Ana Ab Pattern Speckled
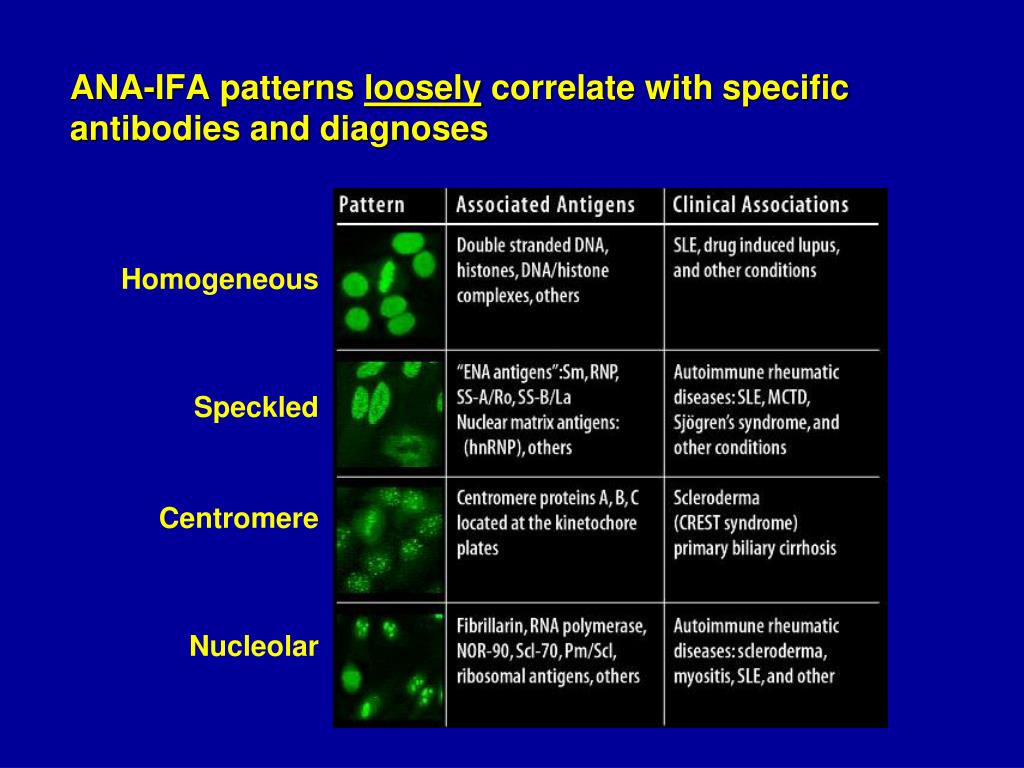
Ana Ab Pattern Speckled - Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Volume 488, january 2021, 112904. Web a positive ana test is usually reported as both a ratio (called a titer) and a pattern, such as smooth or speckled. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. And if the ana test is positive, your blood can be tested for the presence of particular antinuclear antibodies, some of which are specific to certain diseases. Samples are initially diluted to a 1 in 80 dilution (titre 1:80). Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. How the test is performed. A centromere pattern may indicate. A titer (a measure of how much ana is in the blood) and a pattern (where the ana was detected in the cells). A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Updated on october 14, 2022. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. Web the antinuclear antibody dense fine speckled pattern and possible clinical associations: An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. This arrangement is more practical as it. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. A centromere pattern may indicate. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while other patterns were rare representing less than 7% of the patients each.. And if the ana test is positive, your blood can be tested for the presence of particular antinuclear antibodies, some of which are specific to certain diseases. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Positive results are further diluted to a titre of 1:160, 1:320 and a final titre of 1:640. Ana pattern associated. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Common ana patterns and their associated systemic rheumatic diseases; Web testing reveals a 1:40 antinuclear antibody (ana) titer and a weakly positive rheumatoid factor (rf) titer of 22 iu per ml. Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; Common ana pattern is speckled; It’s also called an ana or fana (fluorescent antinuclear antibody) test. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Another pattern, known as a nucleolar pattern, is common in people with scleroderma. How the test is performed. Ana titers were highest in patients with mixed pattern followed by the speckled pattern. Updated on october 14, 2022. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens. Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Web an ana test looks for antinuclear antibodies in your blood. Another pattern, known as a nucleolar pattern, is common in people with scleroderma. Ana pattern associated rheumatic disease; Volume 488, january 2021, 112904. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. The significance of ana pattern. A speckled pattern may indicate various diseases, including lupus and sjögren’s syndrome. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Web the most frequently observed ana patterns were the speckled (52.1%) and homogeneous (35.2%) patterns, while. Another pattern, known as a nucleolar pattern, is common in people with scleroderma. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. Common ana pattern is speckled; Titres are reported in ratios, most often 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, and 1:640. Ana titers were highest in patients with mixed pattern followed by the speckled pattern. Web while an ana test can't confirm a specific diagnosis, it can rule out some diseases. Web a speckled pattern is also found in lupus. The significance of ana pattern. Fine and coarse speckles of ana staining are seen throughout the nucleus. Web testing reveals a 1:40 antinuclear antibody (ana) titer and a weakly positive rheumatoid factor (rf) titer of 22 iu per ml. A centromere staining pattern means the ana staining is present along the chromosomes. This pattern can be associated with systemic lupus erythematosus, sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. Web the classical nuclear patterns are speckled, homogeneous, nucleolar and centromere. Some, but not all labs will report a titre above 1:160 as positive. Ana test results are most often reported in 2 parts: An autoimmune disorder causes your immune system to attack your own cells, tissues, and/or organs by mistake. Understanding the ana blood test (antinuclear antibody test) by carol eustice. Web the most frequent ana patterns were coarse speckled pattern (154 patients, 31.2%), nucleolar pattern (89 patients, 18.0%), fine speckled pattern (57 patients, 11.5%), and speckled pattern (48 patients, 9.7%). Web the speckled pattern in ana (antinuclear antibody) testing is one of the most common and diagnostically significant patterns, characterized by its distinctive, fine or coarse speckled appearance under a fluorescence microscope. A centromere pattern may indicate. This pattern is more commonly associated with antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens.
International consensus on antinuclear antibody patterns definition of
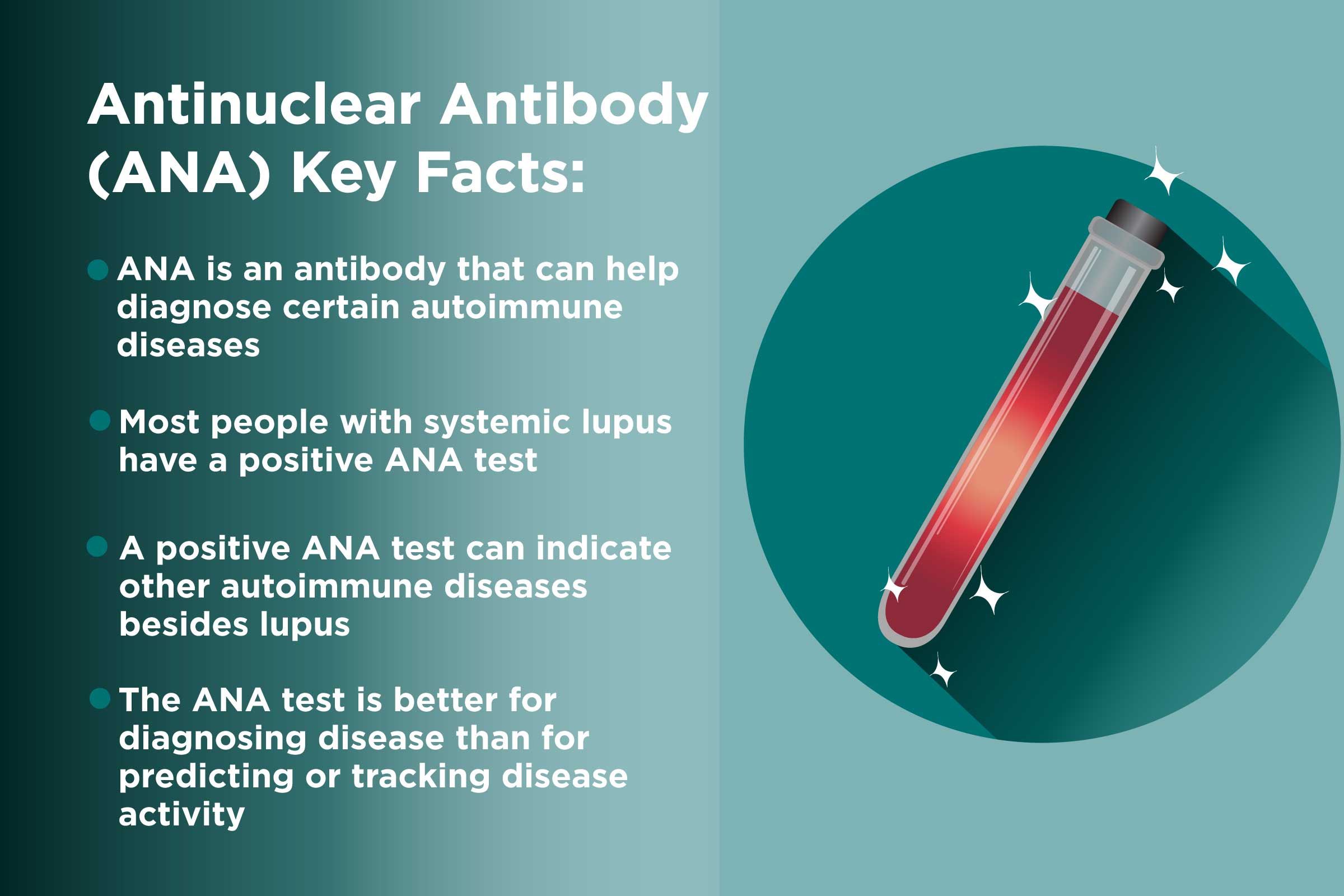
What Is the Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test?

Ana With Speckled Pattern Chumado
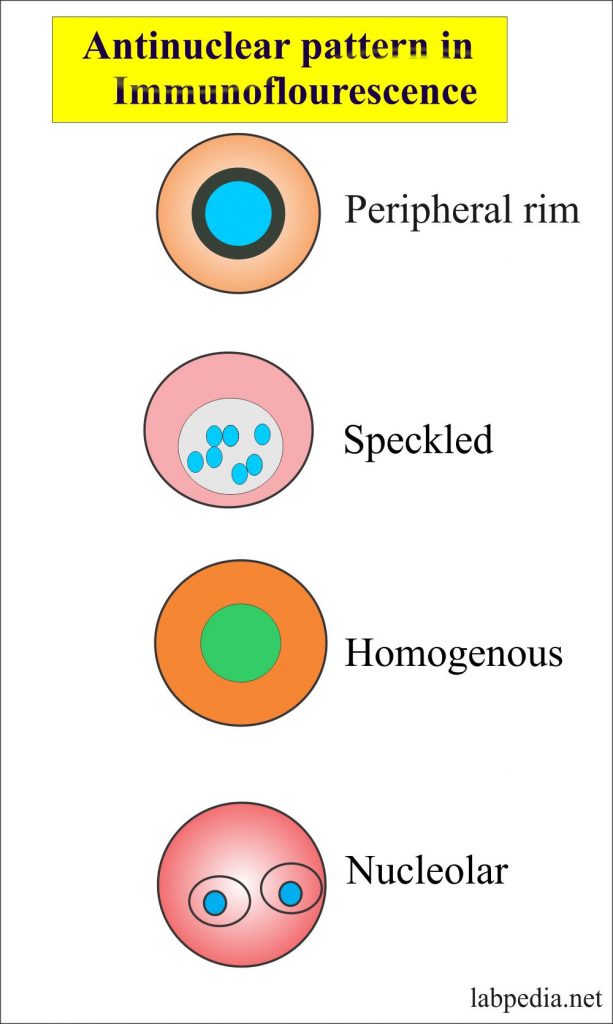
Positive Ana Speckled Pattern Chumado
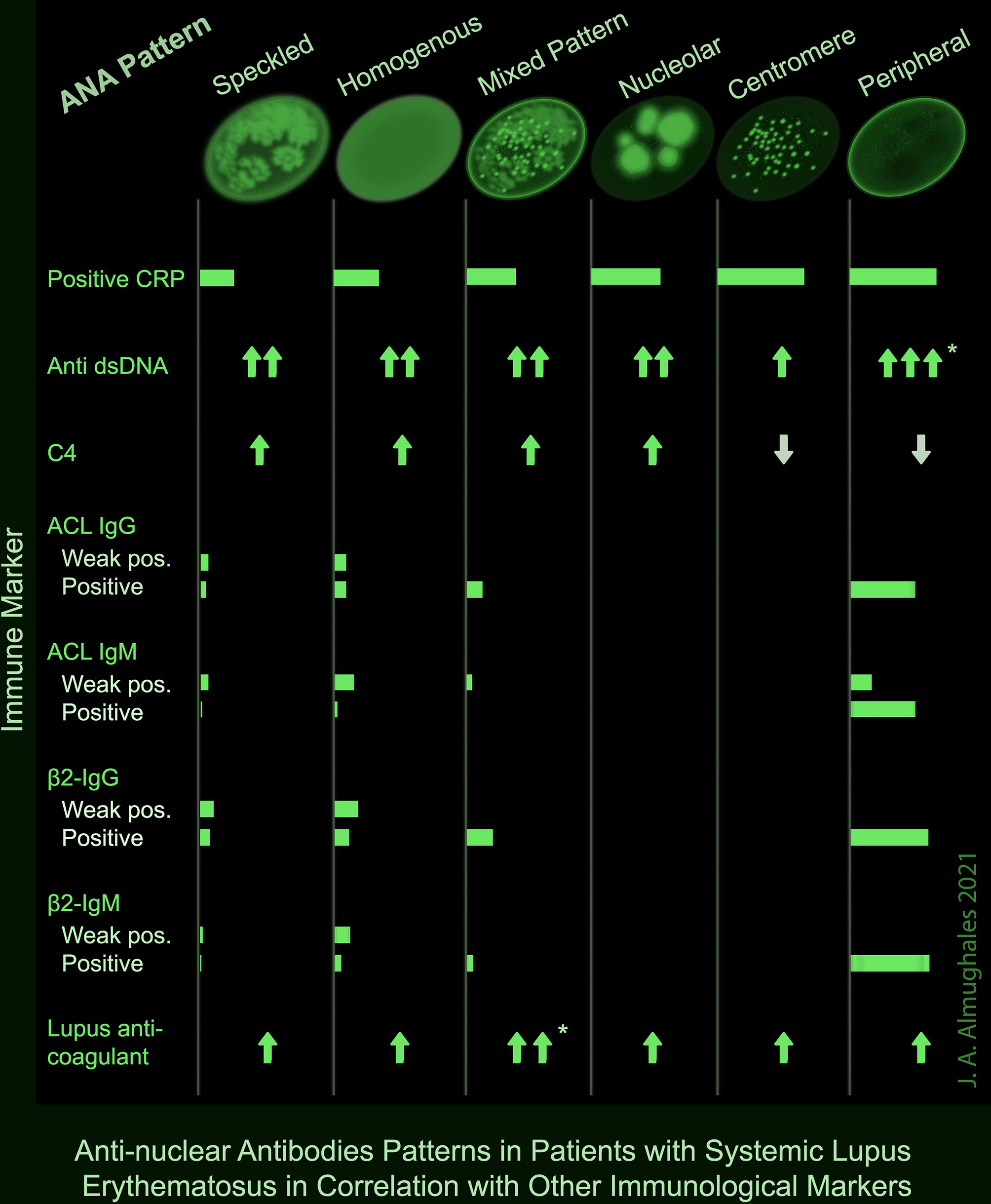
Frontiers AntiNuclear Antibodies Patterns in Patients With Systemic

Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) test and their patterns ANA test What

Ana Test Patterns
Ana Titer 1 160 Speckled Pattern Chumado

Biochemistry, Antinuclear Antibodies (ANA) StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf
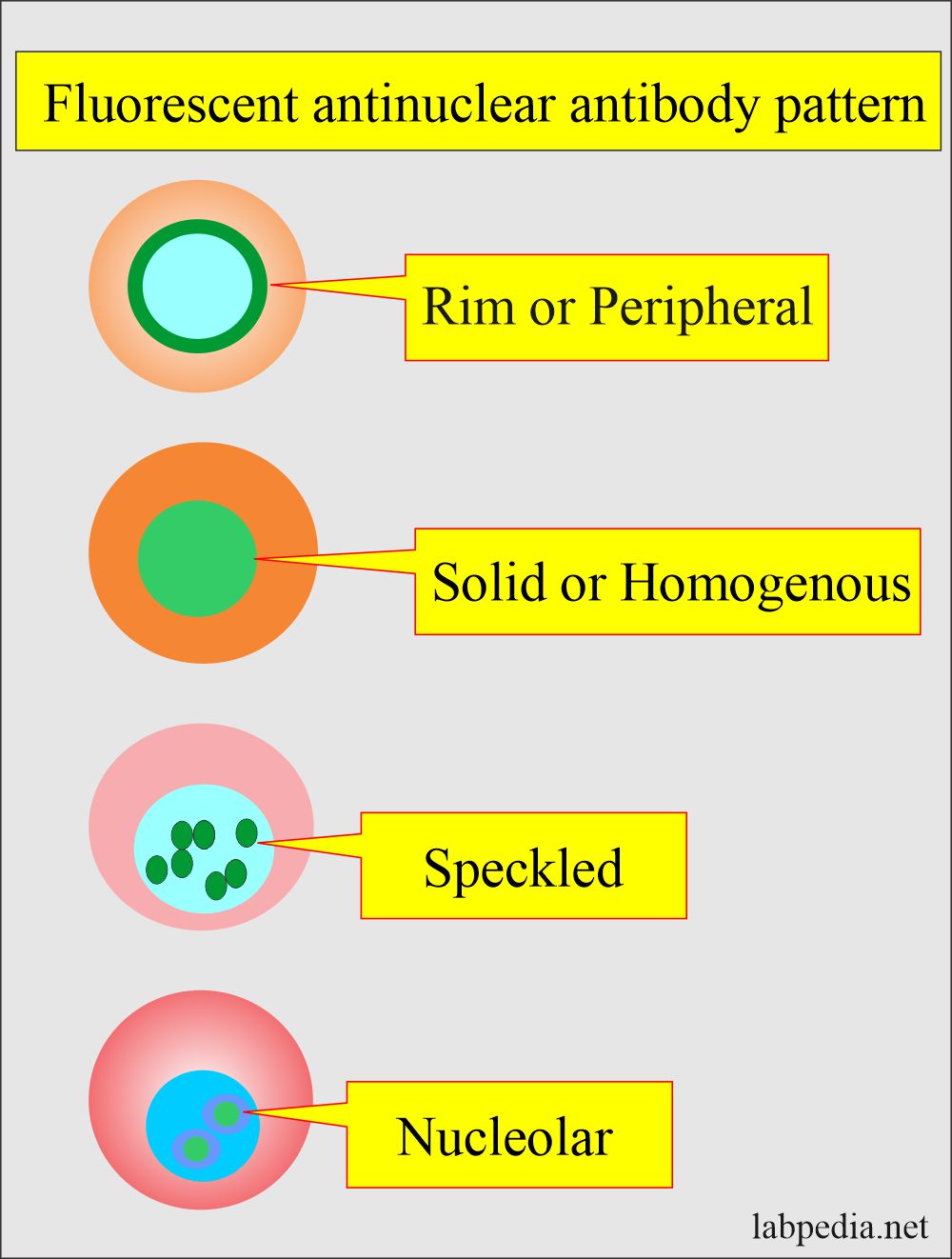
Antinuclear Factor (ANF), Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) and Its
Ana Titers Were Highest In Patients With Mixed Pattern Followed By The Speckled Pattern.
Another Pattern, Known As A Nucleolar Pattern, Is Common In People With Scleroderma.
Web The Antinuclear Antibody Dense Fine Speckled Pattern And Possible Clinical Associations:
A Speckled Staining Pattern Means Fine, Coarse Speckles Of Ana Are Present Throughout The Nucleus.
Related Post: