Alveolar Pattern Dog
Alveolar Pattern Dog - Web alveolar, interstitial or maybe bronchial! This pattern results in more loss of airspace than any other pattern. The only distinction these patterns make with. Web a multifocal marked peripheral alveolar pattern can be identified in all lung lobes and is a common radiographic feature of angiostrongylosis. Web radiographic findings varied, but included abnormal unstructured interstitial (one) and unstructured interstitial and alveolar (five) pulmonary patterns, which were. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. You look at a thoracic radiograph and somehow you do see a bit of every lung pattern. Web important points regarding the alveolar pattern: To evaluate the radiographic lung pattern and topographical distribution in canine eosinophilic. Unremarkable, cardiomegaly, alveolar pattern, bronchial pattern,. Web radiographic findings varied, but included abnormal unstructured interstitial (one) and unstructured interstitial and alveolar (five) pulmonary patterns, which were. Web radiographic findings used as non mutually exclusive labels to train the cnns were: Web thoracic radiography (available in 10 dogs) revealed right cardiomegaly and patchy or diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, with 9 dogs having a normal left. Web. You look at a thoracic radiograph and somehow you do see a bit of every lung pattern. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web alveolar, interstitial or maybe bronchial! This pattern results in more loss of airspace than any other pattern. Web radiographic findings used as. The alveolar pattern is the dominant pattern, and will obscure other patterns by silhouette effect. Web learn how to recognize and differentiate common lung patterns and distributions of pulmonary diseases in dogs and cats using thoracic radiographs. Web a multifocal marked peripheral alveolar pattern can be identified in all lung lobes and is a common radiographic feature of angiostrongylosis. Web. To evaluate the radiographic lung pattern and topographical distribution in canine eosinophilic. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web a multifocal marked peripheral alveolar pattern can be identified in all lung lobes and is a common radiographic feature of angiostrongylosis. Web radiographic findings used as non. Tracheal disease may cause dry, honking, resonant cough (dogs) and dyspnea or strider (cats);. Finally you end up with. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a similar. Web alveolar, interstitial or maybe bronchial! Web certain generalizations have been made about the character of the cough: The alveolar pattern is the dominant pattern, and will obscure other patterns by silhouette effect. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web certain generalizations have been made about the character of the cough: Web a multifocal marked peripheral alveolar pattern can be identified in all lung. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a similar. The alveolar pattern is the dominant pattern, and will obscure other patterns by silhouette effect. Web radiographic findings used as non mutually exclusive labels to train the cnns were: Web alveolar, interstitial or maybe bronchial! Web radiographic evidence of bacterial pneumonia can appear as a focal, multifocal, or diffuse. Multiple air bronchograms are observed in the left hemithorax on. Unremarkable, cardiomegaly, alveolar pattern, bronchial pattern,. The only distinction these patterns make with. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web learn how to recognize and differentiate common lung patterns and distributions of pulmonary diseases in dogs. A total collapse of the alveoli (atelectasis) leads to a similar. To evaluate the radiographic lung pattern and topographical distribution in canine eosinophilic. Web radiographic findings varied, but included abnormal unstructured interstitial (one) and unstructured interstitial and alveolar (five) pulmonary patterns, which were. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within. Web certain generalizations have been made about the character of the cough: Web learn how to recognize and differentiate common lung patterns and distributions of pulmonary diseases in dogs and cats using thoracic radiographs. To evaluate the radiographic lung pattern and topographical distribution in canine eosinophilic. Multiple air bronchograms are observed in the left hemithorax on. Web an alveolar lung. Web an alveolar lung pattern is an opaque lung that completely obscures the margins of the pulmonary blood vessels. Finally you end up with. The only distinction these patterns make with. Web thoracic radiography (available in 10 dogs) revealed right cardiomegaly and patchy or diffuse interstitial to alveolar patterns, with 9 dogs having a normal left. Web radiographic evidence of bacterial pneumonia can appear as a focal, multifocal, or diffuse alveolar pattern, although early in the disease process infiltrates. Web pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, described in dogs and a cat, is a rare disorder resulting from flooding of the alveoli with surfactant. Web radiographic findings used as non mutually exclusive labels to train the cnns were: Tracheal disease may cause dry, honking, resonant cough (dogs) and dyspnea or strider (cats);. This pattern results in more loss of airspace than any other pattern. Web radiographic evidence of bacterial pneumonia can appear as a focal, multifocal, or diffuse alveolar pattern, although early in the disease process infiltrates. Web an alveolar pattern is the result of fluid (pus, edema, blood), or less commonly cells within the alveolar space. Web certain generalizations have been made about the character of the cough: The alveolar pattern is the dominant pattern, and will obscure other patterns by silhouette effect. Web important points regarding the alveolar pattern: Web learn how to recognize and differentiate common lung patterns and distributions of pulmonary diseases in dogs and cats using thoracic radiographs. Multiple air bronchograms are observed in the left hemithorax on.
Figure 6 from Distribution of alveolarinterstitial syndrome in dogs

Visual assessment of the classification results of a

Figure 1 from Topographical distribution and radiographic pattern of

Imaging the Coughing Dog

Imaging the Coughing Dog
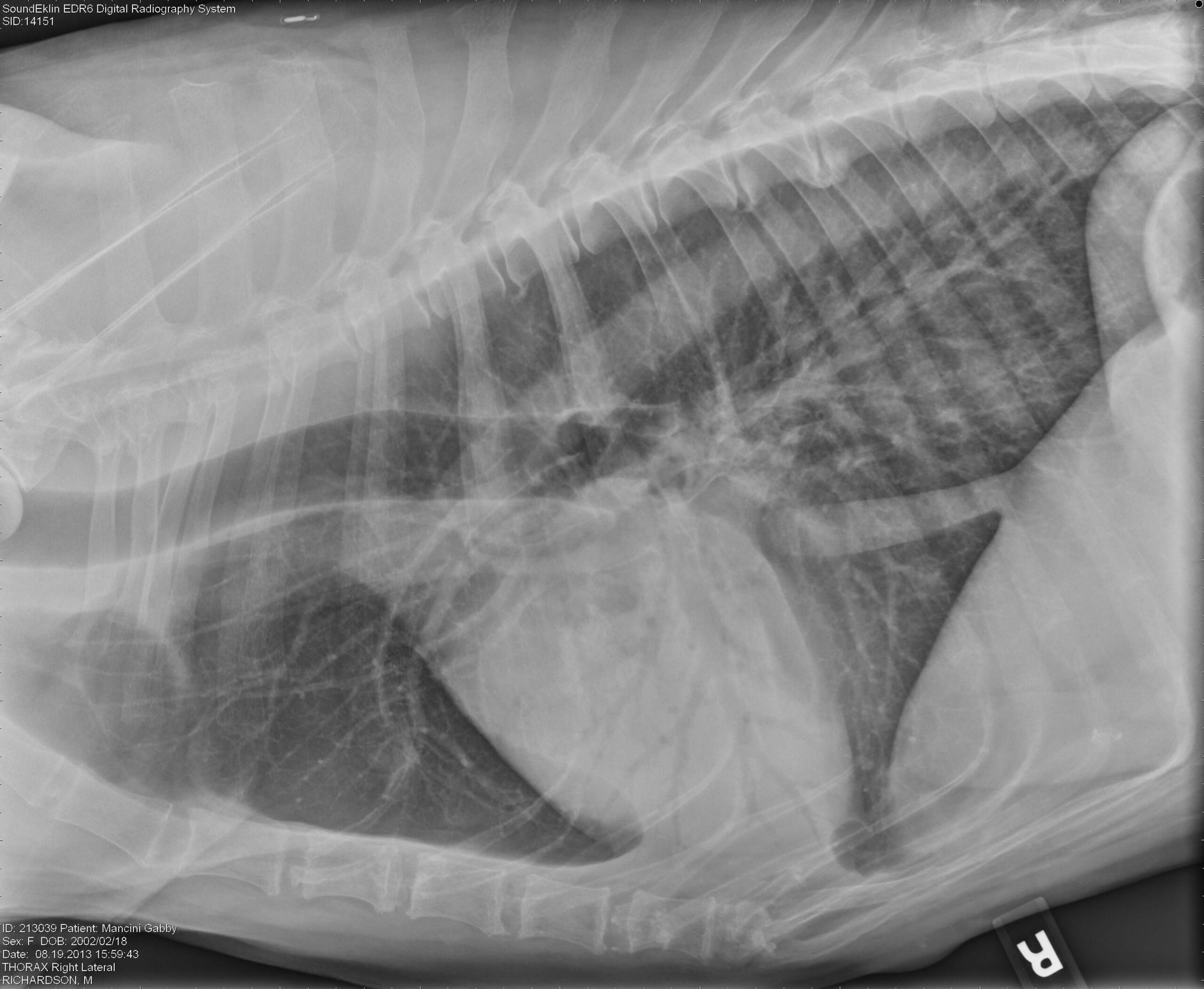
Interpreting thoracic radiograph lung patterns VETgirl Veterinary

Alveolar pattern or normal anatomy in the thorax of a young dog?

Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
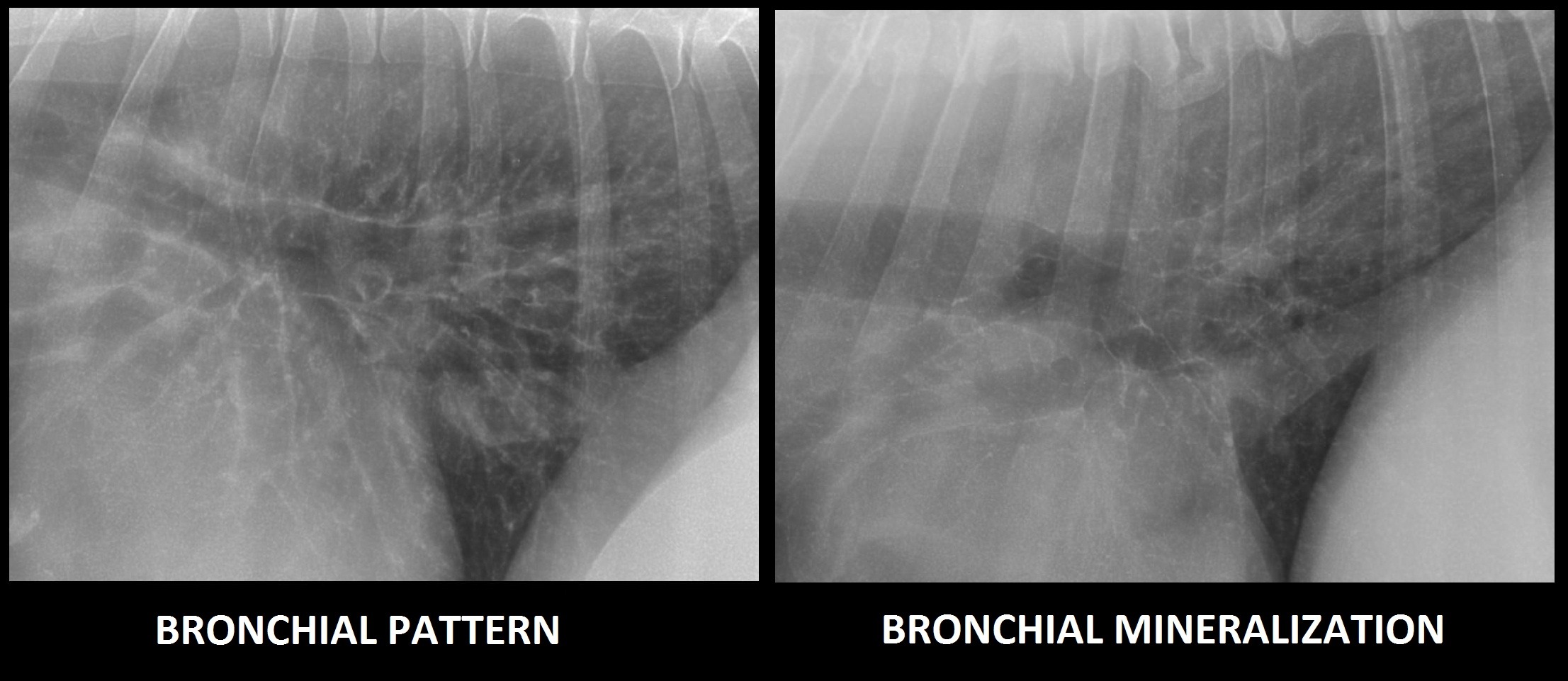
Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell

Radiographic Approach to the Coughing Pet • MSPCAAngell
You Look At A Thoracic Radiograph And Somehow You Do See A Bit Of Every Lung Pattern.
Web Alveolar, Interstitial Or Maybe Bronchial!
Web A Multifocal Marked Peripheral Alveolar Pattern Can Be Identified In All Lung Lobes And Is A Common Radiographic Feature Of Angiostrongylosis.
A Total Collapse Of The Alveoli (Atelectasis) Leads To A Similar.
Related Post: