Bacteria Identification Flow Chart
Bacteria Identification Flow Chart - Web given the wealth of agar media, microscopy stains, and biochemical tests, microbiologists have built flow charts to identity the bacteria surrounding us. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. In the previous chapter we have discussed various methods of isolation of bacteria. You need to employ tests learned during this semester and a few new techniques to characterize morphological, nutritional, physiological and biochemical characteristics of your unknowns. Unknown bacterial species identification flow chart. Web bacteria identification flow chart [classic] | creately. Explain the theory of pcr, its purpose, and applications. Web in this study, we attempted to apply mainly saccharolytic and proteolytic enzyme tests selectively; Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial species. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Web this page titled 22c: Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining), observation of growth characteristics (list of culture media), determination of reactions to organic and inorganic compounds (api gallery, microbiological techniques) and molecular techniques. Paul ingram infectious diseases physician (rph) & microbiologist (pathwest laboratories) example 1 of diagnostic algorithm. Web gram. Web discuss the characterization of microbes based on phenotypic and genotypic methods. Use creately’s easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Gram stain & morphological flowchart some examples gram positive cocci bacilli. The bacteria thus isolated needs to be further identified to genus and species level. Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial species. Use the results from each test to determine what the next test is or what. Gram stain & morphological flowchart. Web organism id job aid for positive and negative result reference. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. Web in this study, we attempted to apply mainly saccharolytic and proteolytic. Gram stain & morphological flowchart some examples gram positive cocci bacilli round in clusters & tetrads. In the previous chapter we have discussed various methods of isolation of bacteria. Paul ingram infectious diseases physician (rph) & microbiologist (pathwest laboratories) example 1 of diagnostic algorithm. Web bacteria identification flow chart [classic] | creately. Recognize the microscopic morphology of important bacterial and. Identification is reached at the end of the tree’s “branches. Web the first thing to prepare for an unknown identification exercise is to make a dichotomous key. In the previous chapter we have discussed various methods of isolation of bacteria. Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for. The bacteria thus isolated needs to be further identified to genus and species level. Yet, the numerous growth and biochemical tests that microbiologists have amassed cannot precisely reveal all of the ways one microbe may be different from another. Explain the theory of pcr, its purpose, and applications. Keys are charts that require decisions at branch points, much like a. Web identifying microbes at the species level: Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial species. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Web given the wealth of agar media, microscopy stains, and. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. Web in this study, we attempted to apply mainly saccharolytic and proteolytic enzyme tests selectively; To this end, we set up an accurate. The tests that are a part of this project are in boxes. Use the results from each test to determine what the next test is or what. Web gram positive cocci obligate anaerobic peptostreptococcus spp., peptinophilus spp., parvimonas spp., anaerococcus spp., atopobium spp., f. Bacteria are identified in laboratories by various methods, including microscopy ( fresh state, after staining), observation. Example of a branching dichotomous key. Paul ingram infectious diseases physician (rph) & microbiologist (pathwest laboratories) example 1 of diagnostic algorithm. Web aerobic gram positive rods flowchart. The bacteria thus isolated needs to be further identified to genus and species level. Web biochemical identification of bacteria. Use the results from each test to determine what the next test is or what. Web the first thing to prepare for an unknown identification exercise is to make a dichotomous key. The procedure for identifying bacteria is similar to the game twenty questions. Once your bacterial species are isolated and you have good gram stain results, begin to follow the flow chart for both of your unknown bacterial species. Web this paper reviewed core concepts of interpreting bacterial culture results, including timing of cultures, common culture sites, potential for contamination, interpreting the gram stain, role of rapid diagnostic tests, conventional antibiotic susceptibility testing, and automated testing. If the answer is no, then do y. Yet, the numerous growth and biochemical tests that microbiologists have amassed cannot precisely reveal all of the ways one microbe may be different from another. In the previous chapter we have discussed various methods of isolation of bacteria. Web employ proper and safe microbiology laboratory techniques for the diagnosis of bacterial and fungal infections in veterinary medicine. Web identification flow charts 2 differentiation via gram stains and cell morphology. Identification is reached at the end of the tree’s “branches.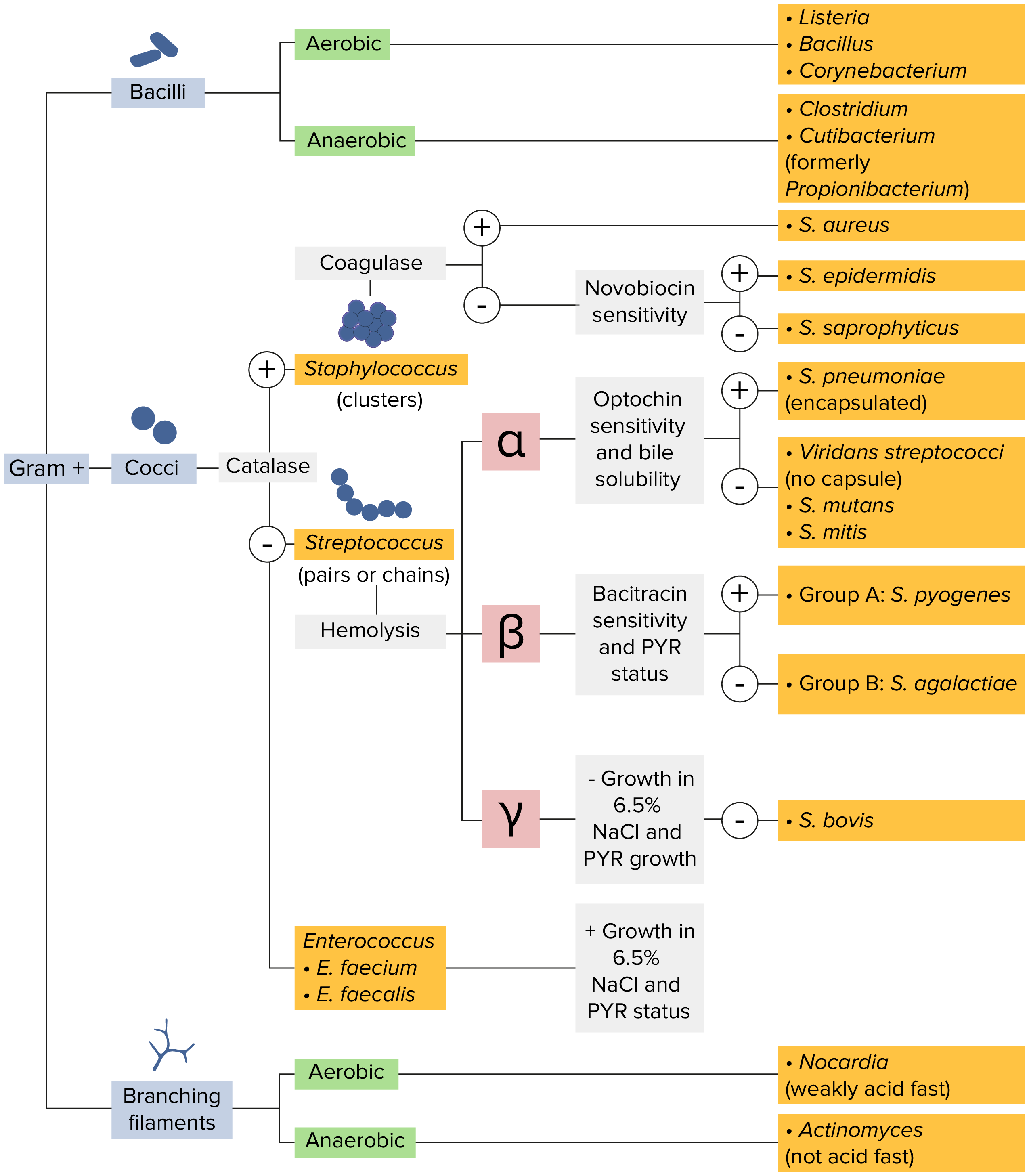
Staphylococcus Concise Medical Knowledge

Microbiology Flowchart Unknown Bacteria amulette
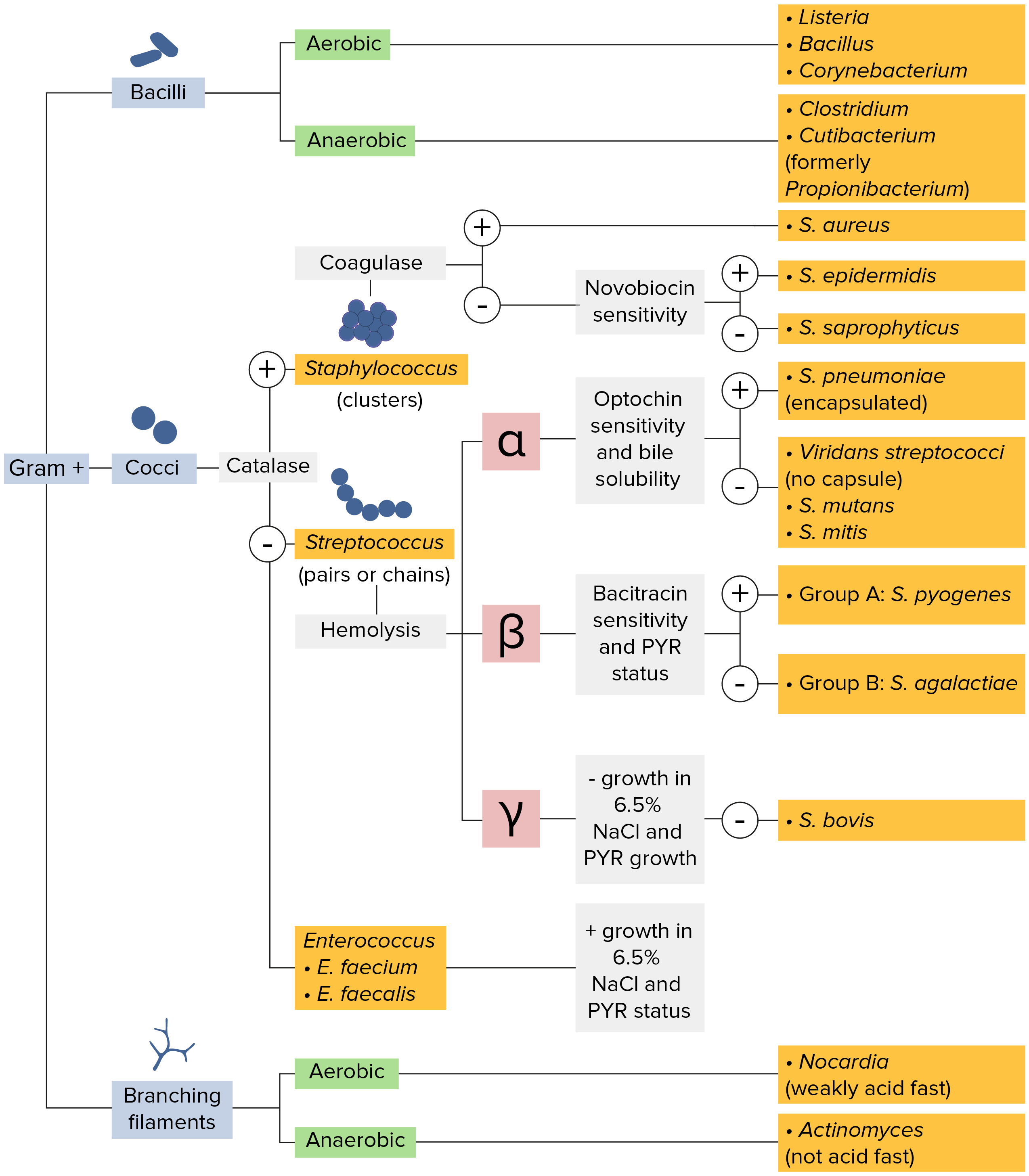
Streptococcus Concise Medical Knowledge

Identifying Bacteria Through Look, Growth, Stain and Strain

bacteria identification flow chart Gram positive Bacteria Flow Chart
88 FLOW CHART UNKNOWN BACTERIA
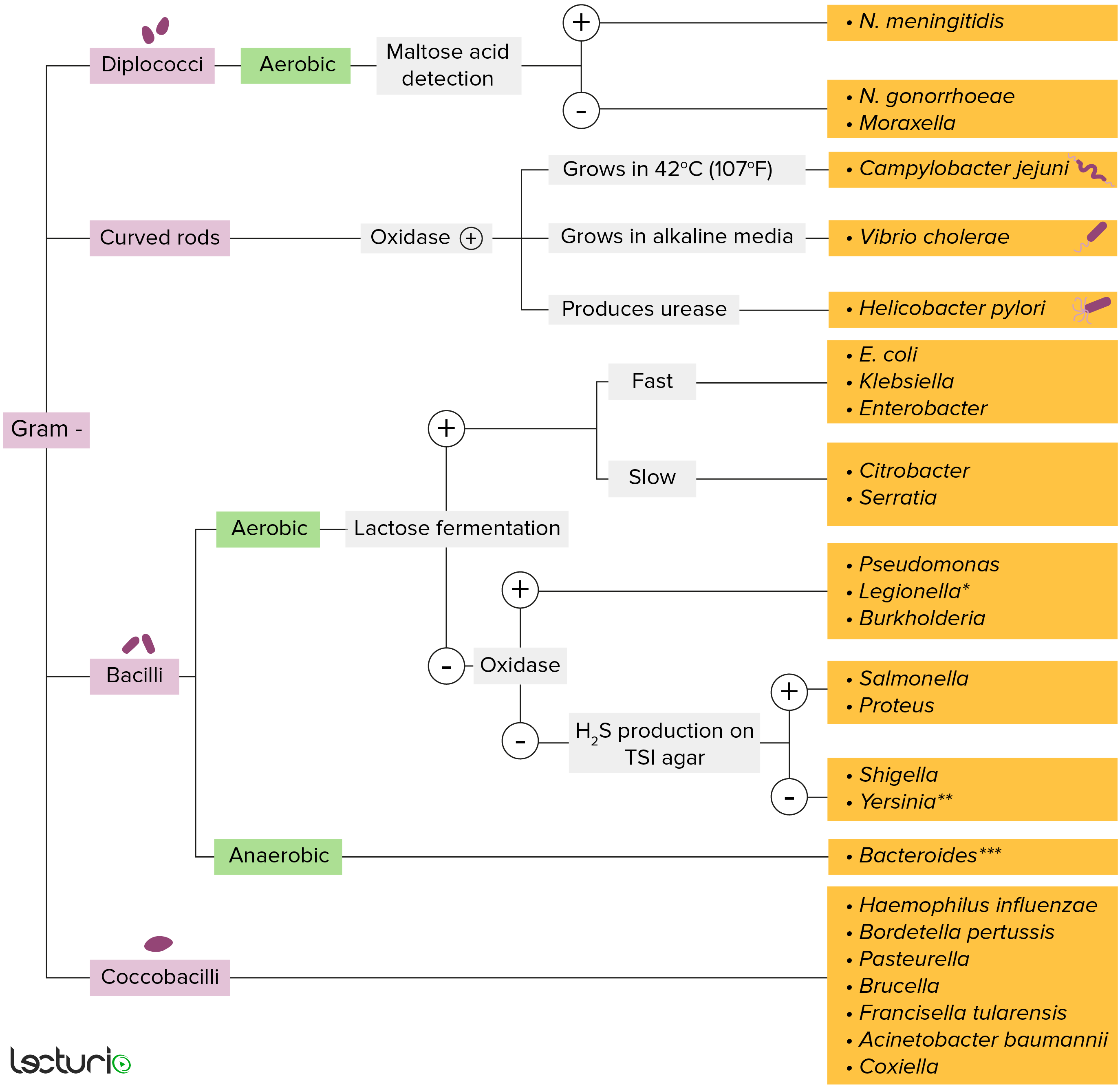
Bacteroides Concise Medical Knowledge

A Basic Flowchart For Microbiologic Identification Infographic

Bacteria Identification Flowchart (Matte) NerdcoreMedical

Microbiology Flowchart Unknown Bacteria amulette
Web Overall, Biochemical Identification Tests May Be Classified Into Two Major Groups:
Recognize The Microscopic Morphology Of Important Bacterial And Fungal Pathogens In Stained Preparations From Clinical Material.
Web Gram Positive Cocci Obligate Anaerobic Peptostreptococcus Spp., Peptinophilus Spp., Parvimonas Spp., Anaerococcus Spp., Atopobium Spp., F.
You Need To Employ Tests Learned During This Semester And A Few New Techniques To Characterize Morphological, Nutritional, Physiological And Biochemical Characteristics Of Your Unknowns.
Related Post: