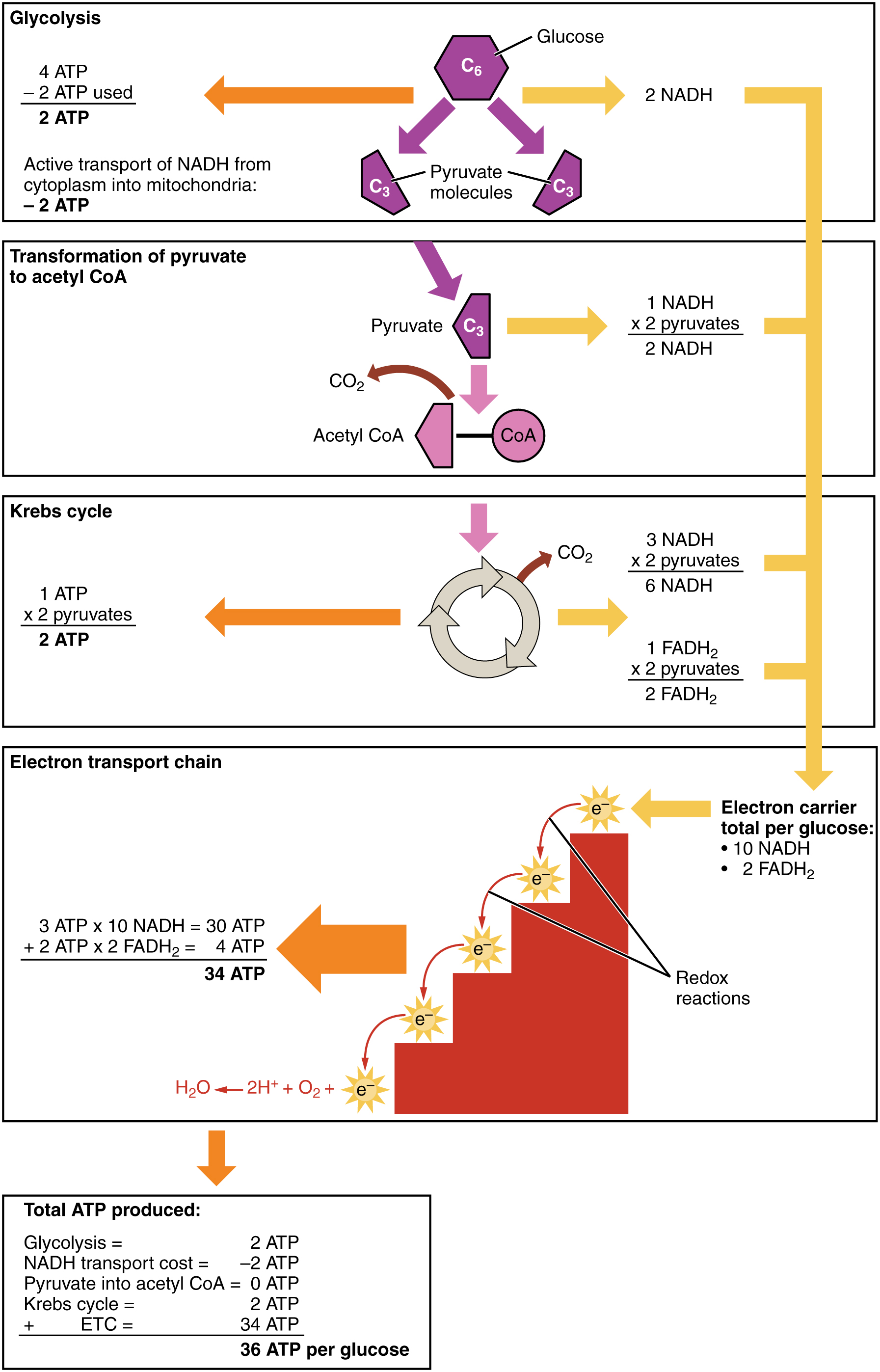
4.10 Cellular Respiration Human Biology
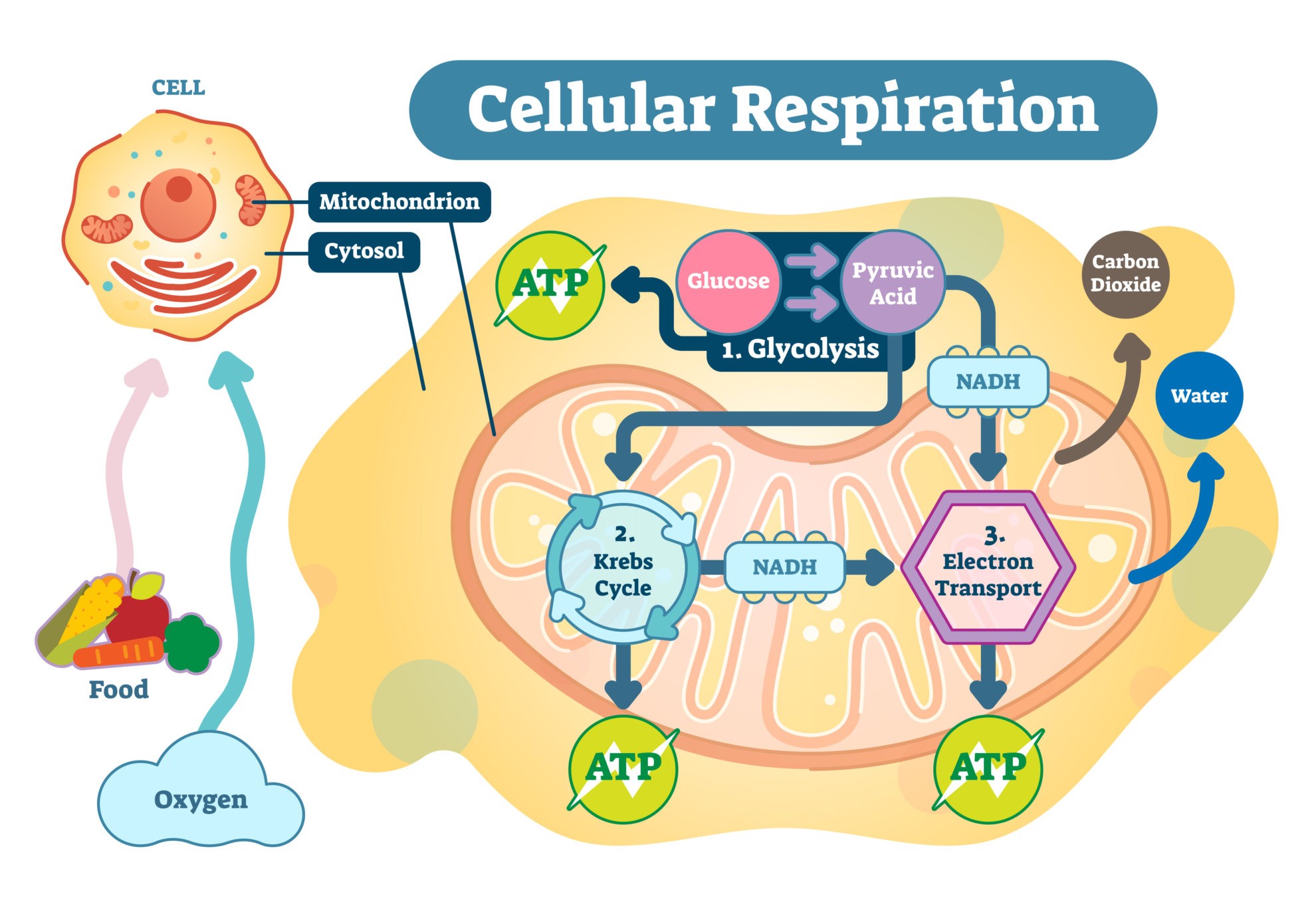
Cell Respiration Biology Online Tutorial
4.4D Respiration and Proton Motive Force Biology LibreTexts

What Are The 3 Stages Of Cellular Respiration
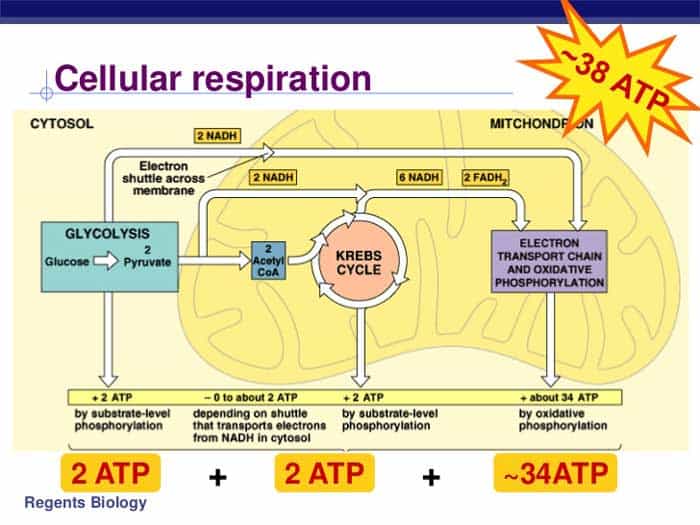
Cellular Respiration Equation, Types, Stages, Products & Diagrams
Cellular respiration Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
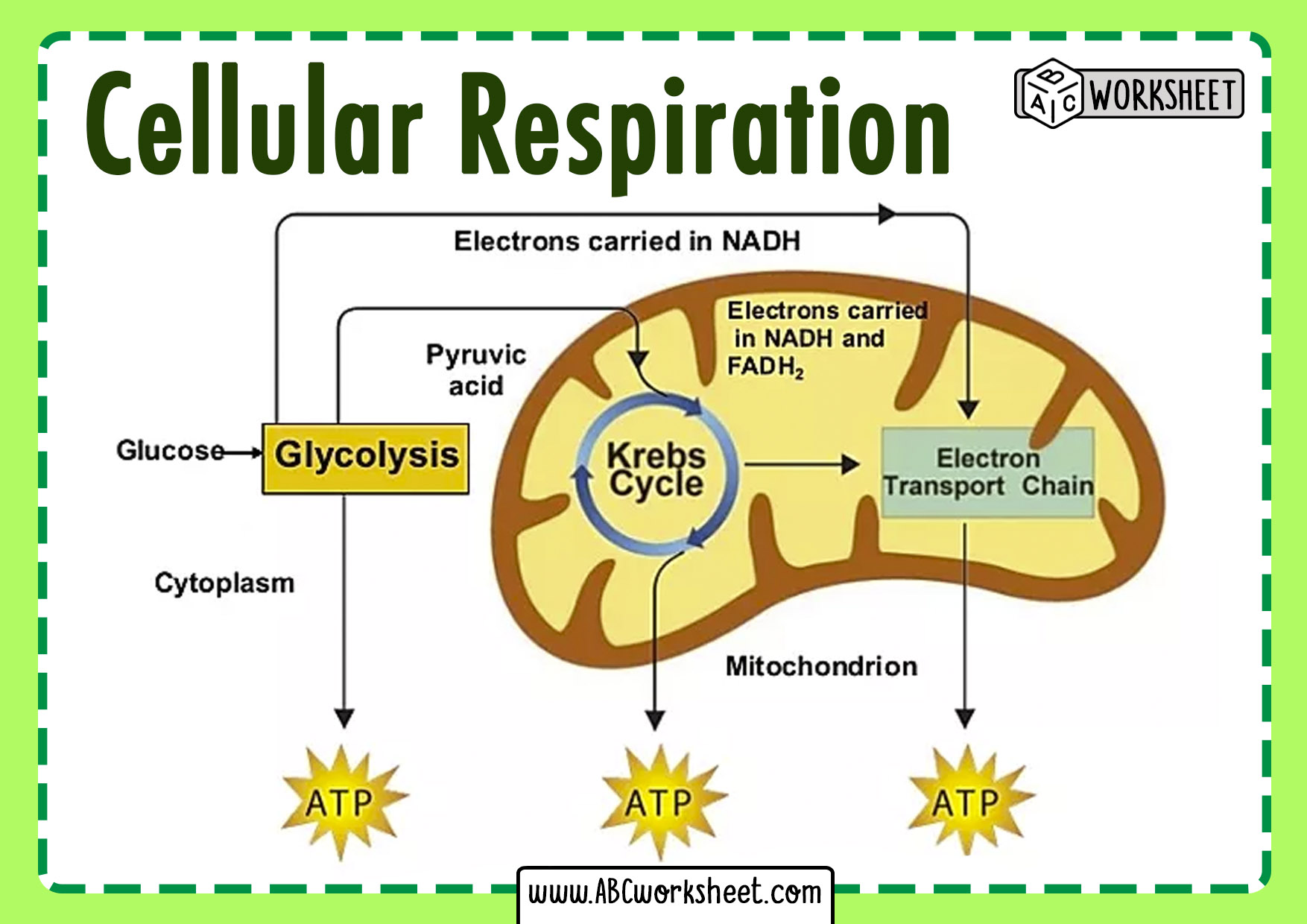
Cellular Respiration Steps ABC Worksheet

Flow Chart Cellular Respiration Pathways Stock Vector (Royalty Free
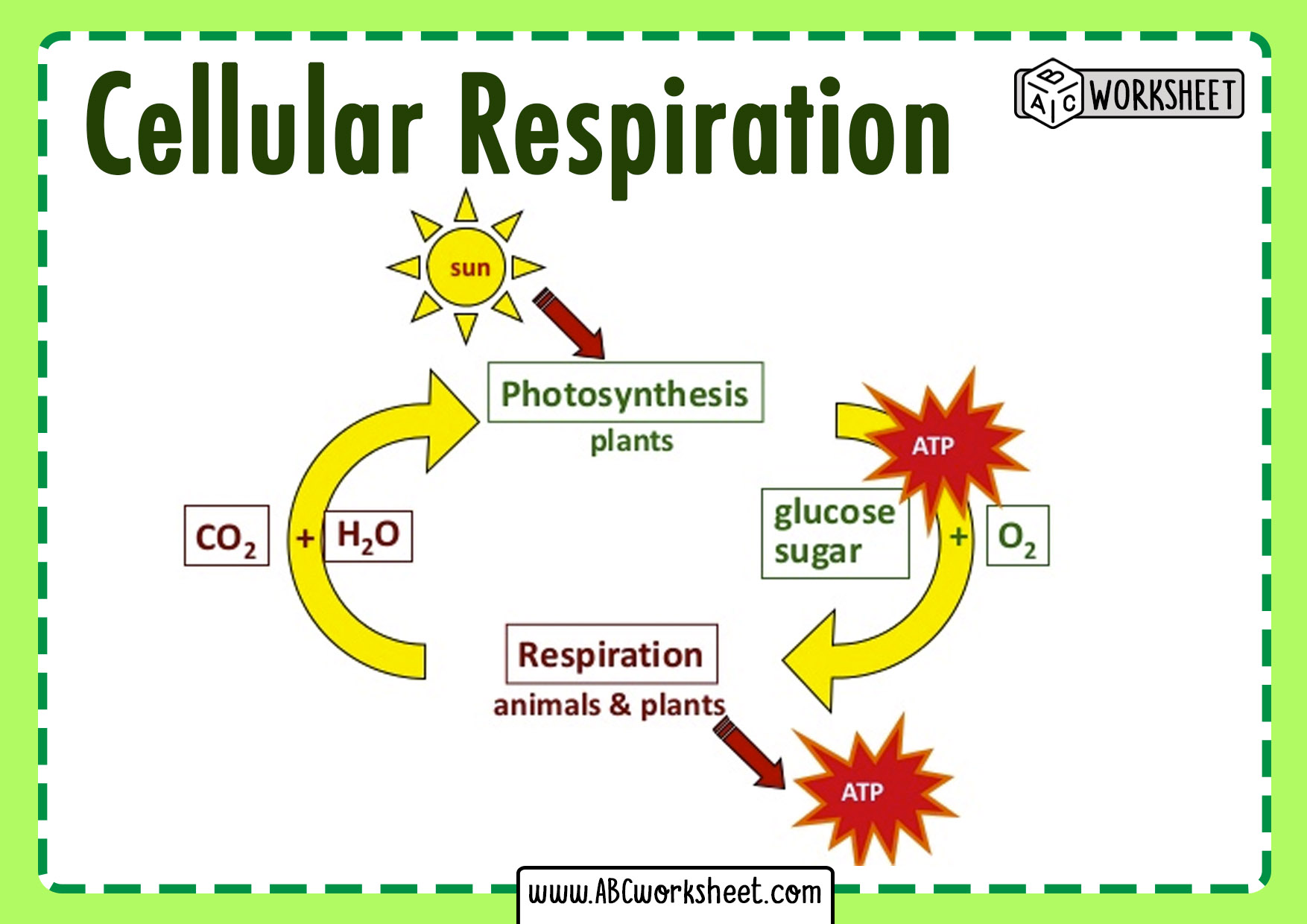
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Flow Chart
Web The Overall Process, However, Can Be Distilled Into Three Main Metabolic Stages Or Steps:
Web Cellular Respiration Is A Set Of Metabolic Reactions And Processes That Take Place In The Cells Of Organisms To Convert Biochemical Energy From Nutrients Into Adenosine Triphosphate (Atp), And Then Release Waste Products.
The Mechanism By Which Organisms Obtain Oxygen From The Air And Release Carbon Dioxide Is Called Breathing.
To Create Atp And Other Forms Of Energy To Power Cellular Reactions, Cells Require Fuel And An Electron Acceptor Which Drives The Chemical Process Of.
Related Post:

